Introduction:
Ensuring a fabric’s functionality and durability in the textile industry is paramount. A crucial aspect of achieving this is evaluating a fabric’s resistance to tearing. This resistance, known as tear strength, determines how well a fabric can withstand rips, snags, or punctures during everyday use or under specific application demands.
Imagine a scenario where a piece of clothing rips easily due to a snag or an upholstery fabric tears prematurely under everyday use. The Elmendorf Tear Tester helps prevent such situations by quantifying a fabric’s tear strength. This article delves into 15 frequently asked questions (FAQs) concerning the Elmendorf Tear Tester, equipping you with a detailed understanding of this essential testing method.
We will explore the core principles behind the test, delve into standardized procedures, and address practical considerations. So, let’s get started:
1. What is the Elmendorf Tear Test?
The Elmendorf Tear Test is a standardized method specifically designed to evaluate a fabric’s resistance to tearing. Tearing refers to the progressive ripping or snagging of fabric fibers, often initiated by a sharp object or concentrated force. This property significantly impacts a fabric’s functionality and durability across various applications.
Imagine a piece of clothing, like denim jeans, that easily rips at the seams due to everyday wear. Or consider upholstery fabric that tears prematurely when brushed against. The Elmendorf Tear Test helps prevent such scenarios by providing a quantitative measure of a fabric’s tear strength.
The test operates on a straightforward principle. A specially designed instrument called the Elmendorf Tear Tester utilizes a pendulum mechanism. A precisely cut fabric sample with a pre-made notch is secured in the tester. The pendulum, with a controlled weight, is raised to a specific height, storing potential energy. Upon release, the pendulum swings down, impacting the fabric specimen at the pre-cut notch.
As the pendulum continues its upward swing, it exerts a force to further tear the fabric. This force required to propagate the tear is precisely measured and recorded. Higher force values indicate greater tear strength, signifying the fabric’s ability to resist ripping or snagging. The measured tear strength value, typically expressed in grams (g) or Newtons (N), serves as a benchmark for assessing the fabric’s suitability for its intended use.
2. What is the Test Principle of the Elmendorf Tear Test?
The Elmendorf Tear Test relies on a fundamental scientific principle: the conversion of energy. The test leverages the concept of potential energy stored in a raised object, which is then converted into kinetic energy during movement and ultimately used to perform work, in this case, tearing the fabric.
Here’s a closer look at the science behind the Elmendorf Tear Test:
Potential Energy:
The Elmendorf Tester features a pendulum, a weighted arm free to swing around a fixed pivot point. When raised to a specific height, the pendulum stores potential energy due to its position and the force of gravity acting upon it.
Conversion to Kinetic Energy:
As the pendulum is released, it begins to swing downward. During this descent, the potential energy gradually converts into kinetic energy, the energy of motion. The pendulum gains speed as it approaches the fabric sample.
Force Application and Tear Propagation:
Upon reaching the bottom of its swing, the pendulum impacts the pre-cut notch in the fabric specimen. This impact applies a concentrated force to the fabric at the weakest point, the notch.
Work Done: Tearing the Fabric:
The force exerted by the pendulum initiates a tear in the fabric. However, the tear doesn’t stop there. As the pendulum continues its upward swing, it pulls against the fabric, further propagating the tear.
Measuring the Resistance:
Here’s where the key measurement occurs. Throughout the tearing process, the Elmendorf Tester precisely measures the force required by the pendulum to keep ripping the fabric. This measured force value represents the fabric’s resistance to tearing.
The higher the force required to propagate the tear, the greater the tear strength of the fabric. This value serves as a crucial data point for evaluating a fabric’s suitability for various applications.
3. Which Fabrics Should be Tested For Tear Resistance Testing?
Tear resistance testing plays a vital role in ensuring the functionality and longevity of various fabrics across diverse applications. Here’s a breakdown of some key fabric categories that benefit from Elmendorf Tear Testing:
A) Fabrics for Everyday Wear and Tear:
Apparel Fabrics:
Fabrics used in clothing, particularly those subjected to frequent wear and tear, benefit from tear resistance testing. This includes denim for jeans, canvas for bags and backpacks, and leather for jackets and shoes. Understanding the tear strength helps ensure these garments can withstand everyday use without ripping easily.
Upholstery Fabrics:
Upholstery fabrics used in furniture need to be resistant to snags and tears. Testing helps assess their ability to handle regular use, occasional snags from pets or sharp objects, and ensure they maintain their appearance over time.
