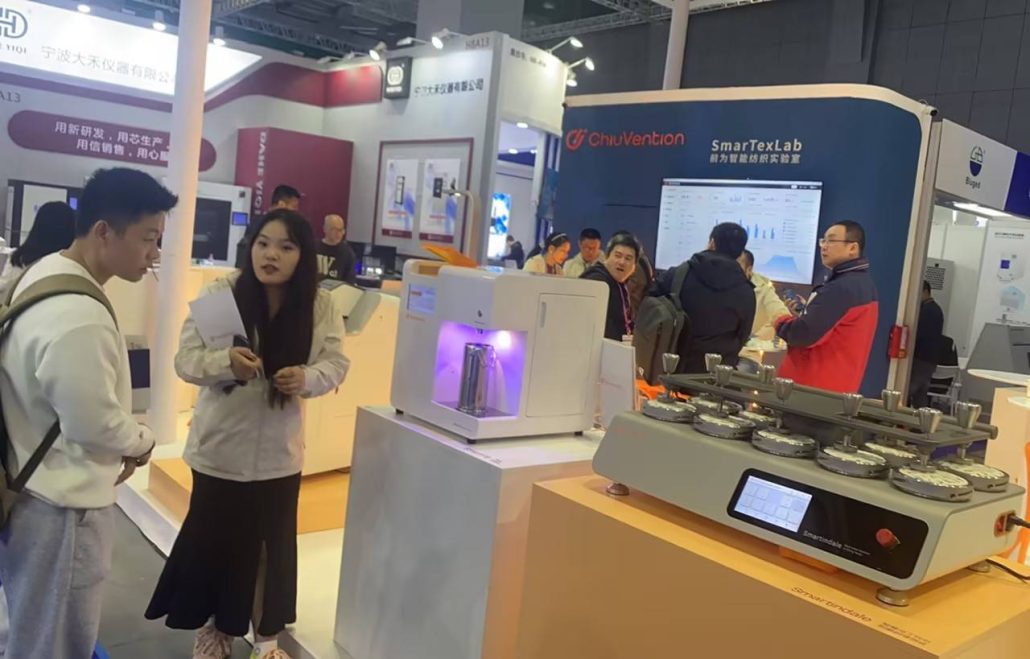
Textile Testing Overview
Textiles are skin-friendly items, we wear them every day. Different fabrics have different levels of comfort, and their performance is not the same.
Fabric will be tested before the processing of clothing production by a variety of textile testing items, so what are the textile testing projects and standards? Generally, we can divide the textile testing into physical testing and chemical testing. Physical testing measures the physical amount of textiles, and finishing analysis to determine some of the physical properties and quality of the textile. Chemical testing uses some chemical testing techniques and chemical instruments to determine the chemical properties of the textile and to analyze the composition of its chemical content. In this article, we will give you a systematic introduction to Textile Testing and Textile Labs, especially for lab construction.
The following are common testing standards and programs for textiles:
Physical properties: density, yarn count, gram weight, yarn twist, yarn strength, fabric structure, fabric thickness, loop length, fabric coverage coefficient, fabric wrinkle or weave shrinkage, curvilinear deformation, tensile strength, tear strength, seam slip, seam strength, bonding strength, single yarn strength, yarn strength per unit of line density, anti-hooking, crease reply angle test, stiffness test, bursting strength, abrasion resistance test, pilling resistance, size, and appearance durability after washing, etc;
Colorfastness: color fastness to soaping, color fastness to rubbing, color fastness to chlorine, color fastness to non-chlorine bleaching, color fastness to dry cleaning, color fastness to washing, color fastness to sunlight, color fastness to sweating, color fastness to pressing, color fastness to saliva, and color fastness to actual washing.
