What is quality control in textile testing?
Quality control in textile testing is indispensable for ensuring the integrity and reliability of the textile products. Textile testing entails several assessments, together with physical, chemical, and performance tests, to verify compliance with requirements and specs.
Testing strategies:
Physical tests include critiques of material strength, sturdiness, and dimensional balance. Tensile energy checks determine a cloth’s resistance to stretching and tearing, at the same time as abrasion resistance assessments investigate its capability to resist friction and wear. Dimensional ability exams degree changes in material dimensions as a result of elements like washing, drying, and ironing.
When it comes to chemical tests aware of fiber composition, dye content, and then colorfastness. Thus, fiber composition evaluates and identifies the sorts of fiber present in a fabric that impact its properties and then its overall play. The colorfastness tests pick a fabric resistance in order to fade while visual to washing, looking, and various ecological things.
Also, the performance test stimulates the real-globe circumstances in order to assess fabric suitability for unique applications. Moisture management checks out the material’s ability to wick moisture and the far away from the skin. In addition, thermal insulation tests measure its capacity to retain heat. Thus, UV protection checks the fabric’s ability to daring UV radiation that is highly needed for outer and activewear.
What is the main objective of textile testing?
In textile testing, the main thing is to make sure that products in textiles need to meet reliable and designated product standard quality and then performance needs. Here are some of the key parts that include;
Ensuring quality:
Well, testing aid to pick out and then rectify mistakes. Also, easily notify the deviations from high-quality standards and make sure that only quality products reach to market. The quality requirements specify the acceptable parameters for elements such as material, colorfastness, and performance properties, and guide to production process in order to meet the client expectations.
Facilitating Innovation:
Testing gives precious comments for product improvement and innovation, enabling producers to create new materials, technologies, and designs that meet evolving client needs. Innovation in fabric testing techniques, inclusive of advanced technology for overall performance evaluation or sustainable materials, drives development in the textile industry by presenting unique solutions to challenges and addressing emerging client needs.
Validating Compliance:
Thus, fabric test easily verifies the product regulatory standards, specifications, and consumer needs for protection, environmental sustainability, and then overall performance. The regulatory complaints include the one set by government or industry organizations, setting a less necessity for the safety of the product and then it overall performance.
Improving overall performance:
Textile testing lets optimized product performance and then client satisfaction as by assessing elements as like comfort, strength, functionality and so more. The overall performance test simulates the real-world conditions in order to assess material capability for precise specifications and then make sure it meets the overall performance of the end-user.
What are the four main components of quality control?
When it comes to quality control in the textile industry, there are four main elements includes;
Process control:
It will measure, monitor, and alter the production process to maintain reliability and consistency. It regulates various factors such as temperature and pace to optimize the manufacturing circumstances. Statistical process control techniques examine data in order to stumble on qualities that allow well-timed inventions to easily prevent defects and then make certain product quality.
Checking out and Inspection:
Well, testing and inspection strategies are crucial for assessing the quality of products at various production ranges. Thus, Physical tests contrast cloth properties including strength, sturdiness, and then dimensional balance. The chemical test decides the material composition, color content, colorfastness, and more. Inspection confirms loyalty to needs and the detects or deviations need corrective action.
Standards and Specifications:
Establishing clear quality standards and specifications is foundational to effective, high-quality manipulation. Standards define applicable parameters for factors like fiber content, colorfastness, and overall performance traits. Specifications offer particular instructions for manufacturing approaches, ensuring consistency and uniformity in product satisfaction.
Non-stop development:
The continuous development initiative goal is to perceive possibilities for enhancing quality, efficiency, and consumer pleasure. Data evaluation equipment includes Six Sigma or Lean methodologies, becoming aware of root reasons for defects and inefficiencies, and guiding centered improvement efforts. Feedback mechanisms and client surveys or employee tips provide treasured insights for refining procedures and riding ongoing development.
What are the stages of quality control in the apparel industry?
Quality control in the apparel industry is generally divided into several stages, every one of which plays a vital function in maintaining product quality:
Manufacturing process control:
For the duration of the manufacturing manner, high-quality management measures are applied to monitor numerous parameters, including temperature, humidity, anxiety, and machine settings. Continuous monitoring enables the pick out and accuracy of any deviations from established standards, thereby ensuring consistency and uniformity in the final product.
