Textile finishing plays a crucial role in enhancing the functionality, appearance, and durability of fabrics. This article delves into various textile finishing techniques that serve different purposes, such as antimicrobial finishing, UV protection, eco-friendly treatments, antistatic properties, and lustrous finishes. By understanding these technologies, textile professionals can improve product performance, meet industry standards, and cater to consumer demands for both aesthetic appeal and practical use. In this third part of the textile finishing series, we explore the methods, applications, and benefits of these advanced textile treatments.
This article is the third part of textile finishing, and parts I and II are reviewed in the following articles.
Antimicrobial Finishing in Textile
Antimicrobial finishing is a post-finishing technology used to endow textiles with antibacterial properties. This treatment can inhibit or kill the growth of microorganisms, thereby reducing odors, protecting the health of the wearer, and prolonging the service life of the product.

The details of antimicrobial finishing are as follows:
Purpose of Antimicrobial Finishing
Inhibit bacterial growth: Reduce the number of bacteria and fungi on textiles.
Reduce odors: Control the odors caused by the decomposition of sweat and other organic substances by bacteria.
Improve hygiene: Provide additional hygienic protection for textiles that frequently come into contact with the skin.
Prolong service life: Extend the service life of textiles by controlling the growth of microorganisms.
Methods of Antimicrobial Finishing
Chemical antimicrobial agents: Use chemical substances with antibacterial properties, such as silver ions, copper ions, triclosan, etc., and fix them on the fibers.
Nanotechnology: Utilize the antibacterial properties of nanoparticles, such as nano-silver, and embed them in the fibers.
Bio-based antimicrobial agents: Use antibacterial substances extracted from natural sources, such as chitosan, tea tree oil, etc.
Physical antibacterial technology: Use physical means, such as ultraviolet irradiation, to damage the DNA of microorganisms.
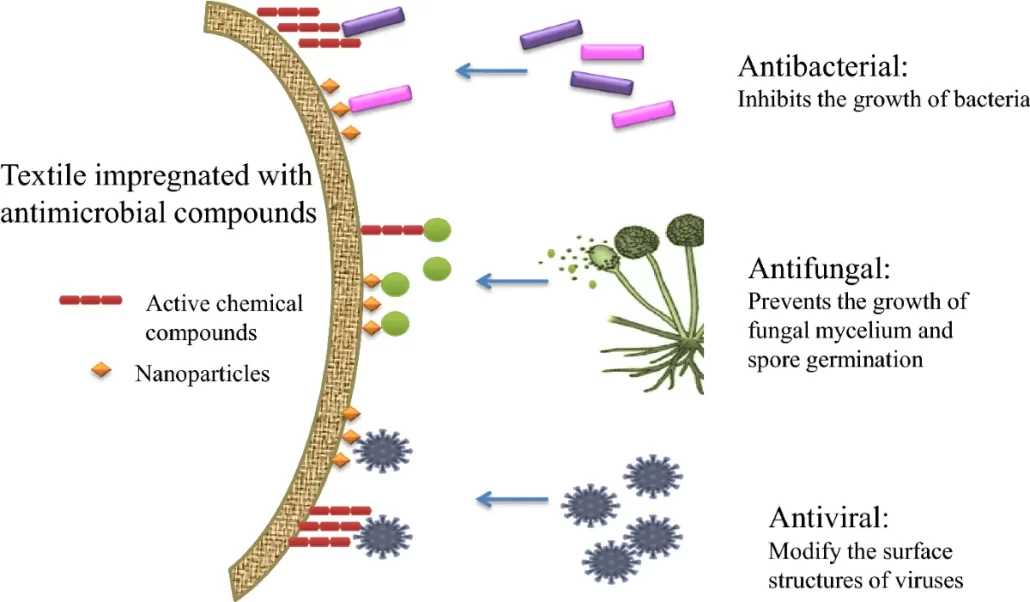
Steps of Antimicrobial Finishing
Pretreatment: Clean the fabric to remove oil stains and other impurities, preparing for the antibacterial treatment.
Application of antimicrobial agent: Immerse the fabric in a solution containing the antimicrobial agent or apply the agent by spraying, etc.