Chemical properties: pH content, formaldehyde content, lead content, azo dye test, heavy metal content test, water absorption, water content, odor, mercerizing effect of cotton, hot pressing,
dry heat, storage sublimation, composition analysis, etc;
Relevant Textile Testing Standards are mainly from
GB China National Technical Code for Basic Safety of Textile Products
DIN German Standards Institute
AATCC American Association of Textile Dyers and Chemists
AS Australian Standards Association
ASTM American Society for Testing Materials
JIS Japanese Industrial Society
US CPSC American Consumer Product Safety Commission
FZ China Textile Industry Association
CAN Canadian Standards Council
Each country has different standards for each test of textiles, very detailed, so if you are working with overseas trade textile enterprises, you should know in advance the standard requirements of the product from the importing country. Thus you can do the fabric testing strictly by the country’s standards, which can help you to pass the country’s spot check.
To ensure the quality of textiles and fabrics, textile testing and quality control are necessary and are of great significance to the various enterprises in the textile supply chain as well as to consumers. Textile fabric testing under different testing standards can analyze the performance of textiles, to make their production of textiles more advantageous, and it also can improve the consumers’ confidence in textiles and clothing.
The following is a brief list of some of the most common textile testing programs:
Textile Physical Testing
1) Main items:
Shrinkage, yarn count, density, gram weight, yarn composition test, tensile strength, tearing strength, seam slippage, seam strength,
top breaking strength, abrasion resistance, anti-pilling, and pilling resistance.
2) Specific instructions:
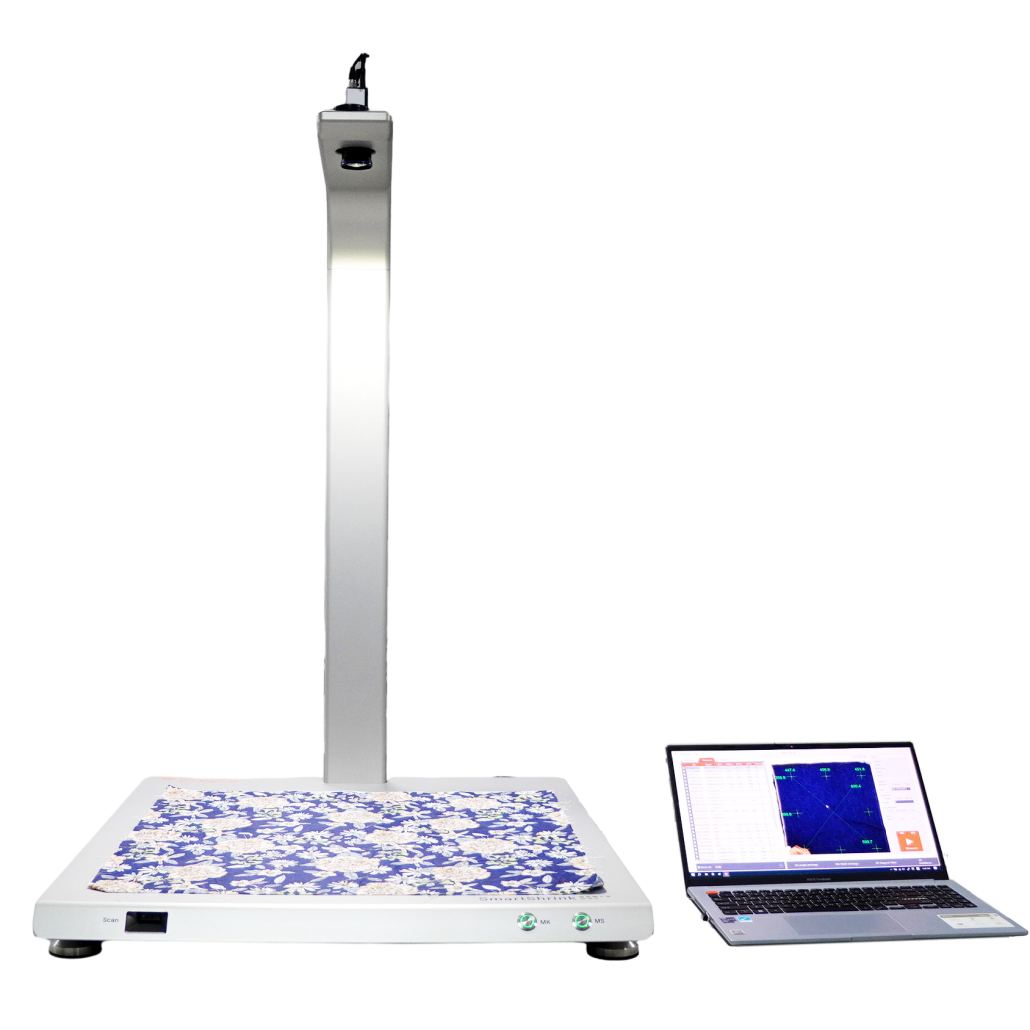
Fabric Shrinkage Test
Purpose: To determine the dimensional stability of woven or knitted fabrics after repeated washing in a washing machine.
