In today’s diverse fashion and industrial fields, textiles are everywhere. From the clothes we wear daily to high – end industrial materials, their quality and performance directly impact our lives and production. Textile finishing technology, as a crucial link in endowing textiles with unique charm and practical value, is playing an increasingly important role. It is like a magical spell that can transform ordinary fabrics, enabling them to possess various excellent characteristics and meet the strict requirements of different scenarios. Next, let’s delve into several common and key textile finishing technologies together.

Singeing
Singeing is an important technique in textile finishing, primarily used to remove loose fibers and fuzz from the fabric surface, thereby enhancing the quality and appearance of the fabric. Here is a detailed introduction to singeing:
Purpose of Singeing:
Remove Fuzz: Burn off loose fibers and fuzz from the fabric surface to make it smoother and cleaner.
Improve Appearance: Singeing results in a more uniform fabric surface, enhancing the fabric’s aesthetic appeal.
Prevent Pilling: Reduce pilling caused by friction during use.
Prepare for Dyeing: Singeing removes impurities that may affect dyeing uniformity, preparing the fabric for the dyeing process.

Steps of Singeing
Preparation: Spread or wind the fabric onto the corresponding part of the singeing machine.
Heating: Heat the fabric using a flame or hot air to burn off loose fibers and fuzz.
Cooling: After heating, the fabric quickly passes through a cooling zone to fix the singeing effect and prevent further burning.
Finishing: The singed fabric may need further finishing, such as stretching or setting, to ensure dimensional stability.

Methods of Singeing
Gas Singeing: Uses a gas flame for singeing, suitable for most fabrics.
Electric Singeing: Uses heat generated by electric heating elements, suitable for fabrics requiring precise temperature control.
Hot Air Singeing: Uses hot air for singeing, suitable for temperature-sensitive fabrics.
Precautions for Singeing
Temperature Control: Strictly control the temperature to prevent over-singeing or incomplete singeing.
Speed Control: Adjust the speed of the fabric through the singeing machine based on the fabric type and requirements.
Safety Measures: Implement appropriate safety measures due to the flames and heat generated during singeing.
Post-Treatment: The singed fabric may require post-treatment, such as washing or softening, to further improve its quality.

Applications of Singeing
Singeing is widely used in the production of various textiles, especially those requiring high surface quality, such as:
Worsted Wool Fabrics: Suit fabrics, coat fabrics, etc.
Cotton Fabrics: Shirt fabrics, bed sheets, etc.
Silk Fabrics: Satin, chiffon, etc.
Synthetic Fabrics: Nylon, polyester, etc.
Singeing is a simple yet effective finishing technique that can significantly improve the appearance and performance of fabrics. However, it requires precise control and professional operation to achieve the best results.
Softening
Softening is a finishing process used in the textile industry to improve the feel and comfort of fabrics. Its treatments make fabrics softer, smoother, and enhance their drape.
Purpose of Softening
Improve Feel: Make the fabric feel softer, enhancing the wearing experience.
Increase Drape: Softened fabrics have better drape, especially suitable for clothing.
Reduce Roughness: Minimize the rough feel of the fabric surface, preventing skin irritation.
Enhance Skin-Friendliness: Make the fabric more suitable for direct skin contact, increasing comfort.
Methods of Softening
Chemical Softening: Uses softeners (e.g., silicone oil, stearic acid, cationic surfactants) to treat the fabric. Softeners fill the uneven parts of the fiber surface, reducing friction between fibers.
Mechanical Softening: Uses mechanical actions (e.g., sanding, brushing) to loosen surface fibers, achieving a softening effect.
Heat Setting Softening: Controls temperature and humidity during heat setting to make fibers softer.
Biological Softening: Uses enzymes to treat the fabric, making the fiber surface smoother.

Steps of Softening
Pre-Treatment: Clean or bleach the fabric as needed to remove impurities affecting softening.
Soaking or Spraying: Soak the fabric in a softener solution or spray the softener evenly onto the fabric surface.
Drying: Dry the treated fabric to fix the softener and activate its effect.

