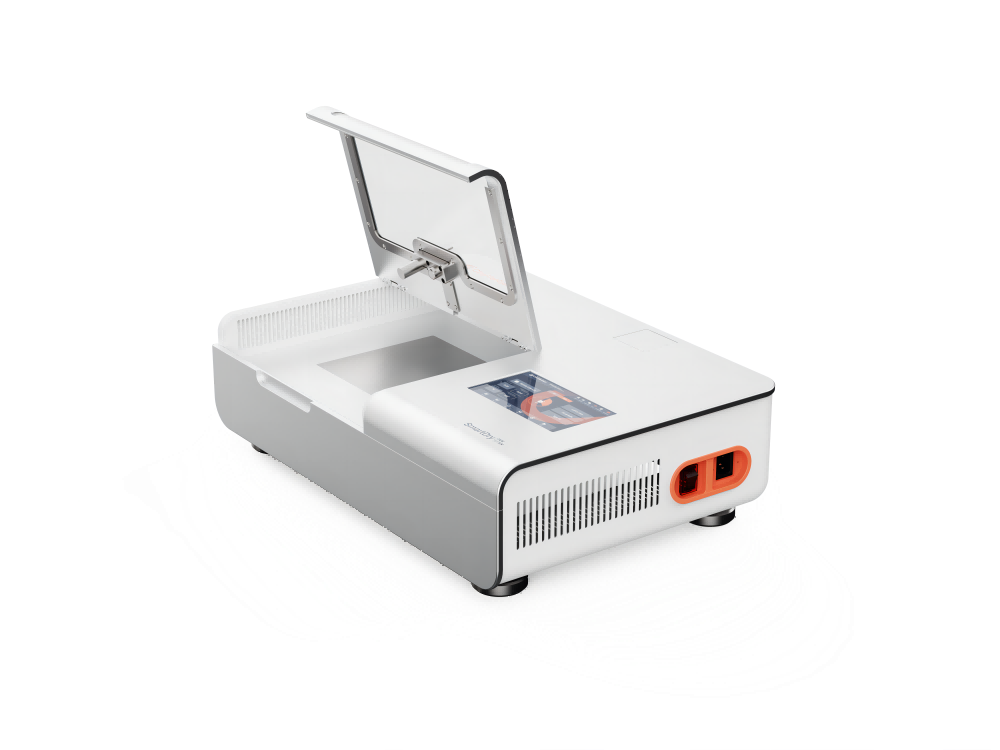
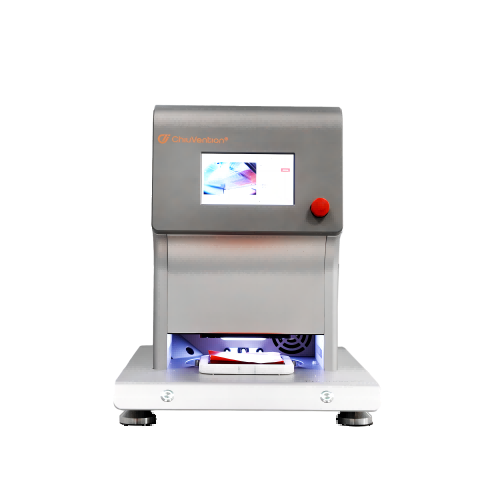
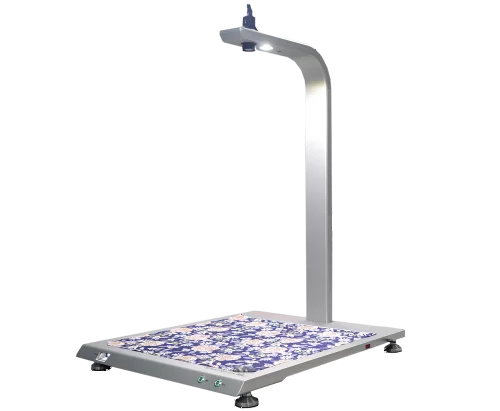
A quick dry test sample is placed on top of a heating plate at a constant temperature of 37° (99°F), and a certain amount of water rises from the bottom of the drying test instrument to the center of the plate and saturates the sample.
An anemometer inside the instrument dries the sample. An infrared temperature sensor measures the change in temperature of the sample to determine if the fabric drying is finished, and then the drying speed is determined by the test drying time.