Principle: Before washing, mark the size of the specimen and judge the size change of the specimen by measuring the change of the mark after washing. Of course, nowadays there are very advanced textile testing machines that can directly measure the shrinkage rate with intelligent visual inspection algorithms.
Process: Choose the washing and drying method, cycle and drying times according to the fabric type and customer requirements, add standard detergent and appropriate water level to start washing and drying, and finally measure the size change manually or calculate by intelligent instrument software to get the test result.
Yarn count: refers to the thickness of the yarn, most of the current use of imperial count, is expressed in Ne. It can be tested by a yarn count testing machine.
Density: the number of yarns per inch.
Grammage: Ounces per square yard of fabric or grams per square meter of fabric.
Composition Yarn Test: fiber content analysis, cotton, linen, wool (sheep, rabbit), silk, polyester, viscose, spandex, nylon, velvet content, fabric composition and content, yarn twist, etc;
Tensile strength
A certain size of fabric is stretched by the tensile strength machine at a constant rate, until the fabric breaks, the force measured is tensile strength. The test of tensile strength has the method of grabbing samples and the method of stripping samples, you can choose a specific test method according to different test standards and customer requirements.
Tear strength
A certain size of the specimen is clamped in the tearing strength instrument. There will be a small cut at the center of the specimen firstly to determine the direction of tearing, then the pendulum of the tearing strength instrument falls to the specimen to tear the whole specimen, the force used is the measured tearing strength. This kind of machine is called Elmendorf Tear Tester.
Seam Slip
Folding a certain size of fabric and sewing along the width, then use the tensile tester to stretch that seam position with a constant rate till there is a seam opening, which is what we measure as seam slip. Seam slip can be measured in two ways: test the force used by constant seam opening and test the seam opening dimension by constant force. The seam slip test is generally only used for woven fabrics.
Seam strength
Nearly the same situation with the seam slip, a certain size of the fabric folded, along the width of the direction of the seam line, cut the sample at a certain distance from the seam line, then use the tensile strength tester with a constant rate of stretch to make the seam line broken, the force used is called seam strength. Seam strength can be carried out at the same time as the seam slip, generally only used for woven fabrics tests.
Top breaking strength
Apply an expansive expansion force to a plane fabric at a suitable angle until the fabric breaks, then this force is the top breaking strength.
Abrasion Resistance
The specimen mounted on the clamp and the standard rubbing cloth are rubbed against each other in a certain trajectory under a certain pressure until the fabric shows the number of broken yarns or holes as required by the customer, and the number of rubbing times at the end of the experiment is recorded, which is the value of the measured abrasion resistance. You should use a Martindale Abrasion Tester.
Anti-pilling
The fabric will be tumbled and rubbed for a certain period under specific conditions to see the surface of its hairy pilling situation, Ball-pilling refers to the formation of pom-pom clusters of entangled fibers on the surface of the fabric. Pilling refers to the fabric surface fiber roughness and (or) fiber hair, resulting in a change in the appearance of the fabric, and these 2 kinds of pilling are assessed by rating the sample photo or comparing the tested sample with the original sample. It also can be done by a Pilling Tester.