Post-Treatment: May include re-washing to remove unbound softener and final setting.
Precautions for Softening
Softener Selection: Choose the appropriate softener based on fabric type and desired feel.
Processing Conditions: Control temperature, time, and pH during processing to ensure softening effect.
Uniformity: Ensure even distribution of the softener on the fabric to avoid uneven softness.
Safety: Pay attention to the safety of softeners to avoid adverse effects on humans or the environment.
Applications of Softening
Softening is widely used in various textiles, especially those requiring high comfort and feel, such as:
Underwear: Requires soft and comfortable feel.
Sleepwear: Needs to be soft and skin-friendly.
Baby Clothing: Requires high softness and safety.
Sportswear: Needs good softness and drape.
Home Textiles: Bed sheets, duvet covers, etc., to improve sleep comfort.
Softening is an important means to enhance textile quality, significantly improving fabric feel and wearing experience. However, it requires precise control and professional operation to achieve the desired effect.
Setting
Setting is a key process in the textile industry used to stabilize fabric dimensions and shape. It ensures that fabrics maintain their shape and size during subsequent use and washing, reducing shrinkage and deformation.
Purpose of Setting
Dimensional Stability: Ensure fabric dimensions remain stable during washing and use, reducing deformation.
Shape Stability: Maintain the fabric’s shape (e.g., pleats, form) over time.
Improve Feel: Setting can improve fabric feel, making it softer or stiffer as needed.
Style Retention: Setting helps maintain specific fabric styles, such as smoothness or texture.
Methods of Setting
Heat Setting: Heat the fabric to a certain temperature and maintain it for a period to fix fiber shape using heat.
Moisture Setting: Use heat and moisture to set the fabric, suitable for fabrics needing additional humidity to improve feel and shape.
Chemical Setting: Use chemicals (e.g., formaldehyde, resins) to increase fiber bonding, fixing the fabric shape.
Combined Setting: Combine heat, moisture, and chemical setting for optimal results.

Steps of Setting
Pre-Treatment: Clean the fabric to remove impurities, preparing it for setting.
Setting Process
- For heat setting, heat the fabric in a heating chamber to a specific temperature and maintain it for a period.
- For moisture setting, expose the fabric to a humid environment.
- For chemical setting, soak or spray the fabric with chemical setting agents.
Cooling or Drying: After heat setting, quickly cool the fabric to fix the shape; after chemical setting, dry to remove excess chemicals.
Post-Treatment: May include washing, softening, etc., to remove residual chemicals and improve feel.

Precautions for Setting
Temperature Control: Precisely control the setting temperature to prevent fiber damage or over-setting.
Time Control: Determine setting time based on fabric type and required setting degree.
Chemical Selection: Choose appropriate chemical setting agents, considering safety and environmental impact.
Uniformity: Ensure even heating or moisture exposure during setting to avoid uneven setting.
Applications of Setting
Setting is widely used in various textiles, especially those requiring high dimensional and shape stability, such as:
Apparel Fabrics: Suits, shirts, skirts, etc., needing shape and size retention.
Home Textiles: Curtains, bedspreads, etc., needing pleat and shape retention.
Industrial Uses: Tents, awnings, etc., needing shape retention in various environments.
Setting is an important means to ensure textile quality and durability. By precisely controlling setting conditions, fabric dimensional and shape stability can be significantly improved, meeting various application needs.
Dyeing
Dyeing is a key technology in textile finishing, involving the application of dyes to fibers, yarns, or fabrics to impart desired colors. It not only enhances the appearance of textiles but also increases their market value.
Purpose of Dyeing
Aesthetics: Provide various colors to meet consumer aesthetic needs.
Identification: Use specific color codes for product identification and classification.
Protection: Some dyes offer UV protection.
Improve Performance: Certain auxiliaries used in dyeing can improve fabric feel or other properties.
Methods of Dyeing
Immersion Dyeing: Immerse textiles in a dye solution, suitable for yarns and loose fibers.
Roll Dyeing: Wind textiles onto rollers in a dye vat for continuous dyeing.
Jet Dyeing: Use jet equipment to spray dye directly onto textiles for rapid dyeing.
Printing: Use printing equipment to print dyes onto textiles, forming patterns or designs.
Pad Dyeing: Pass textiles through a dye pad, then fix the color through heat treatment.