Curing: After drying and heat treatment, make the antimicrobial agent solidify on the fabric to form a stable antibacterial layer.
Post-treatment: May include washing to remove unbound antimicrobial agents, as well as further drying and softening treatments.
Precautions for Antimicrobial Finishing
Selection of antimicrobial agents: Select antimicrobial agents suitable for the fabric type and the expected antibacterial effect.
Safety: Ensure that the antimicrobial agents are safe for the human body without irritation or allergic reactions.
Environmental considerations: Use environmentally friendly antimicrobial agents and processes to reduce the impact on the environment.
Durability: Ensure that the antibacterial effect can be maintained after multiple washes and uses.
Regulatory compliance: Comply with relevant regulations and standards for antibacterial products.
Cost-effectiveness: Consider the cost-effectiveness of the antimicrobial agents and processes to meet the needs of the market and consumers.

Applications of Antimicrobial Finishing
Antimicrobial finishing is widely used in various textiles that need to improve their hygienic performance, such as:
Sportswear: Since people sweat a lot during exercise, antimicrobial finishing can reduce odors.
Medical textiles: Such as surgical gowns, patient gowns, etc., which require a high level of hygiene standards.
Home textile products: Such as bed sheets, pillowcases, etc., to provide a more hygienic sleeping environment.
Underwear: Directly in contact with the skin, antimicrobial finishing can improve personal hygiene.
Public facilities: Such as seats in public transportation, theater seats, etc., to reduce the risk of cross-infection.
Antimicrobial finishing is an important means to enhance the hygienic performance of textiles and protect the health of users. By precisely controlling the finishing process, the fabric can be endowed with lasting antibacterial performance. However, the antimicrobial finishing process needs to be carefully controlled to ensure the consistency of the antibacterial effect and the high quality of the product.
UV Protection Finishing in Textile
UV protection finishing is a post-finishing technology specifically designed to improve the ability of textiles to resist ultraviolet (UV) penetration. This treatment is especially important for textiles that are frequently exposed to sunlight, such as outdoor clothing, umbrellas, tents, swimwear, etc.
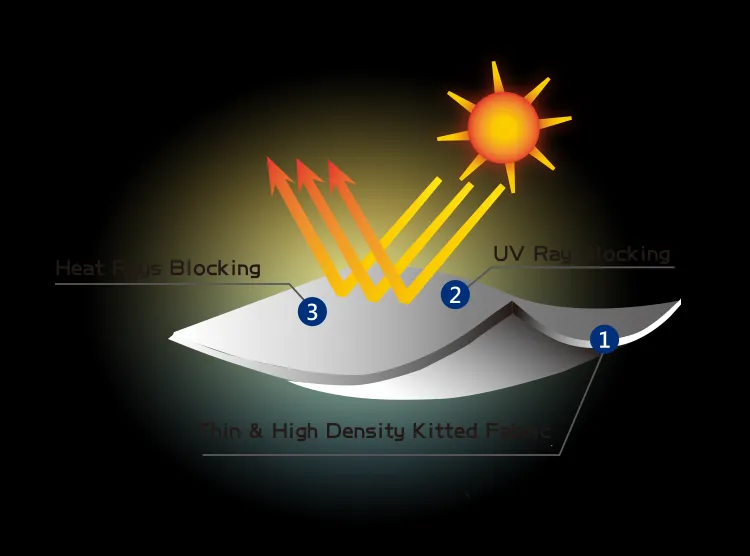
The details of UV protection finishing are as follows:
Purpose of UV Protection Finishing
Protect the skin: Reduce the damage of ultraviolet rays to the skin and lower the risk of sunburn and skin cancer.
Improve durability: UV protection treatment helps to extend the service life of textiles and prevent fading or embrittlement caused by UV irradiation.
Increase functionality: Provide additional functions for textiles and enhance their market competitiveness.
Methods of UV Protection Finishing
Chemical method: Use chemical substances containing UV absorbers, such as benzophenones, salicylates, triazoles, etc., and fix them on the fibers.
Physical method: Apply a physical barrier on the fabric surface that can reflect or scatter ultraviolet rays, such as a metal coating or mineral particles.