Smart fabric drying test
The Fast Drying Fabric Tester is connected via IoT to the SmarTexLab APP in the phone/PC. And The app can connect to ERP/LIMS via an API. Or, the instrument can connect directly to ERP/LIMS. There are test orders and sample information in the system, and the Drying Rate Tester can start the test and record the sample info, test process, and results. The system will then summarize these into a fabric drying test report. The report can be sent to SmarTexLab or ERP/LIMS. The relevant parties can view the report in real-time. Test men can monitor quick drying tests for many instruments at once. They can also change test requirements, get alerts before the fabric dry tests end, and stop or repeat tests remotely. In SmarTexLab, you can set up programs to start or stop the fabric drying rate tester. You can chat with ChiuVention service staff for quick support. You’ll get reminders that instruments need calibration, maintenance, and new consumables. Regular OTA remote upgrades are available.
Efficient, convenient, and more reliable tests
A unique uniform wind speed control and magnetic stripe fixture, making the test more reliable.
The wind is more uniform and smooth during the test. The sample and test plate are closely adhered, all above reproduce the actual evaporation process. A built-in temperature and humidity sensor makes the fabric dry test more reliable.
Fast test, test results are highly consistent with authoritative testing organizations.
A drying rate test can be done in a few minutes. Its results match those of international third-party testing organizations.
Lightweight and easy to use, well-known brands are using it.
Lululemon’s Canadian HQ is using it. It meets adidas’ standards and is widely used by suppliers recognized by adidas, like Jiale Textile Corp. In Indonesia.
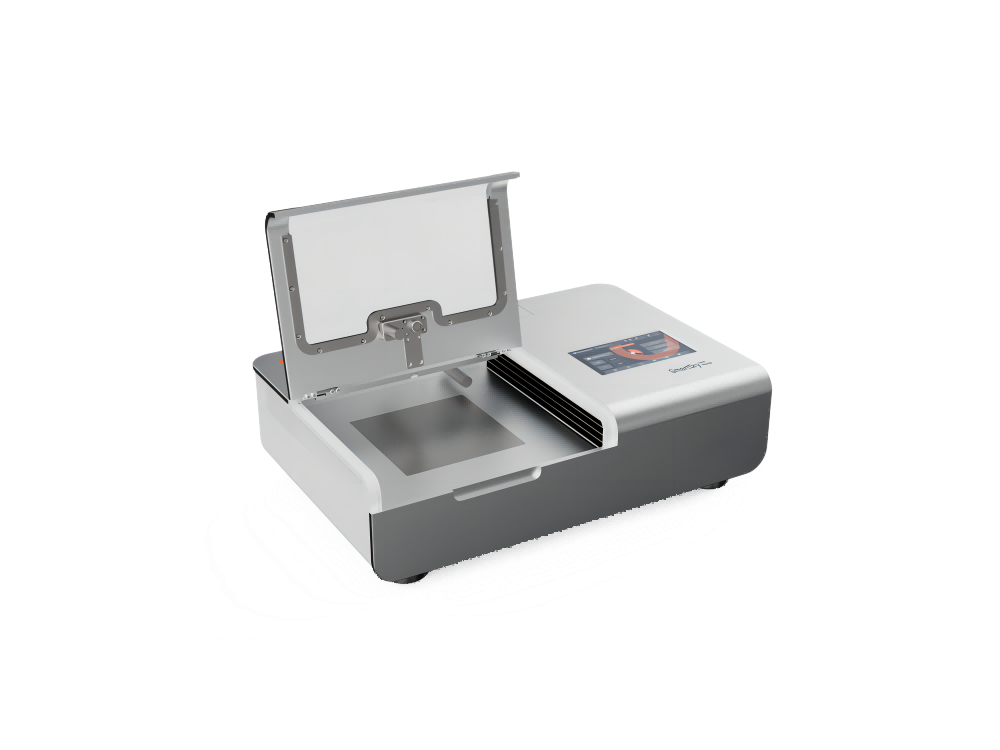


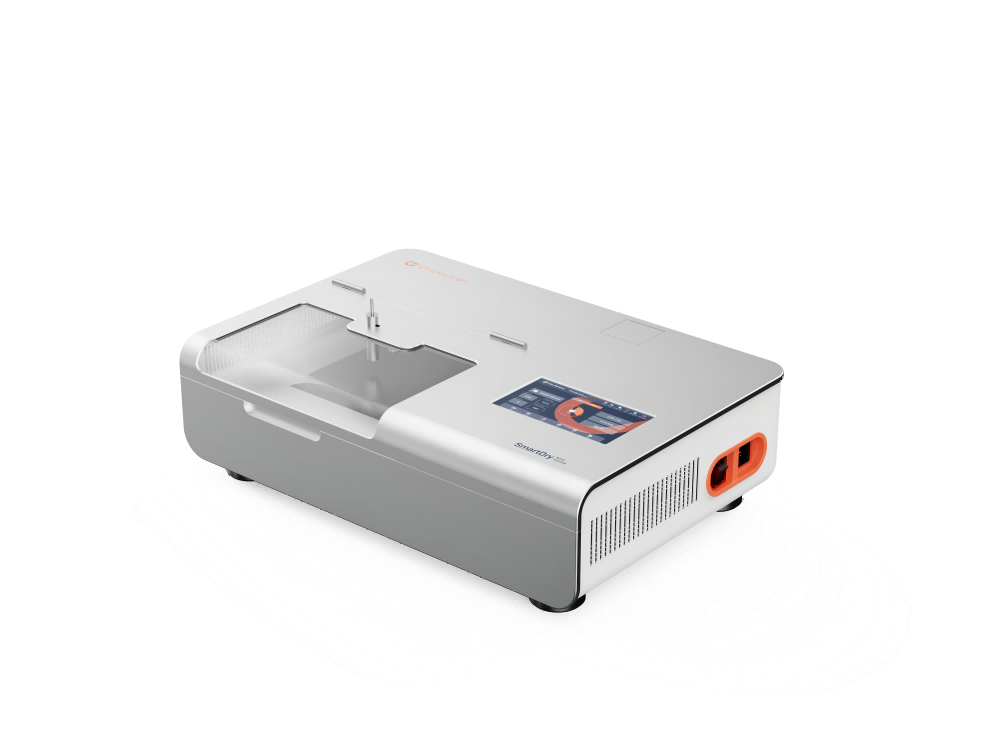
Simple and easy to use
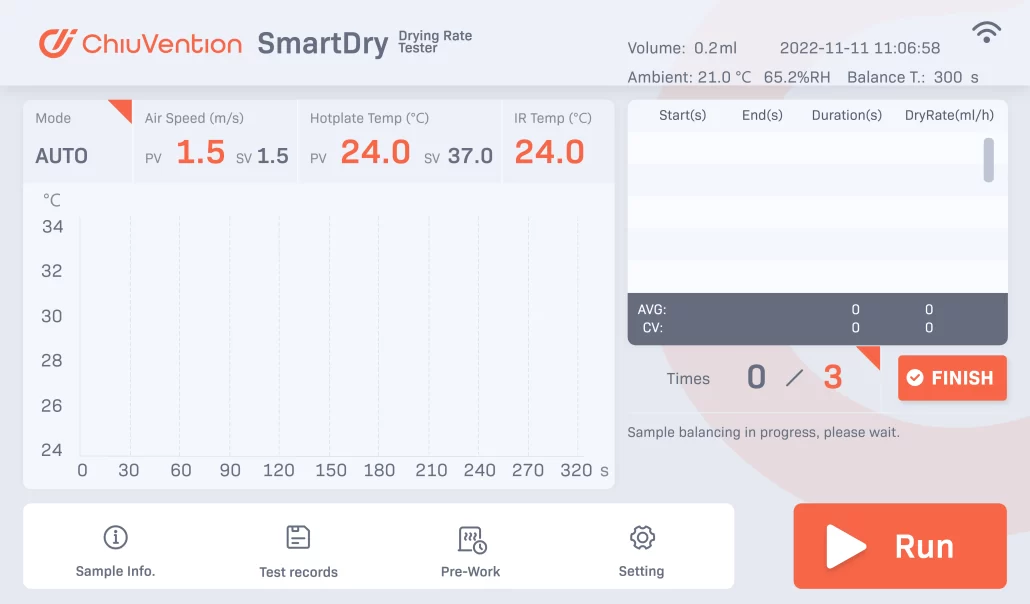
The drying rate tester can show the Fast Drying Fabric Test process on the screen. It will be a clear drying rate curve.
The appearance design is precise. The surface is an aluminum alloy with hard oxidation. It is durable and easy to clean. It has a seven-inch color touch screen.
Designed in Germany, quality is our life.
All our textile testing instruments are developed in-house and in cooperation with a team of renowned German industrial designers, which makes our instruments of outstanding quality. 100% source factory and factory price.