B) Fabrics for Performance and Safety:
Technical Textiles:
Fabrics used in specialized applications, often requiring high strength and tear resistance, benefit from testing. This includes parachute materials, airbags in vehicles, and tents for outdoor use. Ensuring these fabrics possess adequate tear strength is crucial for safety and functionality.
Nonwoven Fabrics:
These fabrics, formed by bonding fibers without weaving or knitting, are used in various applications. Testing tear strength helps assess their suitability for disposable wipes, filters, and insulation materials, where maintaining structural integrity is important.
C) Fabrics for Medical Applications:
Medical Textiles:
Fabrics used in medical settings, such as surgical gowns and drapes, require specific tear-resistance properties. Testing ensures they can withstand handling during procedures while maintaining a barrier function.
By incorporating Elmendorf Tear Testing into quality control procedures, manufacturers can ensure their fabrics meet the demands of their intended use. This not only enhances product performance and durability but also contributes to user safety and satisfaction.
4. Which kind of material has the higher tear strength?
When it comes to tear resistance, understanding which materials generally perform better can be a valuable asset. However, it’s important to remember that tear strength is a complex property influenced by several factors. Here, we’ll explore some key material characteristics that tend to contribute to higher tear strength in fabrics.
A. Fiber Properties:
In general, synthetic fibers like nylon, polyester, and aramid fibers (e.g., Kevlar) often exhibit higher tear strength compared to natural fibers like cotton or silk. This is because synthetic fibers tend to be stronger and more resilient.
The inherent strength of the individual fibers plays a crucial role. Fibers with higher tenacity, meaning they can withstand greater forces before breaking, contribute to a fabric’s overall tear resistance.
B. Fabric Construction:
Weave Type: Woven fabrics generally demonstrate greater tear strength compared to knitted fabrics. This is due to the interlacing of yarns in woven fabrics, creating a more robust structure that resists tearing forces better. The specific weave pattern (e.g., plain weave, twill weave) can also influence tear strength.
Yarn Count and Twist: Fabrics made with a higher yarn count, meaning a thicker yarn, tend to have greater tear resistance compared to those with a lower yarn count. Similarly, yarns with a higher twist, where the fibers are more tightly intertwined, can contribute to improved tear strength.
C. Finishing Treatments:
Certain finishing treatments, such as applying resin coatings, can enhance a fabric’s tear resistance. These coatings act as a protective layer, offering additional reinforcement and reducing the ease of tearing.
5. What is the Tear Test Procedure?
Understanding the process behind the Elmendorf Tear Test is essential for appreciating the method’s accuracy and reliability. So let’s understand the procedure:
A. Sample Preparation:
The testing process begins with meticulous sample preparation. Fabric specimens are cut according to specific standards, typically rectangular with a precise central notch. The notch size and orientation are crucial, as they influence the tear initiation point and subsequent tear path. International standards like ASTM D1424 define the exact dimensions and cutting procedures for sample preparation.
B. Specimen Clamping:
Once prepared, the fabric sample is securely clamped in the Elmendorf tester. The clamping mechanism holds the specimen firmly in place, ensuring a consistent starting point for the tear propagation. Proper clamping ensures the applied force acts solely on tearing the fabric, eliminating any influence from slippage or movement within the clamps.
C. Pendulum Setup and Release:
The Elmendorf tester features a pendulum, a weighted arm free to swing around a fixed pivot point. The pendulum weight is precisely defined by the testing standard. The pendulum is then raised to a specific height, converting its position into potential energy. This standardized height ensures consistent testing conditions and allows for repeatable measurements. Once at the designated height, the pendulum is released, initiating the tear test.
D. Tear Initiation and Propagation:
As the pendulum swings downward, it impacts the pre-cut notch in the fabric specimen. This impact initiates a tear in the fabric at the weakest point, the notch. However, the tear doesn’t stop there. The momentum of the pendulum carries it upwards, and during this upward swing, the pendulum exerts a force on the fabric. This force acts to further propagate the tear along the length of the specimen.
E. Force Measurement and Recording:
Throughout the tearing process, the Elmendorf tester precisely measures the force required by the pendulum to keep ripping the fabric. This measured force value represents the fabric’s resistance to tearing. The tester is equipped with sophisticated sensors and a data acquisition system that captures this force value electronically.