Steps of Dyeing
Pre-Treatment: Clean textiles to remove grease, stains, and other impurities.
Dyeing Preparation: Select appropriate dyes and dyeing processes, prepare necessary chemicals.
Dyeing Process: Place textiles in the dye bath, control dyeing conditions (temperature, pH, time).
Post-Dyeing Treatment: After dyeing, usually wash with soap to remove unbound dyes.
Soft Washing: Use soft water to remove residual chemicals.
Setting: Heat-set textiles to stabilize dimensions and improve feel.
Drying: Dry textiles to fix the color.
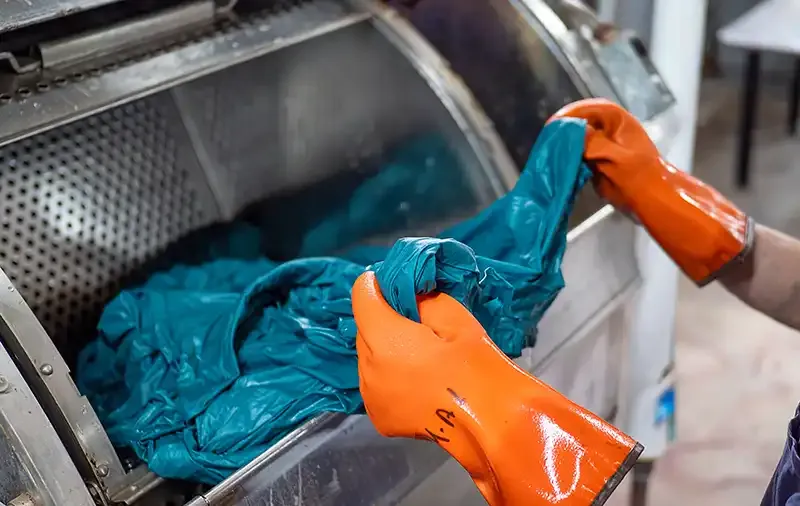

Precautions for Dyeing
Dye Selection: Choose appropriate dyes based on fiber type and desired color effect.
Dyeing Conditions: Precisely control temperature, pH, and time to ensure even dyeing.
Environmental Considerations: Use eco-friendly dyes and processes to reduce environmental impact.
Color Fastness: Ensure dyed textiles have good color fastness to prevent fading.
Health and Safety: Follow safety protocols, as some dyes and chemicals may pose health risks to operators.
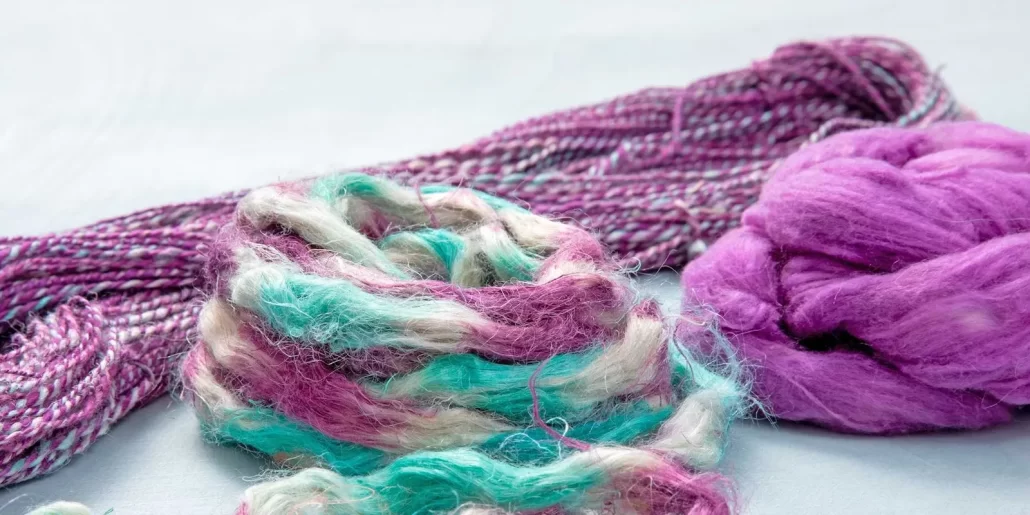