Nanotechnology: Utilize the optical properties of nanomaterials, such as nano-titanium dioxide, to absorb or scatter ultraviolet rays.
Bio-based materials: Use plant extracts that naturally have UV protection functions, such as certain vegetable oils.
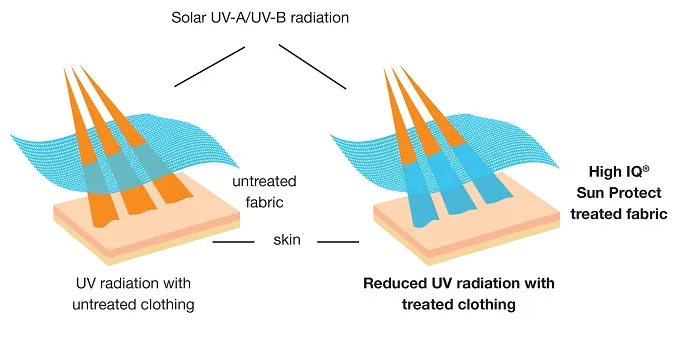
Steps of UV Protection Finishing
Pretreatment: Clean the fabric to remove oil stains and other impurities, preparing for the UV protection treatment.
Application of protective agent: Immerse the fabric in a solution containing the UV protective agent or apply the agent by spraying, etc.
Curing: After drying and heat treatment, make the protective agent solidify on the fabric to form a stable protective layer.
Post-treatment: May include washing to remove unbound protective agents, as well as further drying and softening treatments.

Precautions for UV Protection Finishing
Selection of protective agents: Select protective agents suitable for the fabric type and the expected protection effect.
Safety: Ensure that the protective agents are safe for the human body without irritation or allergic reactions.
Environmental considerations: Use environmentally friendly protective agents and processes to reduce the impact on the environment.
Durability: Ensure that the protection effect can be maintained after multiple washes and uses.
Regulatory compliance: Comply with relevant regulations and standards for UV protection products.
Cost-effectiveness: Consider the cost-effectiveness of the protective agents and processes to meet the needs of the market and consumers.
Applications of UV Protection Finishing
UV protection finishing is widely used in textiles that need to provide additional sun protection, such as:
Outdoor clothing: Such as jackets, hiking pants, etc., to provide sun protection for outdoor activities.
Umbrellas: Provide an additional sun protection layer to reduce UV penetration.
Swimwear: Protect the wearer from UV damage when swimming or sunbathing.
Tents and camping equipment: Provide sun protection for campers.
Car interiors: Such as sunshades, to reduce the temperature rise in the car and protect the people in the car.

UV protection finishing is an important means to enhance the functionality of textiles and protect the health of users. By precisely controlling the finishing process, the fabric can be endowed with lasting UV protection performance. However, the UV protection finishing process needs to be carefully controlled to ensure the consistency of the protection effect and the high quality of the product.
Eco-Friendly Finishing
Eco-friendly finishing aims to:
Reduce pollution: Use biodegradable or low-toxicity chemicals to reduce water and air pollution.
Energy conservation and consumption reduction: Adopt energy-saving processes and technologies to reduce energy consumption and resource waste.
Improve product safety: Ensure that textiles are harmless to the human body and do not contain harmful substances.
Meet regulatory requirements: Comply with international environmental standards and regulations, such as OEKO-TEX Standard 100, GOTS, etc.
Enhance brand image: Demonstrate the enterprise’s commitment to environmental protection and enhance consumer trust.
Methods of Eco-Friendly Finishing
Use of eco-friendly dyes: Select non-toxic and low-environmental-impact dyes, such as plant dyes or synthetic eco-friendly dyes.
Adoption of eco-friendly auxiliaries: Use biodegradable softeners, antimicrobial agents, flame retardants, etc.
Water conservation: Adopt water-saving processes, such as air dyeing, foam dyeing, etc.
Recycling and reuse: Recycle the water and chemicals used in the dyeing and finishing processes for reuse.
Energy-saving technology: Use energy-saving equipment and technologies, such as high-efficiency heat setting machines and heat recovery systems.
Use of organic and recycled materials: Use sustainable materials such as organic cotton and recycled polyester.