Raw Material Inspection:
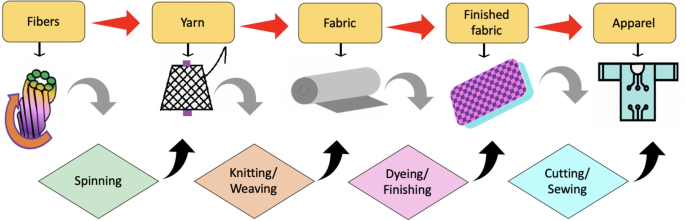
The primary stage includes analyzing incoming raw materials, including fibers, yarns, and fabrics, to ensure that they meet quality specs. This could contain testing for parameters such as fiber content, tensile strength, colorfastness, and dimensional stability.
In-Process Inspection:
At various levels of manufacturing, in-process inspections are performed to check for defects, irregularities, or inconsistencies. This would involve visual inspections, physical testing, and statistical process management strategies to stumble on and address issues promptly.
Finished Product Inspection:
As soon as the production process is whole, finished products go through a rigorous inspection to assess their universally great appearance and performance. This last inspection ensures that only products that meet the required standards are shipped to customers.
What is the difference between QC and QA in textiles?
While Quality control (QC) and quality assurance (QA) are closely associated concepts, they differ in focus and scope:
Quality Control (QC):
Quality control mainly focuses on identifying and correcting defects during production to ensure product quality meets requirements. It involves inspections, trying out, and process tracking to identify deviations from provisions and implement corrective actions. QC activities are commonly performed through manufacturing personnel or devoted quality control groups stationed at key points within the manufacturing method.
Quality assurance (QA):
Quality assurance includes broader activities aimed toward stopping defects and making sure of consistent quality at some stage in the business industry. QA includes setting up quality control systems, enforcing procedures, and training employees to follow requirements and best practices. It focuses on proactive measures to prevent errors instead of simply detecting and correcting them after the fact.
What is the difference between ISO and ASTM on material testing?
Even as both ISO (International Organization for Standardization) and ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) expand standards for cloth testing, they differ in terms of scope, geographical coverage, and organizational shape:
Scope:
ISO requirements are developed through an international consensus manner related to member international locations from around the arena. They cover an extensive range of industries and sectors, which include textiles, manufacturing, healthcare, and environmental management. ASTM standards, on the other hand, are often centered on substances and products used in the United States but are also diagnosed and followed internationally.
Geographical coverage:
ISO standards are globally diagnosed and adopted via international locations worldwide, offering a commonplace framework for quality guarantee, trade, and regulatory compliance. ASTM requirements have a robust presence within the United States and North America but also are used in many other nations, in particular in industries in which U.S. standards are preferred or required.
Organizational structure:
ISO is a worldwide standard Testing organization composed of National Standard bodies from over 160 nations. It develops consensus-based requirements through a rigorous system concerning technical committees, professional reviews, and stakeholder consultations. ASTM is a private agency that develops voluntary consensus requirements through its committees, which consist of representatives from industry, academia, authorities, and other stakeholders.
Notwithstanding these differences, ISO and ASTM requirements regularly supplement each other, and lots of companies adhere to each set of standards to ensure comprehensive insurance and compliance with global best practices in fabric testing.