Application Examples of SmartDry Drying Rate Tester

Sports Fabric

Underwear Fabric

Towels

Bed Sheet
Customer Feedback
“This SmartDry Textile Fast Dry Tester can quickly measure the drying rate of our yoga fabrics in just 10 minutes, which greatly improves work efficiency. With its simple design and user-friendly interface, it is easy to learn and use. Even non-professionals can learn to operate it quickly.”
“This fabric drying rate tester is equipped with data processing and analysis software that automatically generates reports and graphs to help us visually understand and analyze drying rate data. This is very helpful for our research and development of new products.”
The Specification of Dry Rate Tester
The fan can produce an airflow of 0.5-3.5m/s ± 0.1m/s
Heater plate 305mm x 305mm ± 0.5mm
Soft heating plate 305mm x 305mm ± 0.5mm
Heat-insulating cork board 305mm x 305mm ± 0.5 mm
Metal pressure bar 150mm x 40mmx2mm ± 1mm
The Heating temperature 25-40℃ ± 0.5℃ (with overheat protection)
Infrared temperature sensor 15-50℃ ± 0.1°C
Drip accuracy 0.05-1.0 ml ± 0.001 ml
1.0-4.5ml ± 0.01ml
Accessories of Dry Rate Tester
Fuse 2pcs
Sampling plate 1 pc 150mm*150mm
Water bottle 1 pc 60mL
The standard for SmartDry Dry Rate Tester
AATCC201 FZ/T 01176-2024
Power 220V 50/60Hz Other voltages require an external transformer
Weight 20kg
Dimension 400*590*180 mm (D*W*H)
ChiuVention provides more smart textile testing equipment for you. Contact us for details about textile testing machines.
You can also get more valuable textile testing articles.
Frequently Asked Questions for SmartDry Textile Moisture Tester
What is the purpose of a dry rate tester?
The drying testing machine measures how fast materials dry. It measures fabric, clothes, and other materials too. It objectively tests the drying time under controlled conditions.
What are the applications of Fabric Dry Rate Tester?
Sportswear and Functional Fabrics: These fabrics usually emphasize breathability and quick-wicking function, such as polyester, nylon, spandex, etc., especially for outdoor or sports occasions. Towels and washcloths, home textiles: including bed sheets, pillowcases, and curtains; Swimwear and beachwear: quick drying is an important characteristic for these garments; Fast fashion or everyday wear fabrics: such as travel wear and quick-drying pants.
What are the test standards of Fabric Drying Test?
AATCC 201:2014;ISO 17617:2014; JIS L 1096;ASTM D1907;GB/T 21655.2-2009;GB/T 19541-2004;GB/T 21655.1-2008
How many kinds of fast-drying clothing material?
There are several types of fast-drying clothing materials, each designed to wick moisture away from the body and dry quickly. Here are some of the most common ones:
1. Polyester
- Features: Polyester is a synthetic fiber known for its durability and quick-drying properties. It resists water absorption and dries faster than natural fibers like cotton.
- Uses: Often found in athletic wear, outdoor clothing, and swimwear.
2. Nylon
- Features: Nylon is another synthetic material that dries quickly due to its low water absorption rate. It’s strong, lightweight, and commonly blended with other fibers.
- Uses: Used in activewear, swimwear, and outdoor gear.
3. Merino Wool
- Features: Merino wool is a natural fiber that has excellent moisture-wicking abilities and dries faster than regular wool. It’s also odor-resistant and insulating.
- Uses: Popular in outdoor and performance clothing, especially for cooler weather.
4. Rayon
- Features: Rayon, particularly viscose rayon, is semi-synthetic and known for its moisture-wicking properties. Although not as durable as polyester or nylon, it dries faster than cotton.
- Uses: Lightweight summer clothing and activewear.
5. Polypropylene
- Features: Polypropylene is a synthetic fiber that doesn’t absorb moisture, making it extremely fast-drying. It’s also lightweight and often used in layers.
- Uses: Base layers for outdoor activities, winter sports, and technical clothing.
6. Spandex (Lycra, Elastane)
- Features: Spandex is stretchy and usually blended with other materials to improve comfort and flexibility. While it absorbs some moisture, it dries quickly when blended with faster-drying fabrics.
- Uses: Common in activewear, swimwear, and form-fitting clothing.
7. Tencel (Lyocell)
- Features: Tencel is a sustainable fiber made from wood pulp. It wicks moisture away from the skin and dries more quickly than cotton.
- Uses: Eco-friendly fashion, activewear, and travel clothing.
8. Bamboo
- Features: Bamboo fabric is soft, moisture-wicking, and dries faster than cotton. It’s often blended with other materials to enhance its performance.