Biological treatment technology: Utilize enzymes and other biotechnology for pretreatment, bleaching and softening to reduce the use of chemicals.
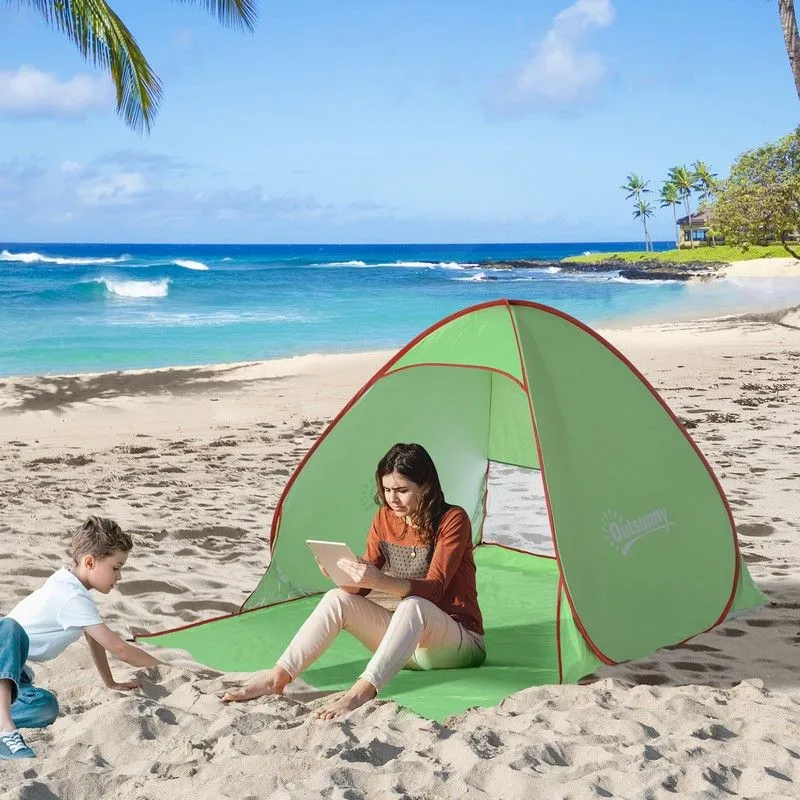

Steps of Eco-Friendly Finishing
Pretreatment: Use environmentally friendly cleaning agents and processes to clean the fabric.
Dyeing and finishing: Use eco-friendly dyes and auxiliaries for dyeing and finishing.
Wastewater treatment: Treat the generated wastewater to remove residual dyes and chemicals.
Energy-saving drying: Use energy-saving drying equipment and technologies.
Post-treatment: Adopt environmentally friendly post-treatment processes, such as biological enzyme softening and formaldehyde-free resin finishing.

Precautions for Eco-Friendly Finishing
Material selection: Carefully select environmentally friendly raw materials and auxiliaries to ensure their safety for the human body and the environment.
Process control: Precisely control the process conditions to ensure the environmental protection effect and product quality.
Certification and standards: Follow relevant environmental protection certifications and standards, such as GOTS, OEKO-TEX, etc.
Education and training: Train employees in environmental awareness and skills.
Continuous improvement: Continuously seek ways to improve processes and materials to further enhance environmental performance.

Applications of Eco-Friendly Finishing
Eco-friendly finishing is widely used in various textiles, especially those markets that need to meet environmental standards, such as:
Infant and children’s clothing: Special attention needs to be paid to the safety and environmental protection of the product.
Underwear and pajamas: Products that directly contact the skin, and consumers have higher requirements for environmental protection and health.
Outdoor equipment: Such as tents, backpacks, etc. Consumers are increasingly inclined to choose environmentally friendly products.
Fashion brands: Many fashion brands have begun to attach importance to environmental protection and launched environmentally friendly product series.
Eco-friendly finishing is an important direction for the future development of the textile industry. By adopting environmentally friendly materials and processes, textile enterprises can not only reduce the impact on the environment but also enhance the market competitiveness and brand image of their products.