F. Result Interpretation:
Once the tear reaches a predetermined length or the pendulum loses its momentum, the test is complete. The recorded force value, typically expressed in grams (g) or Newtons (N), serves as the raw data point for interpreting the fabric’s tear strength. This value is then compared to industry standards or pre-determined specifications for the intended use of the fabric.
6. What is the Elmendorf Tear Test Standard ASTM D1424?
In the world of standardized testing, consistency is paramount. For the Elmendorf Tear Test, ASTM D1424 stands as the most widely recognized international standard. This designation by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) ensures a globally accepted method for measuring fabric tear strength.
ASTM D1424 meticulously outlines the test method and test procedure, guaranteeing that Elmendorf Tear Tests conducted in different laboratories around the world follow the same principles. This standardization allows for reliable comparison of tear strength values across various fabrics and applications.
Now that we have established the significance of ASTM D1424 in standardizing the Elmendorf Tear Test, let’s delve deeper and explore the specific steps involved in the testing procedure. This breakdown will provide a clear understanding of how the test is conducted to measure a fabric’s tear strength.
- Sample Preparation:
The testing process begins with meticulous attention to detail. Fabric specimens are precisely cut according to the dimensions outlined in ASTM D1424. These specimens are typically rectangular and feature a central notch with defined measurements.
2. Specimen Clamping:
Once prepared, the fabric specimen is securely fastened within the Elmendorf tester’s clamps. This clamping mechanism ensures a consistent starting point for the tear.
3. Pendulum Setup and Release:
The Elmendorf tester features a pendulum, a weighted arm free to swing around a fixed pivot point. The weight of the pendulum is clearly defined by ASTM D1424. This pendulum is then raised to a specific height, converting its position into potential energy.
4. Tear Initiation and Propagation:
As the pendulum swings downward, it impacts the pre-cut notch in the fabric specimen. This impact initiates a tear in the fabric at its weakest point, the notch. However, the tear doesn’t stop there. The momentum of the pendulum carries it upwards, and during this upward swing, the pendulum exerts a force on the fabric.
5. Force Measurement and Recording:
Throughout the tearing process, the Elmendorf tester precisely measures the force required by the pendulum to keep ripping the fabric. This measured force value represents the fabric’s resistance to tearing. The tester is equipped with sophisticated sensors and a data acquisition system that electronically captures this force value.
7. What other international tear test standards?
While ASTM D1424 stands as the preeminent international standard for the Elmendorf Tear Test, it’s important to acknowledge the presence of other recognized standards employed globally. These alternative standards often share core principles with ASTM D1424 but might incorporate slight variations to cater to specific testing requirements or regional practices. Here’s a glimpse into four noteworthy international tear test standards:
ISO 13934-1 – Tear properties of fabrics:
Determination of tear force of trouser-shaped test specimens (single tear method). This ISO standard closely aligns with ASTM D1424, utilizing the Elmendorf Tear Tester and employing a similar trouser-shaped specimen with a central notch. However, minor differences in specimen dimensions, clamping conditions, or data analysis procedures might exist.
ISO 9073-4 – Test methods for nonwovens:
Determination of tear resistance. This standard caters specifically to nonwoven fabrics, materials formed by bonding fibers without weaving or knitting. While the Elmendorf Tear Tester might still be used, the specimen shape and testing parameters might be adapted to better reflect the unique properties of nonwoven materials.
DIN 53859-5 – Tear Growth Test:
This German standard focuses on a different tear propagation method compared to the Elmendorf Tear Test. It utilizes a trapezoidal-shaped specimen and a different testing apparatus to evaluate a fabric’s resistance to a growing tear initiated by a small incision.
JIS L 3301: (Elmendorf-type).
This Japanese Industrial Standard (JIS) outlines a method for determining the tear strength of woven fabrics using the Elmendorf Tear Tester. Similar to ISO 13934-1, it shares many core principles with ASTM D1424 but might have slight variations in specific aspects of the testing procedure.
8. What are the differences between the tear test and the tensile test?
While both the Elmendorf Tear Test and the tensile test play crucial roles in evaluating fabric properties, they assess distinct aspects of a fabric’s behavior under stress. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the appropriate test method for your specific needs.
Tear Test: The Elmendorf Tear Test concentrates on measuring a fabric’s resistance to tearing or ripping. This property is crucial for fabrics that experience snags, nicks, or cuts during everyday use. Think of a piece of clothing that easily rips at the seams due to wear and tear, or upholstery fabric that tears prematurely when brushed against. The Elmendorf Tear Test helps predict how a fabric will withstand such scenarios.