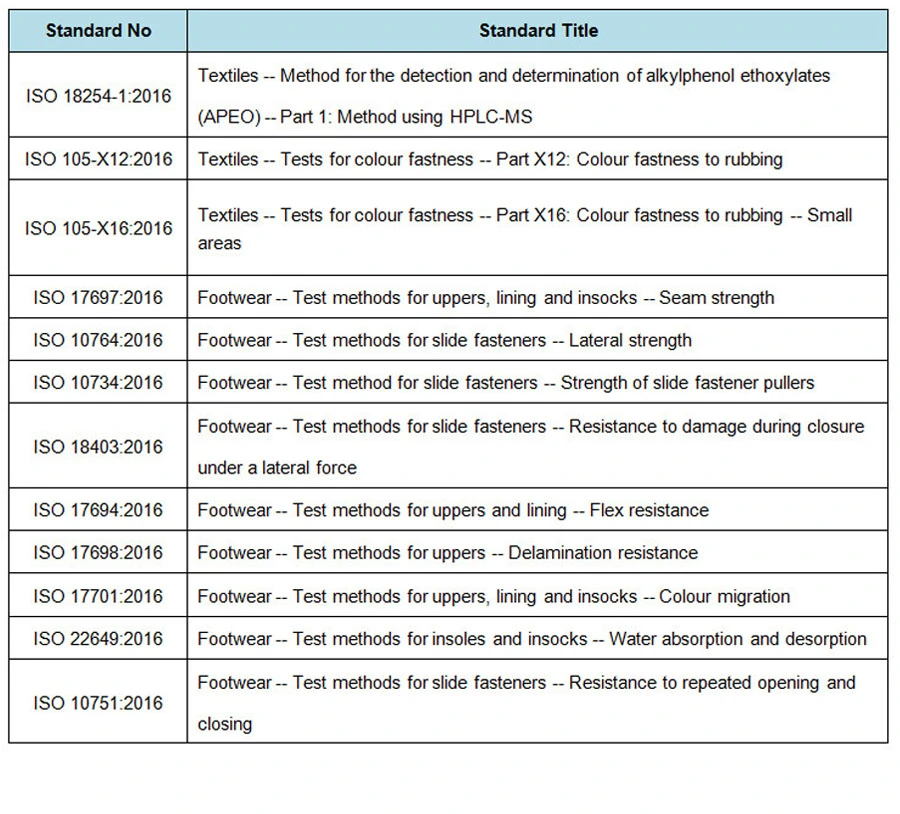
What are the ISO textile testing standards?
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has advanced a complete set of standards for fabric testing and excellent guarantees. Those standards cover various aspects of fabric manufacturing, testing strategies, performance necessities, and environmental considerations. Some key ISO fabric testing requirements include;
ISO 105
The ISO 105 series of standards specifies test strategies for assessing colorfastness properties of textiles beneath various situations. Those include colorfastness to washing, mild rubbing, perspiration, and water exposure. Compliance with ISO 105 standards ensures that textile products hold their shade integrity and look through the years, assembly client expectancies for quality and sturdiness.
ISO 139
ISO 139 standards address methods for figuring out the dimensional balance of textiles subjected to diverse treatments, which include washing, drying, and ironing. These standards make sure that fabric product preserves their size and structure below everyday use situations, stopping shrinkage, distortion, or stretching that might have an effect on product quality or look.
ISO 206
ISO 206 standards cover take a look at strategies for evaluating the mechanical properties of textiles, consisting of tensile strength, tear resistance, abrasion resistance, and seam power. Compliance with ISO 206 requirements ensures that fabric products meet minimum necessities for structural integrity, sturdiness, and overall performance, enhancing product reliability and durability.
ISO 6330
ISO 6330 specifies procedures for washing and drying textiles below controlled situations to evaluate their dimensional modifications, colorfastness, and average overall performance. These requirements make certain that fabric merchandise preserves its look, shade, and best traits after repeated laundering, assembly consumer expectations for sturdiness, and washability.
ISO 170
ISO 170 standards outline procedures for testing the flammability of textiles and fabric products to evaluate their resistance to ignition and spread of flame. Compliance with ISO 170 requirements lets us ensure product protection by lowering the hazard of fire dangers related to textile materials, especially in packages where flammability is a subject, including kidder’s sleepwear or upholstery fabrics.
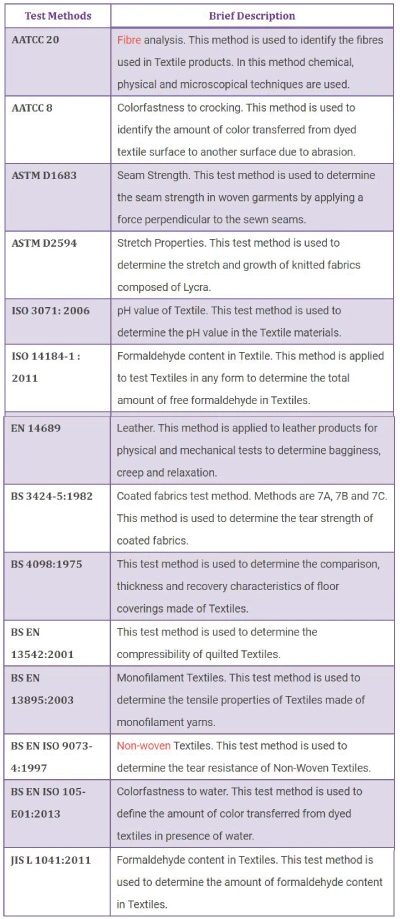
How do you measure fabric quality?