Antistatic Finishing in Textile
Antistatic finishing is a post-finishing technology used in the textile industry to reduce the accumulation of static electricity on the surface of textiles. This treatment is very important for improving the comfort and safety of textiles, especially in specific applications where static interference needs to be reduced.
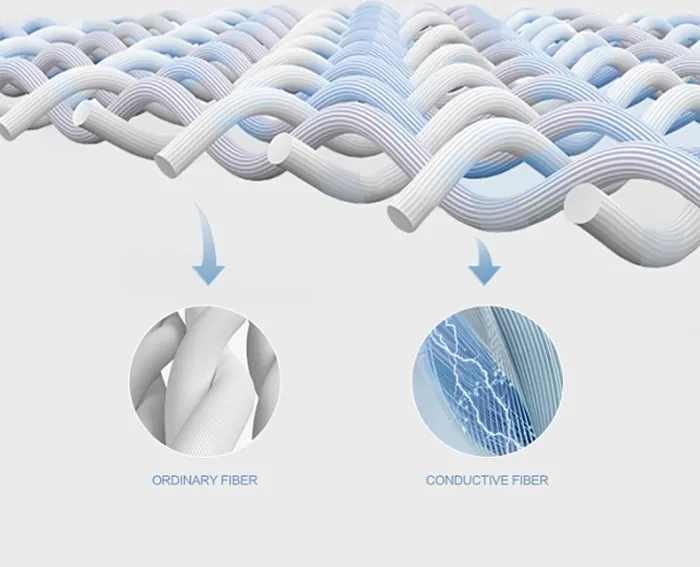
The details of antistatic finishing are as follows:
Purpose of Antistatic Finishing
Reduce static electricity: Prevent the generation and accumulation of static electricity in the textile during the friction process.
Improve comfort: Static electricity can adsorb dust and cause discomfort, and antistatic treatment can enhance the wearing experience.
Safety protection: In flammable and explosive environments, reduce the risk of sparks caused by static electricity.
Improve processing performance: Reduce the problems of adhesion and entanglement of the fabric during the processing.
Methods of Antistatic Finishing
Chemical method: Use antistatic chemicals, such as antistatic agents, and apply them to the fabric by impregnation or coating.
Physical method: Change the surface characteristics of the fibers through mechanical friction or special processes to reduce the generation of static electricity.
Fiber blending: Blend with conductive fibers such as carbon fibers or metal fibers and utilize the antistatic properties of the conductive fibers.
Coating finishing: Apply a conductive coating on the fabric surface, such as a metal coating or a carbon-based coating.
Steps of Antistatic Finishing
Pretreatment: Clean the fabric to remove oil stains and other impurities, preparing for the antistatic treatment.
Application of antistatic agent: Immerse the fabric in a solution containing the antistatic agent or apply the agent by spraying, etc.
Drying and curing: Dry and heat-treat the treated fabric to make the antistatic agent solidify on the fabric.
Post-treatment: May include washing to remove unbound antistatic agents, as well as further drying and softening treatments.
Precautions for Antistatic Finishing
Selection of antistatic agents: Select antistatic agents suitable for the fabric type and the expected antistatic effect.
Treatment conditions: Precisely control the temperature, time and treatment method of the antistatic treatment to ensure the best effect.
Durability: Ensure that the antistatic effect can be maintained after multiple washes and uses.
Safety: Ensure that the antistatic agents are safe for the human body without irritation or allergic reactions.
Environmental considerations: Use environmentally friendly antistatic agents and processes to reduce the impact on the environment.
Cost-effectiveness: Consider the cost-effectiveness of the antistatic agents and processes to meet the needs of the market and consumers.