Tensile Test: In contrast, the tensile test focuses on a fabric’s strength and elongation capabilities under pulling forces. It measures the maximum force a fabric can withstand before breaking and the extent to which it stretches before reaching its breaking point. This information is vital for applications where fabrics experience significant pulling forces, such as parachute materials or straps in backpacks.
| Features | Elmendorf Tear Test | Tensile Test |
| Focus | Resistance to tearing and ripping | Strength under pulling forces |
| Test Method | Measures force to propagate a pre-cut tear | Measures force to break a fabric specimen |
| Applications | Fabrics prone to snags(upholstery, apparel) | Fabrics under tension (ropes, parachutes, airbags) |
9. How to evaluate the test results of the Elmendorf Tear Test?
Having conducted the Elmendorf Tear Test and obtained the raw data, the next crucial step lies in interpreting the results effectively. The process of transforming the measured force value into meaningful information that can be used to evaluate a fabric’s suitability for its intended application.
1. Understanding the Units:
The Elmendorf Tear Tester typically displays the measured force value in grams (g) or Newtons (N). This value represents the force required by the pendulum to propagate the tear through the fabric specimen. Higher force values indicate greater resistance to tearing, while lower values suggest a fabric more susceptible to rips and snags.
2. Establishing Benchmarks and Specifications:
Interpreting the test results requires comparing the obtained force value to established benchmarks or pre-determined specifications. These benchmarks can be set by industry standards (e.g., minimum tear strength for specific fabric types), manufacturer guidelines, or internal quality control requirements.
For instance, a fabric intended for use in upholstery might have a minimum tear strength specification of 300g as determined by internal quality control procedures. If the Elmendorf Tear Test yields a value above 300g, the fabric passes the test and meets the required tear resistance level for upholstery applications.
3. Considering Fabric Type and Application:
The significance of a particular tear strength value also depends on the fabric type and its intended use. For example, a tear strength of 100g might be considered adequate for a lightweight, disposable wipe, while the same value might be insufficient for a heavy-duty canvas used in tents or backpacks.
4. Statistical Analysis for Robust Interpretation:
In many cases, conducting multiple Elmendorf Tear Tests on identical fabric specimens is recommended. Statistical analysis of the collected data helps account for minor variations that might occur during testing. This analysis, often involving calculating the average tear strength and standard deviation, provides a more robust interpretation of the fabric’s overall tear resistance.
10. How can fabric tear test results be more accurate and reliable?
The Elmendorf Tear Test serves as a vital tool for assessing a fabric’s resistance to tearing and snags. Understanding the test method, procedure, and interpretation of results empowers professionals in the textile industry to make informed decisions about material selection.
Interpreting Elmendorf Tear Test results effectively requires considering factors such as the measured force value, established benchmarks, fabric type, and intended use. Statistical analysis of multiple tests further enhances the reliability of the data. Consulting a textile expert can provide valuable insights, particularly when interpreting results or applying them to specific fabrics and applications.
Optimizing the test’s accuracy and reliability is paramount. Strict adherence to testing standards, calibrated equipment, a controlled testing environment, proper sample handling, and statistical analysis are all crucial aspects to consider. By implementing these strategies, you can ensure the Elmendorf Tear Test yields valuable data that empowers informed decision-making within the textile industry.
11. What is the price range of Elmendorf Tear Testers?
The price range of Elmendorf Tear Testers varies depending on several factors, making it essential to consider your specific needs before making a purchase decision. Here’s a breakdown of some key elements that influence the cost:
1.Functionality and Features:
Elmendorf Tear Testers come in a range of functionalities. Basic models might offer core testing capabilities, while more advanced models might include features like automatic sample feeding, data analysis software, and enhanced digital displays.
2. Testing Capacity and Range:
The testing capacity of an Elmendorf Tear Tester refers to the maximum force it can measure. Testers with a higher capacity are suitable for evaluating heavier fabrics or materials requiring a greater tearing force.
3.Brand Reputation and Manufacturing Origin:
The reputation of the Elmendorf Tear Tester manufacturer can also affect the cost. Established brands with a proven track record of quality and reliability might command a higher price compared to lesser-known manufacturers.