Air Permeability Test
Air permeability is the measure of airflow passed through a given area of a fabric. This parameter influences the thermal comfort properties of fabrics to a large extent. It is generally accepted that the air permeability of a fabric depends on its air porosity, which in turn influences its openness. The machine used for this test is called an air permeability tester.
Colorfastness test
Main items:
Colorfastness to washing, color fastness to dry cleaning, color fastness to rubbing, color fastness to sunlight,
color fastness to sweat, color fastness to water, color fastness to chlorine bleaching, color fastness to non-chlorine bleaching, color fastness to hot pressing, etc.
Washing color fastness: the specimen is sewn together with the standard lining fabric, washed, cleaned dried, and washed under suitable temperature, alkalinity, bleaching, and friction conditions so that the test results can be obtained in a shorter period. The friction effect is accomplished by tumbling and impacting of small bath ratio and an appropriate number of stainless steel beads, and finally, the standard post-lining fabric and specimen are rated with a colorfastness special gray card to get the test results. Different test methods have different temperatures, alkalinity, bleaching and abrasion conditions, and specimen size, and it depends on the specific test standard and customer requirements. Generally, the colors with poor color fastness to washing are Cuiran, Brilliant Blue, Black Big Red, Navy Blue, and so on.
Colorfastness to dry cleaning: the same as colorfastness to washing, only the washing is changed to dry cleaning.
Color fastness to friction: Put the specimen on the friction fastness meter, and rub the standard friction white cloth with it for a certain number of times under a certain pressure, each group of specimens needs to do dry friction color fastness and wet friction color fastness. The color stained on the standard rubbing cloth is graded by a gray card, and the grade obtained is the color fastness to rubbing measured. The color fastness to rubbing requires both dry and wet rubbing tests, and all colors on the specimen should be rubbed.
Colorfastness to sunlight
textiles are usually exposed to light when in use, light can destroy the dyes and thus lead to the well-known “fading”, so that the colored textiles change color, generally lighter, and darker, and some also appear color light change, so, it is necessary to test the color fastness to sunlight. Sunlight color fastness test, that is, the specimen with different levels of blue wool standard cloth together in the prescribed conditions for sun exposure, the specimen and blue wool cloth for comparison, assess the color fastness to light, the higher the level of blue wool standard the more light-resistant.
Most color fastness to sunlight tests are done by a Xenon Arc Test Chamber. It uses a full-spectrum xenon arc lamp light source. Through a special filter glass, in the test chamber to produce a specific glass window sunlight spectrum, exposure to the specimen. Then with a combination of temperature, humidity, rain, condensation, and other natural environment simulations, comprehensive action on the specimen. When the test is completed, the light fastness and aging of the test material are evaluated mainly by observing the fading, discoloration, brittleness, cracking, cracking, color peeling, and other phenomena of the material. The fading and aging grade of the product is usually evaluated with a gray sample card and blue wool standard (blue standard).
Sweat color fastness
the specimen and the standard lining fabrics are sewn together, put in the sweat solution treatment, clamped on the sweat color fastness meter, put in the oven at a constant temperature, and then the specimen’s lining fabrics are dried separately, finally, the standard lining fabrics and the specimen are rated with a special gray card for color fastness to get the test results. Different test methods have different ratios of sweat stains, different specimen sizes, and different test temperatures and times.
Water stain color fastness
the specimen and the standard lining fabrics were sewn together, put in certain conditions of the water after full immersion, clamped on the color fastness to perspiration instrument, put in the oven at a constant temperature, and then the specimen lining fabrics were dried, and finally, the standard lining fabrics and the specimen with the color fastness to the special grey card for grading, to get the test results. Different test methods have different specimen sizes, different test temperatures, and times.
Chlorine bleaching color fastness: After the fabric is washed in chlorine bleaching solution under certain conditions, the degree of color change is assessed, which is the chlorine bleaching color fastness.