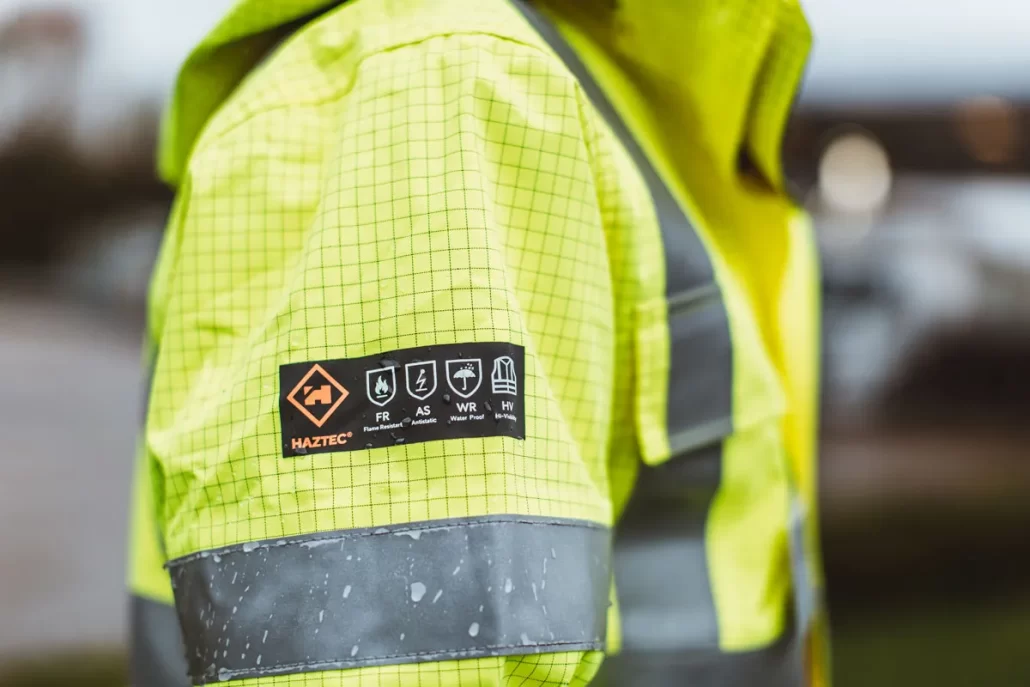

Applications of Antistatic Finishing
Antistatic finishing is widely used in various textiles that need to reduce static electricity, such as:
Work clothes: Antistatic work clothes worn in work environments such as electronic factories, gas stations, hospitals, etc.
Carpets and floor coverings: Reduce static electricity and dust adsorption when walking.
Packaging materials: Antistatic packaging materials used for packaging sensitive electronic components.
Bedding and clothing: Improve the comfort of daily wear.
Antistatic finishing is an important means to enhance the functionality and safety of textiles. By precisely controlling the finishing process, the fabric can be endowed with lasting antistatic performance. However, the antistatic finishing process needs to be carefully controlled to ensure the consistency of the antistatic effect and the high quality of the product.
Lustrous Finishing in Textile
Lustrous finishing is a textile finishing technology used to improve the glossiness and appearance of the fabric, making it have a smoother and shinier surface. This treatment is usually used to enhance the appearance and market value of natural fiber fabrics such as silk, synthetic fibers or cotton.
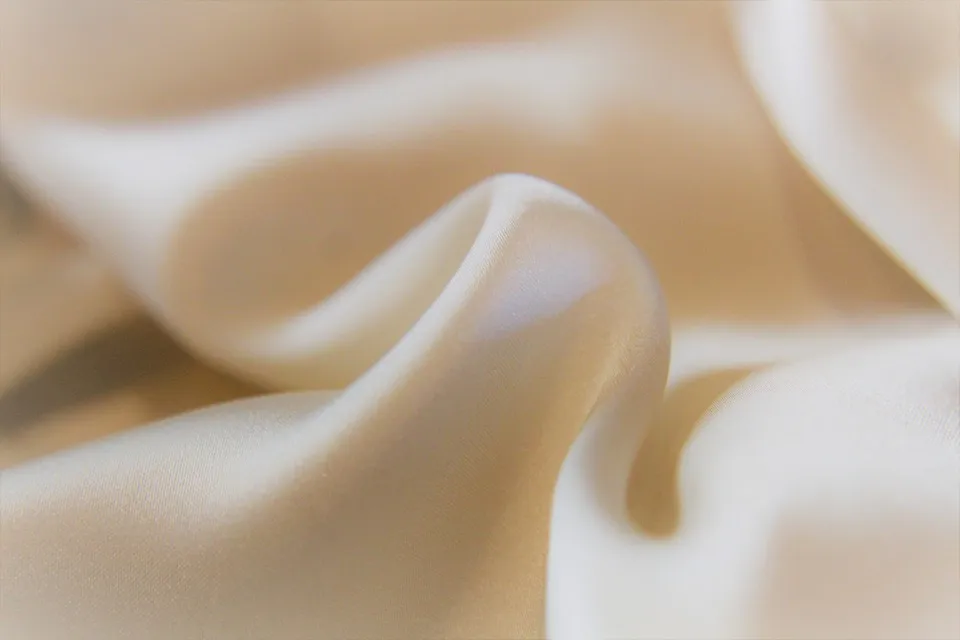

The details of lustrous finishing are as follows:
Purpose of Lustrous Finishing
Enhance appearance: Increase the gloss of the fabric to make it look more upscale and attractive.