4. Price Range and Considerations:
Considering these factors, the price range for Elmendorf Tear Testers can span from roughly USD 2,000 for basic models to upwards of USD 10,000 or more for advanced models with extensive features and high testing capacities. When making a purchase decision, carefully evaluate your testing requirements and budget constraints to select the Elmendorf Tear Tester that best aligns with your needs.
12. What is the Tear Test for paper and how to evaluate whether the paper is qualified?
Paper, similar to fabric, can be susceptible to tearing. The Elmendorf Tear Test can be adapted to assess a paper’s resistance to rips and tears. This information is crucial for various paper products, including:
Envelopes:
Paper used in envelopes needs to withstand the force of inserting items and potential snags during mailing. The Elmendorf Tear Test helps ensure envelopes possess adequate tear resistance to fulfill their function.
Maps and charts:
These documents are often handled frequently and might be susceptible to tears. The Elmendorf Tear Test helps paper manufacturers select materials with appropriate tear resistance for such applications.
High-quality printing paper:
Paper used for high-quality printing, like brochures or photographs, should resist tearing during handling and finishing processes. The Elmendorf Tear Test aids in selecting a paper that meets these requirements.
Evaluating paper with the Elmendorf Tear Test typically follows similar principles as fabric testing. However, specific adjustments might be made to the testing parameters, such as specimen size or clamping pressure, to accommodate the unique properties of paper.
13. Example of the real application of the fabric tear test:
durability is a key factor when choosing any product. This is especially true for our garments and fabrics. That’s why we leverage a scientific method called the Elmendorf Tear Test to ensure the materials we use meet the highest standards.
This test isn’t just about random numbers. It allows us to simulate real-world scenarios where your clothes might snag or rip. By testing various fabrics and comparing their tear resistance, we can select materials that are built to last. This translates into clothing that you can depend on, wash after wash, adventure after adventure. Ultimately, the Elmendorf Tear Test is our way of guaranteeing that the quality you see is the quality you experience.
Here are a few additional examples of its real-world applications:
Apparel Manufacturing: Selecting fabrics for clothing requires considering tear resistance. The Elmendorf Tear Test helps evaluate fabrics for jackets, pants, and workwear, ensuring they can withstand everyday wear and tear without ripping easily.
Upholstery Selection: Upholstery fabrics need to resist snags and tears during use. The Elmendorf Tear Test helps furniture manufacturers choose upholstery materials that meet the necessary durability standards.
Medical Textiles: Some medical textiles, like surgical gowns, require a balance between tear resistance and breathability. The Elmendorf Tear Test aids in selecting materials that offer both qualities for optimal performance.
14. The well-known fabric Elmendorf Tear Tester Manufacturers in the world:
Selecting a reliable Elmendorf Tear Tester is crucial for generating accurate and dependable results. Here, we explore some of the well-established manufacturers recognized for their quality testing instruments:
TESTEX (China): This leading Chinese manufacturer offers a comprehensive range of textile testing equipment, including Elmendorf Tear Testers. They cater to various testing needs with models featuring different functionalities and capacities.
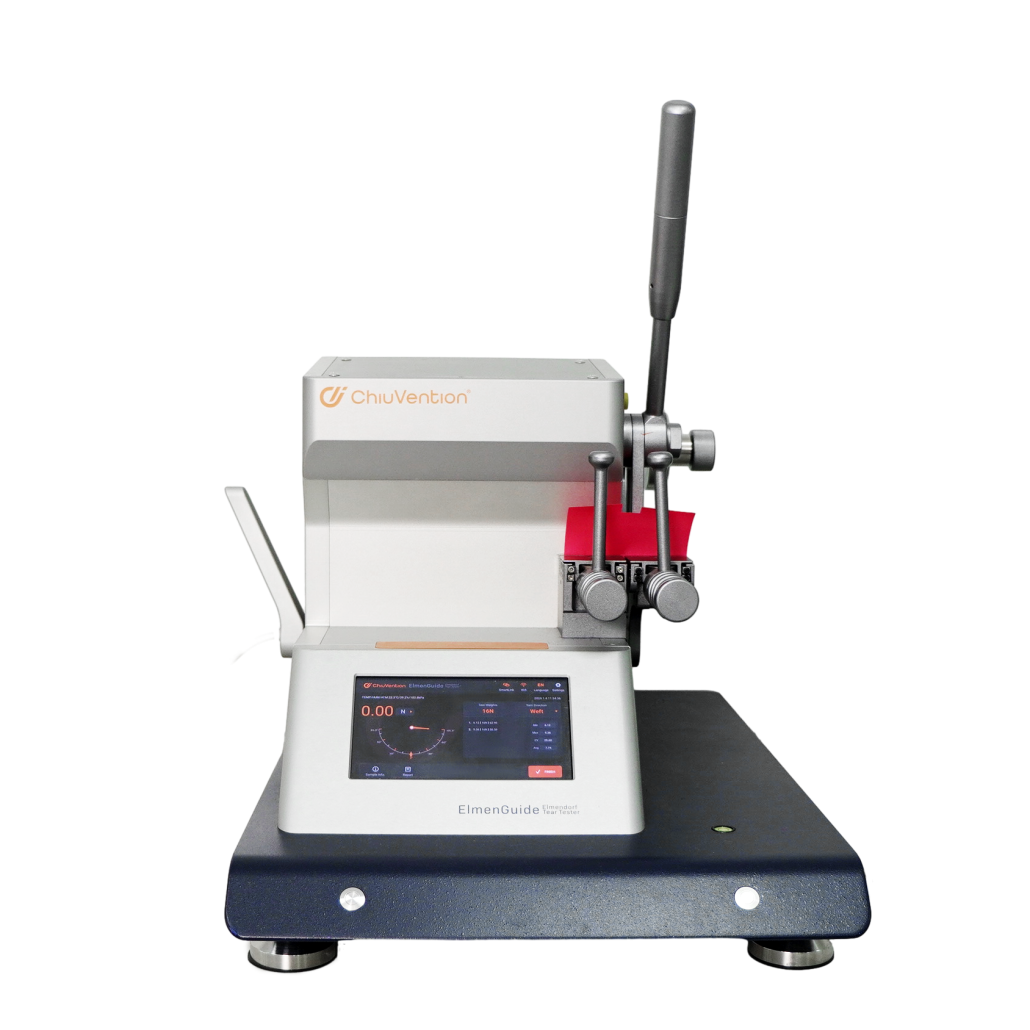
ChiuVention (Designed in Germany and Manufacturered in China): This brand developed a series of intelligent textile testing instruments and its machines are nearly equipped with IoT technology, so you can improve the test efficiency. The ChiuVention Elmendorf Tear Tester
Thwing-Albert Instruments (USA): Renowned for their expertise in material testing instruments, Thwing-Albert Instruments provides Elmendorf Tear Testers known for their durability and user-friendly operation.
Favila (Switzerland): A well-regarded Swiss manufacturer, Favila offers Elmendorf Tear Testers appreciated for their precision and adherence to international testing standards.
Instron (USA): This prominent testing equipment manufacturer provides Elmendorf Tear Testers alongside a vast array of material testing instruments. Their testers are known for their advanced features and data analysis capabilities.
Yamaten (Japan): A trusted Japanese manufacturer, Yamaten offers Elmendorf Tear Testers known for their reliability and innovative design elements.
It’s important to note that this list is not exhaustive, and numerous other manufacturers produce Elmendorf Tear Testers. When making a selection, consider factors like the specific features required, your budget, and the manufacturer’s reputation and after-sales service.
15. How to calibrate the Elmendorf Tear Test?
For the Elmendorf Tear Tester to deliver consistent and reliable results, regular calibration is essential. Calibration ensures the instrument accurately measures the force applied during the tear test. The calibration process typically involves using certified calibration weights with known masses. Here’s a simplified overview of the general steps involved:
- Preparation: Consult the Elmendorf Tear Tester’s user manual for specific calibration instructions. Ensure you have the necessary tools and certified calibration weights with documented traceability to national standards.
- Warm-Up: Allow the Elmendorf Tear Tester to warm up for the recommended period as specified by the manufacturer. This ensures the instrument’s internal components are at optimal operating temperature for accurate measurements.
- Zero Calibration: Following the manufacturer’s instructions, perform a zero calibration to ensure the tester reads zero force when no weight is applied to the pendulum.
- Calibration Weight Testing: Methodically raise the pendulum arm to its designated release height for each calibration weight. Release the pendulum with each weight and record the force value displayed on the tester.
- Data Comparison: Compare the recorded force values with the certified values of the calibration weights. If there are significant deviations, adjustments to the Elmendorf Tear Tester might be necessary.
- Calibration Certificate: Upon successful calibration, obtain a calibration certificate from a qualified technician. This certificate documents the date of calibration, the weights used, and the measured versus certified values, serving as proof of the instrument’s accuracy.