Applications of Dyeing
Dyeing is widely used in various textiles, including:
Apparel Fabrics: T-shirts, shirts, pants, etc.
Home Textiles: Bed sheets, duvet covers, curtains, etc.
Decorative Items: Sofa covers, cushions, etc.
Industrial Uses: Tents, safety clothing, etc.
Dyeing is an important technology in the textile industry, enhancing both the aesthetics and functionality of textiles. However, the dyeing process requires precise control to ensure consistent dyeing results and high product quality.
Coating
Coating is a finishing process in the textile industry used to provide additional functions or improve fabric performance. By coating, one or more layers of material can be added to the fabric surface to achieve waterproof, stain-resistant, wear-resistant, flame-retardant, and other effects.
Purpose of Coating
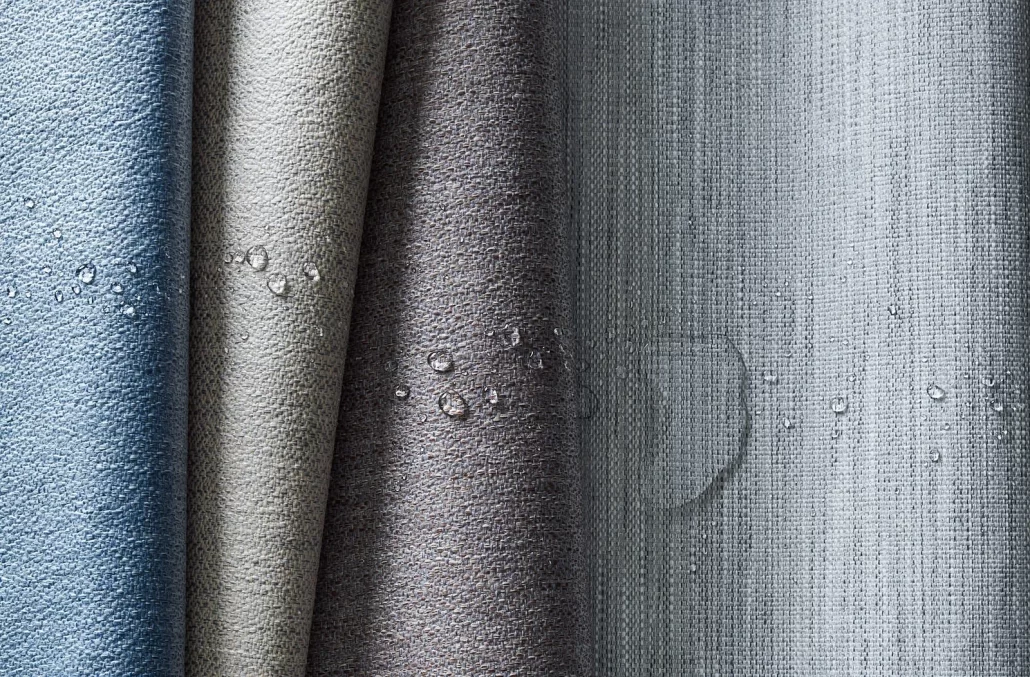
Water and Stain Resistance: Improve fabric’s waterproof and stain-resistant properties.
Wear Resistance: Some coating materials enhance fabric wear resistance.
Flame Retardancy: Coatings can impart flame-retardant properties.
Aesthetics: Coatings can improve fabric appearance, such as adding gloss or changing color.
Additional Functions: Coatings can provide extra functions like antibacterial, UV protection, and anti-static properties.
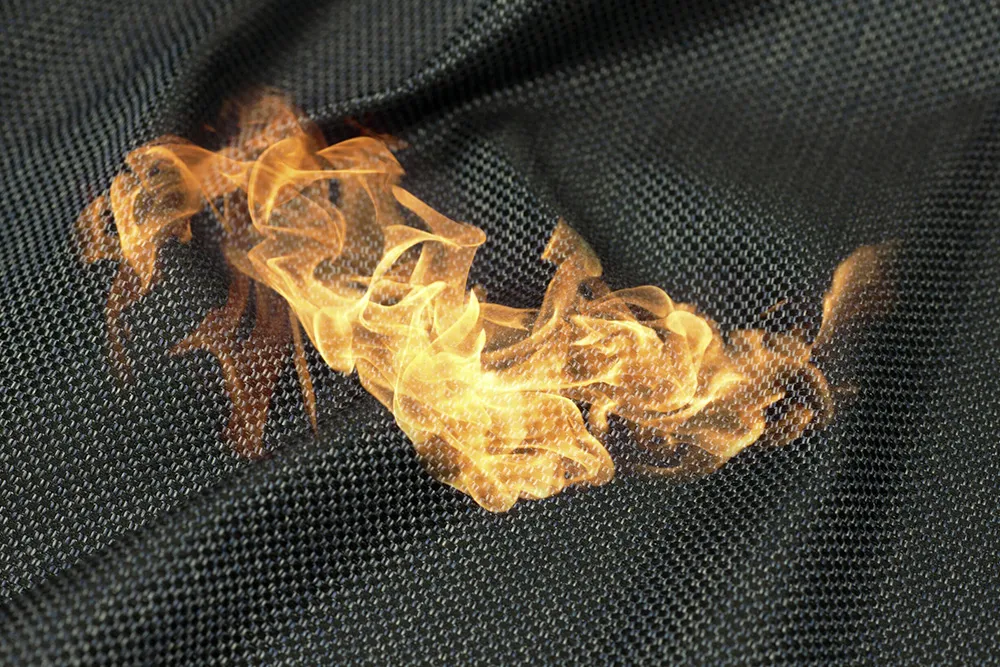