Improve handle: The fabric after lustrous finishing has a softer and smoother handle.
Enhance durability: Some lustrous finishing processes can increase the abrasion resistance of the fabric.
Increase product added value: Improve the market competitiveness of the product by enhancing the appearance and handle.
Methods of Lustrous Finishing
Mechanical finishing: Use mechanical friction or pressure, such as sueding, brushing or polishing, to make the fabric surface produce gloss.
Chemical finishing: Apply chemical auxiliaries, such as softeners or gloss agents, to increase the glossiness of the fabric.
Coating finishing: Apply a transparent gloss coating on the fabric surface, such as polyester or acrylic resin.
Heat setting: Improve the gloss of the fabric through temperature and humidity control during the heat setting process.
Steps of Lustrous Finishing
Pretreatment: Clean the fabric to remove oil stains and other impurities, preparing for the lustrous finishing.
Application of lustrous finishing agent: According to the selected method, apply the lustrous finishing agent to the fabric.
Drying: Dry the treated fabric to fix the gloss effect.
Post-treatment: May include further cleaning, drying and setting to improve the handle and appearance.
Precautions for Lustrous Finishing
Selection of finishing agents: Select finishing agents suitable for the fabric type and the expected gloss effect.
Treatment conditions: Precisely control the temperature, humidity and treatment time during the lustrous finishing process.
Uniformity: Ensure that the lustrous finishing agent is evenly distributed on the fabric to avoid uneven gloss.
Environmental considerations: Use environmentally friendly finishing agents and processes to reduce the impact on the environment.
Durability: Ensure that the gloss effect can be maintained after multiple washes and uses.
Cost-effectiveness: Consider the cost-effectiveness of the lustrous finishing agent and process to meet the needs of the market and consumers.
Applications of Lustrous Finishing
Lustrous finishing is widely used in various textiles that need to enhance the appearance, such as:
Women’s clothing fabrics: Such as silk, satin, etc., which need gloss to enhance the feminine appearance.
Home decoration: Such as curtains, sofa covers, etc., where gloss can add a sense of luxury to the interior decoration.
Fashion accessories: Such as ties, scarves, etc., where gloss can enhance the grade of the product.
Performance costumes: Such as stage costumes, dance costumes, etc., where gloss can enhance the visual effect.
Lustrous finishing is an important means to enhance the appearance and handle of textiles. By precisely controlling the finishing process, the fabric can be endowed with unique gloss and style. However, the lustrous finishing process needs to be carefully controlled to ensure the consistency of the gloss effect and the high quality of the product.
The choice of textile finishing technology depends on the requirements and intended uses of the final product. Different finishing technologies can be used alone or in combination to achieve the best performance and appearance effects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, textile finishing techniques like antimicrobial, UV protection, eco-friendly, antistatic, and lustrous finishes are essential in meeting the evolving demands of the textile industry. These treatments not only improve the performance and aesthetics of fabrics but also contribute to sustainability and user comfort. By adopting the right finishing methods, manufacturers can enhance the quality of their products while responding to the growing consumer demand for both functionality and environmental consciousness. The precise application of these finishes ensures that textiles meet both regulatory standards and consumer expectations.
For more information on smart textile testing instruments and fabric finishing techniques, or to obtain professional testing solutions, please contact us!
Email: sales@chivention.com
WhatsApp: +86 180 2511 4082
Linkedin: Chiuvention