Non-chlorine bleaching color fastness: the fabric will be washed under washing conditions with non-chlorine bleaching, after assessing the degree of color change, which is non-chlorine bleaching color fastness.
Hot pressing color fastness: the dry specimen with cotton lining fabric cover, in the specified temperature and pressure of the heating device under pressure for a certain period of time, and then use gray sample card to assess the specimen color change and lining fabric staining. Hot pressing color fastness test is done by dry pressure, moisture pressure, or wet pressure, according to different customer requirements and test standards.
Fabric Chemical Performance Test
Main test items:
Formaldehyde test, pH test, water repellant test, oil repellant test, anti-fouling test, flame retardant test, fiber composition analysis, banned azo dyes test, etc.
Formaldehyde test
the free formaldehyde in the fabric sample is extracted by dissolving the fabric pieces and then the formaldehyde content is calculated by colorimetric test.
Nowadays, in the market, textile products can be finished with resin to improve the wrinkle resistance of the products, and this resin finishing agent is directly synthesized by formaldehyde, so the fabrics that have been finished with these resins will have a certain amount of formaldehyde residue. In addition, to improve the dyeing fastness, the cross-linking agent in the paint printing paste and the color fixing agent used after dyeing with direct and reactive dyestuffs, etc. will leave a certain amount of formaldehyde on the clothing material. These formaldehyde can be measured by certain test methods.
pH test
the acidity or alkalinity of the fabric solution is measured accurately with a pH meter, and the value read out on the pH meter is the measured pH value.
Water repellency, oil repellency, and stain resistance test
The resistance of the fabric to water, oil, and stains is measured in a certain way, mainly for the fabrics that have undergone three-proof finishing.
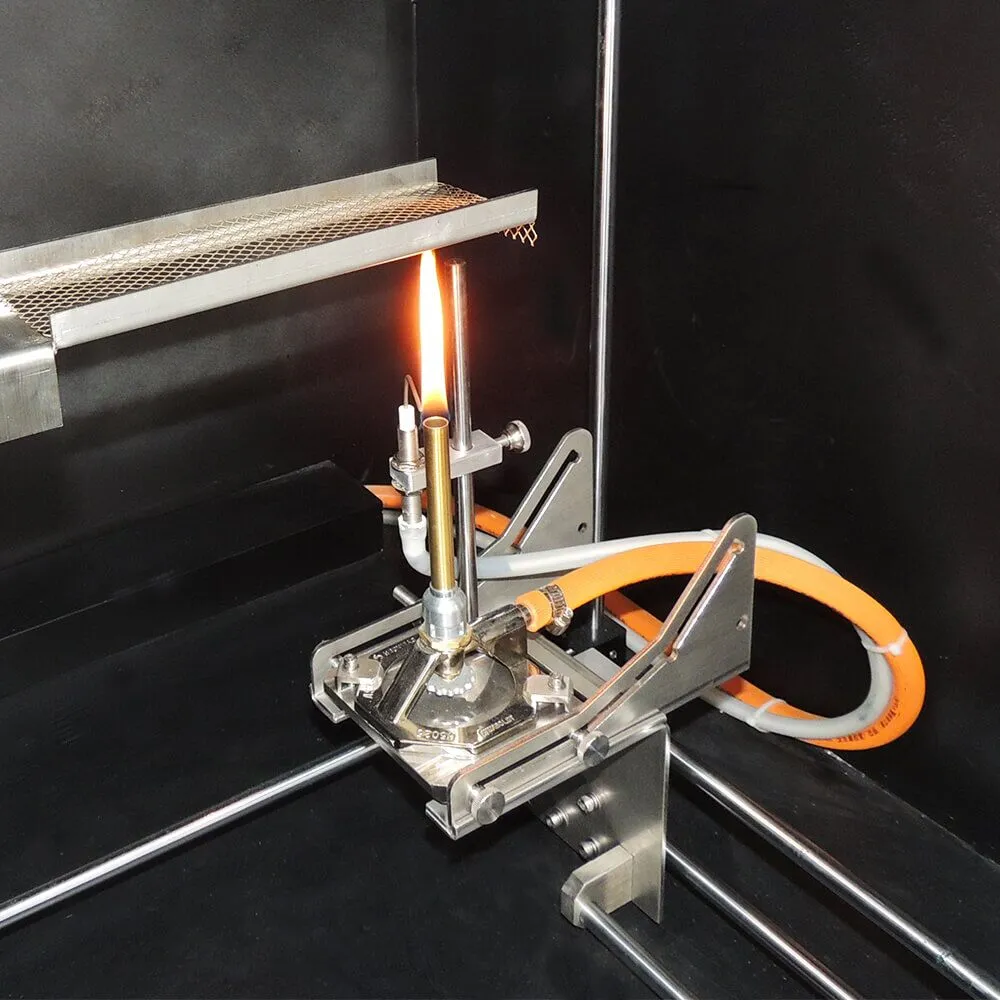
Flame retardant test
put the specimen on the flame retardant tester according to the regulations to burn and see the flame spread time.