- Uses: Casual clothing, activewear, and eco-friendly textiles.
9. Microfiber
- Features: Microfiber is a synthetic material made from ultra-fine fibers of polyester or nylon. It absorbs little water and dries quickly.
- Uses: Used in towels, sportswear, and swimwear.
10. Blends (Polyester-Cotton, Nylon-Spandex)
- Features: Fabric blends that combine synthetic fibers with natural ones (like polyester-cotton or nylon-spandex) balance the comfort of natural fibers with the quick-drying properties of synthetics.
- Uses: Everyday clothing, activewear, and travel wear.
Factors affecting the rate of fabric drying?
Factors affecting the drying rate of textiles mainly include the following:
1. Fiber type
Hygroscopicity: the hygroscopicity of different fibers will directly affect the drying rate. For example, natural fibers such as cotton and wool are absorbent, dry slower, and synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon, with low water absorption, dry faster.
Fiber structure: the molecular structure of the fiber affects the water retention time inside the fiber, an open molecular structure of the fiber will make it easier to absorb moisture and extend the drying time.
2. Fabric structure
Density and thickness: thicker and denser fabrics will have more fibers and pores to store moisture, resulting in longer drying time; relatively loose or thin fabrics dry faster.
Weave: The woven or knitted structure of a fabric affects air circulation and moisture diffusion. Mesh fabrics and loosely knitted fabrics usually dry faster.
3. Surface treatment
Waterproof coating: Some textile surfaces have been treated with waterproof or moisture-resistant treatments to minimize moisture penetration, thus speeding up drying.
Moisture-wicking treatment: Functional textiles often incorporate moisture-wicking chemical treatments that help to draw moisture away from the surface of the textile and promote evaporation.
4. Textile weight
The larger the weight of the textile, the more water content, so the drying time is longer. On the contrary, lighter fabrics have a faster drying rate due to less water content.
5. Environmental factors
Airflow: Good air circulation accelerates water evaporation and increases the drying rate. In still air, fabric drying will be slower.
Temperature: Higher temperature can accelerate water evaporation and increase the drying rate. On the contrary, in a low-temperature environment, water evaporation is slow and drying time is prolonged.
Humidity: When the ambient humidity is high, the moisture content in the air is higher, the evaporation rate is slowed down and the drying time is prolonged; in a dry environment, the evaporation will be accelerated.
6. Water absorption and water transfer
Rate of water absorption: the speed of water absorption of a textile directly affects its drying speed, the faster the water absorption, the slower the drying.
Moisture diffusivity: the diffusion rate of moisture on the surface of the textile also affects evaporation; materials with a fast diffusion rate are more likely to evaporate moisture and accelerate drying.
7. Color and dyeing process
Color shades: dark-colored fabrics tend to absorb more heat and speed up the rate of moisture evaporation; while light-colored fabrics may dry more slowly.
Dyeing treatment: certain dyeing processes can change the hygroscopicity and water discharge capacity of fibers, thus affecting drying time.
8. Surface area of fabrics
The larger the surface area of the fabric (e.g. towel-like fabrics), the more it can be in contact with the air, the faster the rate of evaporation of moisture will be, the shorter the drying time.
In summary, the drying rate of textiles is affected by the combination of fiber type, fabric structure, surface treatment, weight, environmental conditions, and other factors.
How does a drying rate tester work?
The Heated Plate method tests how fast fabric dries when it is exposed to water. It does this while the fabric is on a heated plate. This test uses a hot plate at 37 degrees Celsius or 99 degrees Fahrenheit. It is to replicate the temperature at which the human body starts to perspire. The temperature drops when the specimen is wet. As it dries, the temperature slowly rises. The start time, end time, and drying time. The goal is to calculate the drying rate.
What parameters can a drying rate tester control?
including airflow/circulation, material application thickness, and test interval times. More advanced models allow customizing multiple parameters to mimic real-world drying conditions.
How precisely can a drying rate tester measure drying time?
Lab-grade testers can measure drying within just a few minutes. Accuracy depends on the model and sensors. Some claim accuracies of just 1-2 minutes. This depends on the test parameters and material.
The drying testing machine measures how fast materials dry. It measures fabric, clothes, and other materials too. It objectively tests the drying time under controlled conditions.