Material quality may be assessed through the usage of numerous quantitative and qualitative techniques, including:
Fabric Testing:
Physical tests check material properties associated with strength, sturdiness, and overall performance. Tensile power exams degree a fabric’s resistance to stretching and tearing, indicating its structural integrity. Tear resistance tests examine a fabric’s capability to withstand tearing forces, which is essential for packages requiring durability and sturdiness.
Chemical evaluation:
Chemical evaluation determines fabric composition, dye content, and colorfastness. Fiber composition tests determine the sorts and proportions of fibers found in a fabric, influencing its properties and performance. Colorfastness exams investigate a fabric’s resistance to fading whilst exposed to washing, light, or different environmental elements.
Visual Inspection:
Visible inspection evaluates material look, finish, and surface traits. Inspectors examine factors like shade consistency, print clarity, and floor defects, which could affect product aesthetics or capability. Magnification tools, such as microscopes or magnifying lenses, help detect quality details or imperfections that the open eye might not see.
Overall performance Testing:
Overall performance testing fakes real-global circumstances to measure fabric suitability for specific programs. Moisture control exams examine a fabric’s ability to wick moisture far away from the skin, which is essential for active wear or sports clothing. Thermal insulation tests the degree of a material’s capability to hold warmth, which is imperative for cold-climate clothing or exterior gear.
How does an excellent textile fabric enterprise typically implement quality control?
Superb textile fabric organizations commonly implement comprehensive quality control measures throughout all components of production, from raw material sourcing to the very last product delivery. A few key characteristics of their quality management practices encompass:
Dedication to Quality Excellence
Top management’s commitment to quality excellence sets the tone for the organization, emphasizing the significance of excellence as a strategic priority and using continuous development tasks.
Clear quality guidelines and objectives
Establishing clear quality regulations, targets, and overall performance objectives guarantees alignment with patron necessities, regulatory standards, and industry quality practices.
Quality control system Certification
Acquiring certification across the world identified best control systems, inclusive of ISO 9001, demonstrates the corporation’s commitment to quality warranty, non-stop improvement, and client pleasure.
Strong provider Qualification and evaluation
Enforcing rigorous supplier qualification and evaluation processes ensures that only reliable, reputable suppliers who meet stringent quality criteria are decided on to offer raw materials and additives.
Advanced testing and Inspection centers
Making an investment in trendy trying-out and inspection facilities, prepared with advanced instrumentation and system, allows a thorough assessment of raw materials, intermediate products, and completed goods to ensure compliance with quality standards.
Continuous Training and skill improvement
Imparting ongoing training and skill development opportunities for employees at all degrees enhances their competency, knowledge, and recognition of fantastic necessities, developing a culture of quality excellence.
Data-driven decision-Making
Making use of data analytics, overall performance metrics, and quality signs allows information-driven choice-making, letting well-timed identity of best issues, root motive evaluation, and implementation of corrective actions.
Client-Centric approach
Prioritizing consumer pleasure, comments, and engagement develops long-term relationships, loyalty, and belief, positioning the organization as a desired supplier of super-fabric products.
Importance of measuring fabric quality
Measuring fabric quality is supreme in numerous industries, which include style, indoor layout, and manufacturing. Quality material guarantees the longevity, overall performance, and common pleasure of the end product. Right here’s why measuring fabric quality is critical:
Comfort: Fabric of advanced quality provides comfort to the wearer or user. They are soft in opposition to the skin, breathable, and provide the proper level of insulation, enhancing consolation in various climates and conditions.
Client satisfaction: Ultimately, the quality of material immediately influences user pleasure. Product made from extremely good cloth is valued by consumers for their comfort, sturdiness, and aesthetic enchantment, leading to fantastic brand popularity and repeat enterprise.
Performance: One-of-a-kind packages require precise overall performance attributes from cloth, which include moisture-wicking for active wear or flame resistance for commercial use. Measuring cloth quality guarantees it meets the crucial performance standards for its meant reason.
Sturdiness: Splendid material is durable, withstanding wear and tear over the years. It resists fraying, tearing, and fading, making sure clothes and products keep their integrity even after repeated use.