Fiber composition analysis
first of all, do qualitative analysis for the fiber of the fabric, there are a lot of qualitative analysis methods, such as the melting point method, hand-feeling and the visual method, microscope slice analysis method, etc., and the microscope slice analysis method is usually used. The fibers were sliced with a slicer and then observed under a microscope to determine the type of fiber based on its external appearance, to determine the types of fibers, and then according to the different fibers with different solvents were a qualitative analysis, to calculate the specific composition of the content.
Banned azo dyes test
It is the most important quality control project in the international textile and garment trade, and also one of the most basic quality indexes of eco-textiles, which is mainly analyzed and tested by gas chromatography at present. The Azo dye test is divided into three applications, textiles (except polyester and leather textiles), polyester (polyester), and leather (leather), to do azo test you should provide the composition of the product.
For more fabric testing equipment, you can also visit: www.testextextile.com
How Do Textile Enterprises Generally Conduct Testing?
Textile enterprises generally carry out textile testing through various channels, including commissioning third-party testing organizations, establishing independent quality inspection departments, and purchasing their testing equipment. Commissioning a third-party testing organization can obtain professional test reports to ensure that the products meet the standard requirements; the establishment of an independent quality inspection department can achieve comprehensive internal monitoring and management; the purchase of their testing equipment can improve the efficiency and flexibility of testing.
Who Needs to Set Up Its Textile Lab?
It depends on several factors, including the size of the company’s production, product range, market demand, regulatory requirements, and the company’s quality management system. The following are some of the factors that may influence the decision:
Production scale
The larger the production scale, the number of samples to be tested will increase accordingly. A large-scale manufacturer may need a larger, more efficient testing laboratory to cope with the demand.
Product range
If a company produces many different types of textiles, it may need a more comprehensive testing program and more testing equipment.
Market demand
If the market generally needs high-quality products, the company may need to establish a more stringent quality control and testing system.
Regulatory requirements
Different regions and countries may have different regulatory requirements for textile quality and safety standards. Companies need to ensure that their products comply with these regulations, which may require the establishment of appropriate testing laboratories.
Quality management systems
Some companies may have implemented quality management systems such as ISO 9001. These systems may require the establishment of testing laboratories to ensure effective quality management.
Generally speaking, small and medium-sized textile enterprises may choose to outsource testing services, while large enterprises may prefer to establish their testing laboratories. The specific size and equipment requirements need to be assessed in their real situation.
The Factors That Affect Planning A Textile Testing Lab
These include the objectives of the laboratory, testing programs, equipment selection, space layout, personnel training, and quality management. Below is a general step-by-step approach to planning and setting up:
Define laboratory objectives and testing programs
Determine the main goal of the laboratory, is it for internal quality control or to meet external regulations and market demands?
List the tests to be performed, including physical properties, chemical composition, fiber composition, durability, etc.
Understand regulations and standards
Ensure that you are aware of the regulations and standards in your region and industry to ensure that the lab is built to meet the relevant requirements.