Sportswear and Functional Fabrics: These fabrics usually emphasize breathability and quick-wicking function, such as polyester, nylon, spandex, etc., especially for outdoor or sports occasions. Towels and washcloths, home textiles: including bed sheets, pillowcases, and curtains; Swimwear and beachwear: quick drying is an important characteristic for these garments; Fast fashion or everyday wear fabrics: such as travel wear and quick-drying pants.
AATCC 201:2014;ISO 17617:2014; JIS L 1096;ASTM D1907;GB/T 21655.2-2009;GB/T 19541-2004;GB/T 21655.1-2008
There are several types of fast-drying clothing materials, each designed to wick moisture away from the body and dry quickly. Here are some of the most common ones:
1. Polyester
- Features: Polyester is a synthetic fiber known for its durability and quick-drying properties. It resists water absorption and dries faster than natural fibers like cotton.
- Uses: Often found in athletic wear, outdoor clothing, and swimwear.
2. Nylon
- Features: Nylon is another synthetic material that dries quickly due to its low water absorption rate. It’s strong, lightweight, and commonly blended with other fibers.
- Uses: Used in activewear, swimwear, and outdoor gear.
3. Merino Wool
- Features: Merino wool is a natural fiber that has excellent moisture-wicking abilities and dries faster than regular wool. It’s also odor-resistant and insulating.
- Uses: Popular in outdoor and performance clothing, especially for cooler weather.
4. Rayon
- Features: Rayon, particularly viscose rayon, is semi-synthetic and known for its moisture-wicking properties. Although not as durable as polyester or nylon, it dries faster than cotton.
- Uses: Lightweight summer clothing and activewear.
5. Polypropylene
- Features: Polypropylene is a synthetic fiber that doesn’t absorb moisture, making it extremely fast-drying. It’s also lightweight and often used in layers.
- Uses: Base layers for outdoor activities, winter sports, and technical clothing.
6. Spandex (Lycra, Elastane)
- Features: Spandex is stretchy and usually blended with other materials to improve comfort and flexibility. While it absorbs some moisture, it dries quickly when blended with faster-drying fabrics.
- Uses: Common in activewear, swimwear, and form-fitting clothing.
7. Tencel (Lyocell)
- Features: Tencel is a sustainable fiber made from wood pulp. It wicks moisture away from the skin and dries more quickly than cotton.
- Uses: Eco-friendly fashion, activewear, and travel clothing.
8. Bamboo
- Features: Bamboo fabric is soft, moisture-wicking, and dries faster than cotton. It’s often blended with other materials to enhance its performance.
- Uses: Casual clothing, activewear, and eco-friendly textiles.
9. Microfiber
- Features: Microfiber is a synthetic material made from ultra-fine fibers of polyester or nylon. It absorbs little water and dries quickly.
- Uses: Used in towels, sportswear, and swimwear.
10. Blends (Polyester-Cotton, Nylon-Spandex)
- Features: Fabric blends that combine synthetic fibers with natural ones (like polyester-cotton or nylon-spandex) balance the comfort of natural fibers with the quick-drying properties of synthetics.
- Uses: Everyday clothing, activewear, and travel wear.
1. Fiber type
2. Fabric structure
3. Surface treatment
4. Textile weight
5. Environmental factors
6. Water absorption and water transfer
7. Color and dyeing process
8. Surface area of fabrics
The Heated Plate method tests how fast fabric dries when it is exposed to water. It does this while the fabric is on a heated plate. This test uses a hot plate at 37 degrees Celsius or 99 degrees Fahrenheit. It is to replicate the temperature at which the human body starts to perspire. The temperature drops when the specimen is wet. As it dries, the temperature slowly rises. The start time, end time, and drying time. The goal is to calculate the drying rate.
including airflow/circulation, material application thickness, and test interval times. More advanced models allow customizing multiple parameters to mimic real-world drying conditions.
Lab-grade testers can measure drying within just a few minutes. Accuracy depends on the model and sensors. Some claim accuracies of just 1-2 minutes. This depends on the test parameters and material.
OUR BROCHURE

Place the test sample on a heating plate at a constant temperature of 37°C±1°C
(99°F±2°F). A specified volume of water rises from the tester bottom to the heating plate center, and the sample is saturated and dried with an airflow rate of 1.5 m/s ± 0.5 m/s.
Sense the change of fabric temperature using the infrared temperature sensor, to determine whether the fabric drying is over. The drying rate is obtained according to the test time.