Methods of Coating
Direct Coating: Apply coating material directly onto the fabric surface.
Transfer Coating: Apply coating material onto a special transfer paper, then transfer it to the fabric via heat press.
Foam Coating: Use foam to evenly apply coating material onto the fabric.
Spray Coating: Use a spray gun to apply coating material onto the fabric.
Roller Coating: Pass fabric through rollers coated with coating material, transferring it to the fabric under pressure.
Steps of Coating
Pre-Treatment: Clean and dry the fabric to ensure coating uniformity and adhesion.
Coating Preparation: Select appropriate coating materials and ratios based on desired effects.
Coating Application: Evenly apply coating material onto the fabric.
Curing: Heat-treat or UV-cure the coated fabric to fix the coating.
Post-Treatment: After curing, may include washing, drying, setting, etc.
Precautions for Coating
Coating Material Selection: Choose appropriate coating materials based on required functions and performance.
Coating Uniformity: Ensure even distribution of coating material to avoid uneven thickness.
Coating Adhesion: Ensure good adhesion of coating material to prevent peeling during use.
Environmental and Safety: Use eco-friendly coating materials and ensure safe coating processes.
Cost-Effectiveness: Consider the cost-effectiveness of coating materials and processes to meet market and consumer needs.

Applications of Coating
Coating is widely used in various textiles, especially those requiring additional functions or performance improvements, such as:
Outdoor Apparel: Jackets, raincoats, etc., needing waterproof and windproof properties.
Medical Supplies: Protective clothing, surgical gowns, etc., needing antibacterial and stain-resistant properties.
Home Textiles: Curtains, sofa covers, etc., needing waterproof and stain-resistant properties.
Industrial Uses: Tents, awnings, etc., needing wear-resistant and UV-protective properties.
Coating is an important means to enhance textile functionality and added value. By selecting appropriate coating materials and processes, various additional functions and performance improvements can be imparted to fabrics. However, the coating process requires precise control to ensure coating uniformity and quality.
The choice of textile finishing techniques depends on the final product requirements and intended use. Different finishing techniques can be used individually or in combination to achieve optimal performance and appearance.
Conclusion
In summary, each of the textile finishing technologies, such as singeing, softening, setting, dyeing, and coating, has its unique functions and roles. Singeing makes the fabric surface smooth and lays a good foundation for subsequent processes; softening treatment improves wearing comfort and makes the fabric more skin – friendly; setting ensures the dimensional stability of the fabric and maintains its aesthetics and durability; dyeing endows the fabric with rich colors to meet diverse aesthetic needs; coating adds various special functions to the fabric and expands its application fields. These technologies cooperate with and complement each other. Whether it is clothing fabrics, home textile products, or industrial fabrics, they all require the careful refinement of these technologies. With the continuous progress of science and technology, textile finishing technologies are also continuously innovating and developing. In the future, they will surely bring us more high – performance, multi – functional, and aesthetically pleasing textiles.
ChiuVention focuses on smart textile testing instruments. For more information about laboratory testers or to obtain professional testing solutions, please contact us!
Email: sales@chivention.com
WhatsApp: +86 180 2511 4082
Linkedin: Chiuvention