Determine laboratory space and layout
Determine the size of the laboratory space based on testing items and equipment requirements.
Plan the layout of the laboratory to ensure rational workflow and equipment placement to improve work efficiency.
Select appropriate textile lab equipment
Select appropriate textile lab equipment according to testing items, such as tensile testing machine, combustion performance tester, infrared spectrometer, etc.
Ensure that the equipment meets the requirements of regulations and standards, and has sufficient accuracy and reliability.
Set up a quality management system
Establish a quality management manual to clarify the laboratory’s quality policies and procedures.
Implement a quality management system, such as ISO 17025, to ensure the credibility and traceability of the laboratory.
Train laboratory personnel
Ensure that laboratory personnel have adequate professional knowledge and skills by training them in the proper use of testing equipment and execution of testing procedures.
Ensure textile testing instrument maintenance and calibration
Establish a textile testing instrument maintenance program to ensure proper operation and stability of the equipment.
Regularly calibrate testing equipment to ensure the accuracy of test results.
Establish a data management system
Have a data management system in place to ensure traceability and security of laboratory data.
Conduct Risk Assessments
Conduct risk assessments on all aspects of the laboratory to ensure that safety and environmental measures are properly implemented.
Collaborate with relevant organizations
Work with relevant regulatory bodies, industry associations, or accreditation bodies to gain support and recognition.
Textile Lab Construction Points
1. The textile laboratory should meet fireproof and moisture-resistant requirements; the ground should be solid and wear-resistant, waterproof and non-slip, not accumulate dust, and acid-resistant, corrosion-resistant properties; the ground should be clean, not dusty; the laboratory should not be ceiling, it is desirable to use the natural lighting and try to avoid direct sunlight. Laboratory should be considered to reserve exhaust ducts and independent sewage pipes. Toxic, hazardous gases and liquids left by the tests should be discharged by secondary treatment to meet the emission standards.
2. Laboratory electricity grounding protection is also a very important issue, to make sure there are multiple grounding protection measures, do not connect zero wire instead of a grounding wire.
3. In the design, the general laboratory door is mainly open to the inside, but taking into account the safety factors, such as the explosion risk of the room, the room door should be open to the outside, the room door material is best to choose the pressure glass.
4. Office: the office is proposed to be built independently with the monitoring area, and the office is mainly equipped with desks, office chairs, office computers, printers, and so on.
5. Sample receiving room: the sample receiving room needs to be equipped with a sample receiving workstation.
6. Data room: the data room is mainly used for storing test records reports and other information documents, this area can be used to place file cabinets, can be locked, but also be equipped with smoke alarms fire extinguishers, and other related fire facilities.
7. Colorfastness test to lightroom: This room will be placed in the color fastness to light test chamber, and it is equipped with hangers for hanging samples. This color fastness to light test instrument needs to exhaust, so in the laboratory planning, you should consider ventilation.
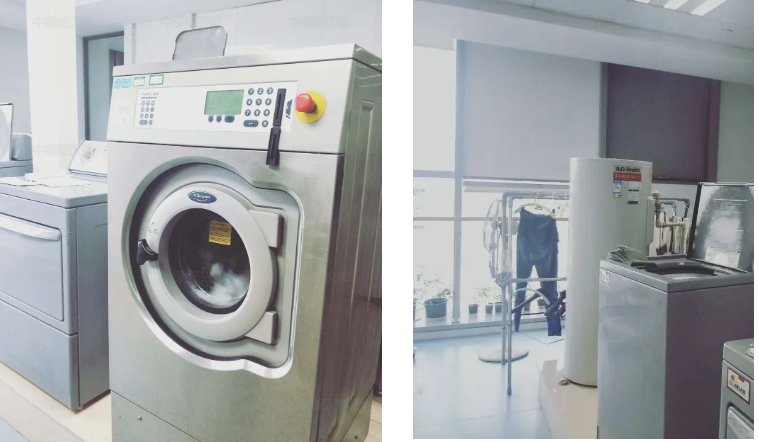
8. Washing room: the washing machine, dry cleaning machine, washing color fastness tester, and sweat stain racks are placed in the washing room. The floor is generally non-slip ground and needs to deal with water intake and drainage (to prevent the drainage from being smooth, it is recommended to reserve a floor drain). In addition, the washing machine power needs to leave a separate power supply.