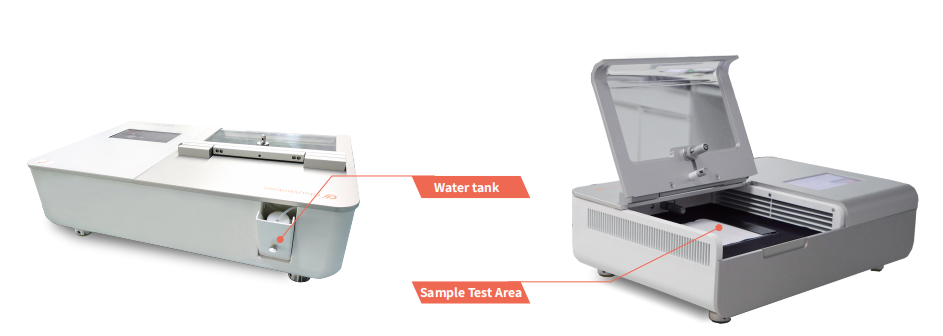
1. Open the water tank cover, and make sure the water is enough.
2. Connect the power cord to turn on the power.
The preheating starts automatically when the instrument is switched on.
3. Open the operation cover.
Lay the sample flat in the test area. The area’s right side is pressed tightly by the magnet-absorbing adhesive strips. Then, gently close the cover. (Note: Different placements of the sample and pattern at the front and back cause the different test results.)
4. Click “Mode” in the main interface to enter Test Setting interface.
Modify the data according to the test requirements. This includes water dispensing mode, water volume, unit, equilibrium time, and hot plate temperature. It also includes wind speed, etc. In automatic mode, water is dispensed according to the set value. In manual mode, water is injected manually. The volume is controlled by the operator.
5. Select the number of samples to be tested to complete the whole set of tests.
6. Click “Run” to start the test.
It simulates human sweating to find how fast textiles dry. You can see live data, including wind speed and hot plate temperature. It records the hot plate temperature.
7. When all the samples of the same type are done, click “Finish”.
Note: Click Finish after the test ends. Otherwise, the next test cannot start. After you press “Finish,” the data in the current list box will go into the report list. The data in the history list box will be cleared. Check the detailed data records in the report list.