Appearance: The advent of cloth plays a huge role in the aesthetics of the very last product. Quality cloth continues its shade, texture, and structure, contributing to a polished and expert look.
Measuring cloth quality is necessary for handing over products that meet or exceed customer expectations, ensuring satisfaction, sturdiness, and performance throughout various industries.
How can we improve quality in the textile industry?
Process Optimization:
Process optimization entails streamlining manufacturing workflows, evading bottlenecks, and enhancing performance to enhance product quality and reduce fees. This will include implementing lean manufacturing principles, adopting superior manufacturing technologies, and optimizing delivery chain management practices to decrease waste and maximize value-added activities.
Training and Education:
Education and training applications provide employees with the knowledge, skills, and competencies needed to hold quality requirements and perform their roles successfully. This can include training on excellent control methods, equipment operation, protection protocols, and compliance necessities. Continuous studying opportunities and expert improvement initiatives help empower employees to contribute to pleasant development efforts and live abreast of industry trends.
Dealer Collaboration:
Taking part with providers is fundamental for making sure the satisfaction and reliability of raw materials and components used in textile manufacturing. Organizing strategic partnerships with trusted providers, conducting provider audits, and implementing exceptional guarantee agreements assist in maintaining supply chain integrity and mitigating dangers associated with quality deviations or disruptions.
Customer Feedback:
Purchaser feedback provides valuable insights into product overall performance, pleasure tiers, and regions for development. Enforcing client comments mechanisms, consisting of surveys, opinions, and proceedings managing procedures, permits manufacturers to perceive consumer picks, deal with issues proactively, and continuously enhance product quality and client satisfaction.
Technology Adoption:
Adopting advanced technologies and digital solutions can revolutionize high-quality control processes inside the fabric industry. This consists of implementing automated inspection systems, sensor-based total tracking technologies, and facts analytics equipment to discover defects, optimize manufacturing parameters, and enhance choice-making primarily based on real-time insights.
How is quality control maintained throughout the apparel production process?
Maintaining quality management at some stage in the clothing manufacturing system requires a close interest in detail, adherence to mounted requirements, and proactive measures to save you from defects and deviations. Some key practices for maintaining quality control include:
Raw material selection
Careful choice and assessment of raw materials based on quality, overall performance, and suitability for the supposed application laid the inspiration for high-quality garb production.
Process monitoring and manipulate
continuous tracking of production procedures, which includes spinning, weaving, knitting, dyeing, printing, and completing, facilitates pick out and accurate deviations from satisfactory requirements, ensuring consistency and uniformity within the final product.
Quality Assurance Procedures
Implementing quality assurance procedures, together with visual inspections, dimensional measurements, and physical testing, at numerous tiers of production facilitates detect defects, mistakes, or irregularities early in the system, minimizing rework and scrap.
Worker Training and Engagement
Presenting training, guidance, and incentives for employees fosters a lifestyle of quality consciousness, duty, and teamwork, encouraging active participation in quality improvement tasks.
Provider and supplier management
Setting up clear quality necessities, specs, and performance expectancies for suppliers and carriers guarantees the steady quality of raw substances, additives, and services at some stage in the supply chain.
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
The usage of statistical strategies, inclusive of control charts, procedure capability analysis, and Pareto evaluation, enables screening overall performance, perceiving trends, and taking proactive measures to keep quality and balance.
Non-stop improvement tasks
Encouraging remarks, soliciting pointers, and enforcing corrective and preventive moves based on data evaluation and overall performance metrics force ongoing development in quality, performance, and customer pleasure.
Conclusion
Quality control in the textile industry is typical for ensuring that textile products meet distinctive requirements of best, overall performance, and protection. From raw material selection to final product inspection, careful attention to elements, rigorous trying out, and continuous improvement projects are supreme to accomplishing excellence in apparel production. By enforcing robust quality management measures, embracing technological improvements, and fostering a tradition of pleasant awareness, fabric establishments can supply superior products that meet client expectations and power sustainable commercial enterprise growth.
Want to know more about textile quality control? Just visit the complete guide.
For more information on textile testing methods/standards
or textile testing machines, contact us:
What’s App: +86 180 2511 4082
Tel: +86 769 2329 4842
Fax: +86 769 2329 4860
Email: sales@chiuvention.com