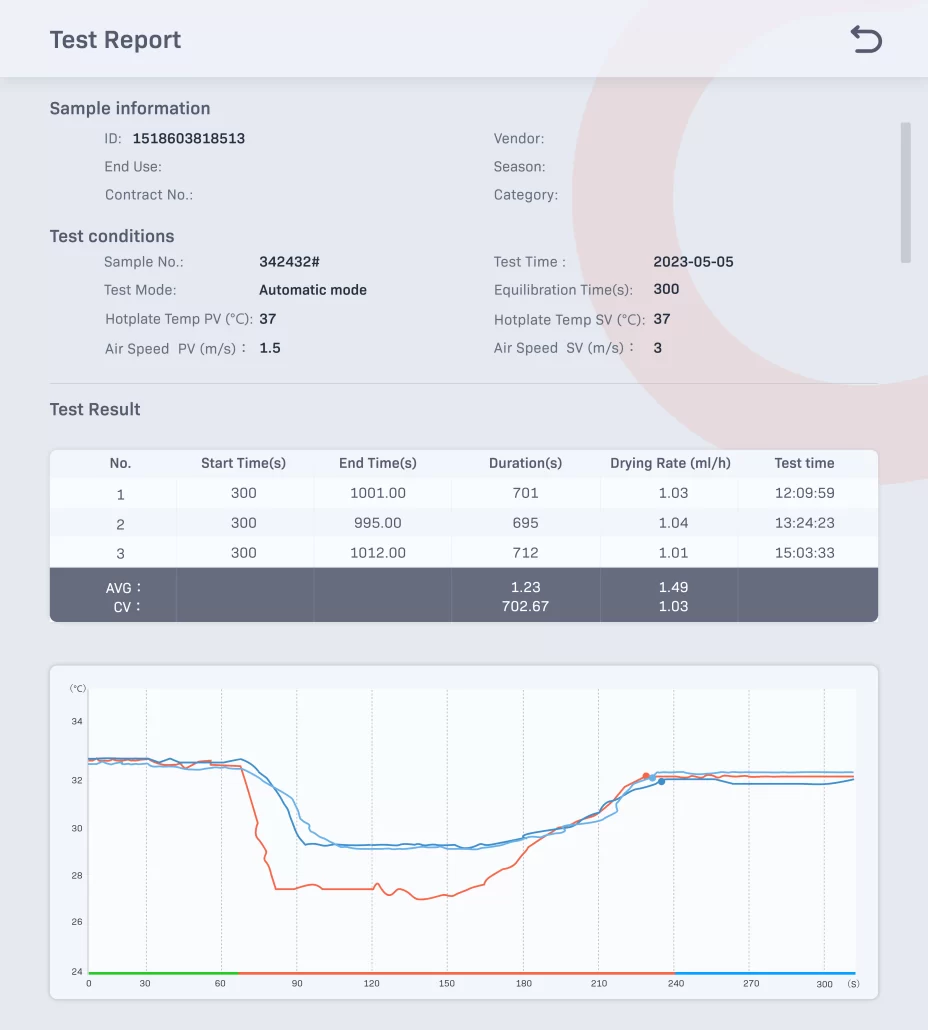
8. After the test is done, enter the Report List.
It shows the stored records, sample info, and report data. Click on the report column to open the report. This will bring you to the Detailed Report interface. There, you can delete the test records.
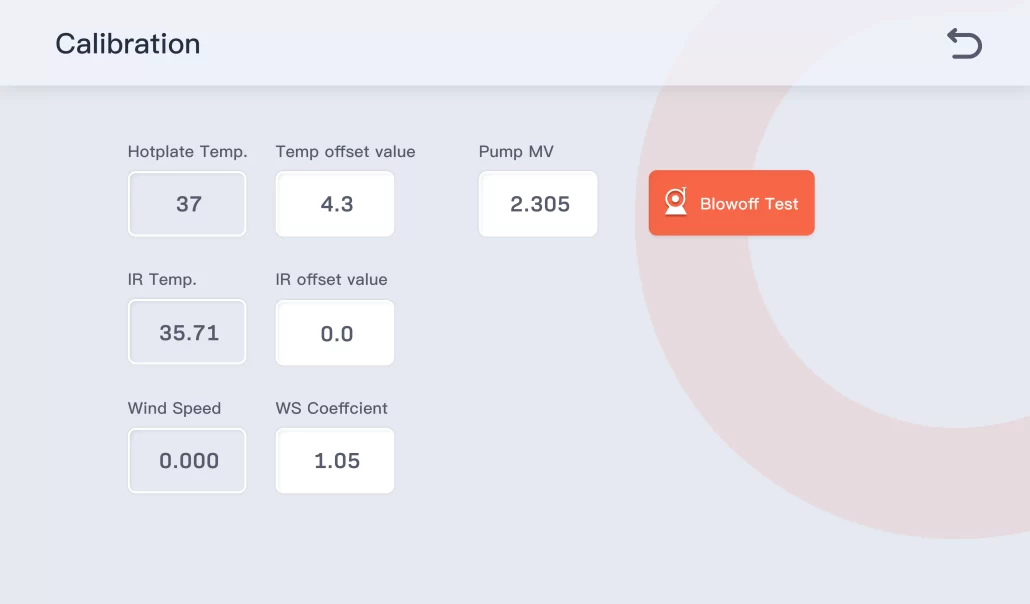
1. When calibrating the temperature of the hot plate, it is necessary to connect the temperature calibrator externally to ensure that their temperature is consistent with each other. But if the temperature calibrator deviates from the temperature of the hot plate, enter the temperature offset value.
2. The IR temperature is judged against the calibrated hot plate temperature and the IR offset value is entered if there is an offset.
3. Wind speed calibration requires an external wind speed calibrator. if there is any deviation, enter the offset coefficient.
4. The pump measurement value is to calibrate the pump discharge accuracy. The discharge test is carried out within the specified time, and the weighted data is the pump measurement value.
5. The SmartDry drying rate tester is strictly calibrated at the factory and should not be calibrated by non-professional engineers.
Care & Maintenance
Keep the instrument and control system clean and hygienic frequently.
Prevent high temperature, excessive humidity, dust, corrosive media, water, etc. from immersing inside the instrument or control system.
Regularly check and maintain the integrity of parts and components.
Regularly calibrate the instrument to ensure the accuracy of the measurement value. Non-professional personnel shall not dismantle the instrument.
Each time after dismantling and repair, a metrological performance test must be performed for the instrument in case the instrument is out of calibration.
Cautions
The instrument has been calibrated before leaving the factory, non-professionals shall not arbitrarily calibrate it, otherwise, the instrument fails to measure force accurately.
After the instrument is switched off, wait for 10 seconds before it is powered on again, otherwise it may cause damage to the instrument. During use, the instrument shall not be interfered with by a strong electromagnetic environment. The instrument shall be maintained regularly.