9. Hanging dry room: this function is relatively simple, used to hang dry clothes, mainly placed some hangers, in general, this area needs to be planned in a ventilated dry space, while in the laboratory renovation needs to be considered when the floor of the non-slip.
10. Cleaning room: Mainly used for a chemical laboratory of washing experimental vessels. The scale of the room should be decided according to the daily workload, the location of the washing room should be close to the pre-treatment room, the room is usually equipped with a washing table, drying oven and utensil cabinets, etc., the room must have a good exhaust make-up air facilities, the ground must have a good drainage slope and floor drains. Of course, if the test tasks are less, this room is not necessary.
11. Darkroom: the dark room is mainly placed in the light source color box, the test project for the chromaticity rating, to exclude interference with external light sources. A dark room environment requires a different external environment, with darkroom light stability, light sources need to be closed or isolated, walls and floors to avoid reflections, and laboratory decoration needs to be low reflectivity and darker tone of the material.
12. Balance room: analytical balance is a common instrument necessary for chemical laboratories. High-precision balances have certain requirements on the environment: vibration, dust, wind, direct sunlight, corrosive gas erosion, and a more constant temperature, and therefore usually set the balance in a special balance room to meet these requirements. In addition, to improve the efficiency of testing, the balance room should be close to the pre-processing room.
13. Combustion chamber: The combustion chamber will house the flammability test tester, fume hoods, and lab benches, and the need for ventilation needs to be considered.
14. Storage room: Usually a sample storage room and drug storage room. The cabinets in it should be able to pass the passage between the cart, and the storage room requires good ventilation, to avoid direct sunlight, dry, and clean, the sample storage room, according to the nature of the samples of the temperature and humidity requirements, and there should be a thermo-hygrometer to detect and make records.
The sample room needs to be managed by a person, in and out of the door needs to be locked and set permissions. In the drug storeroom, different chemical storage has different developed requirements, they should compound national standards for safety and fire safety requirements. You should set up a clear sign of the storage equipment and those safety facilities should be tested regularly, the library also sets up automatic fire extinguishing devices, with locked cabinets and access with permission, anyone shall not enter the storage room without approval.
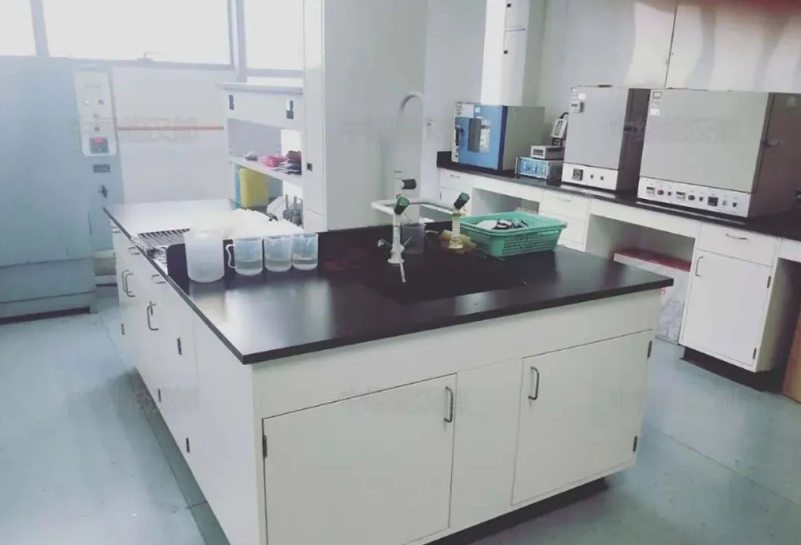
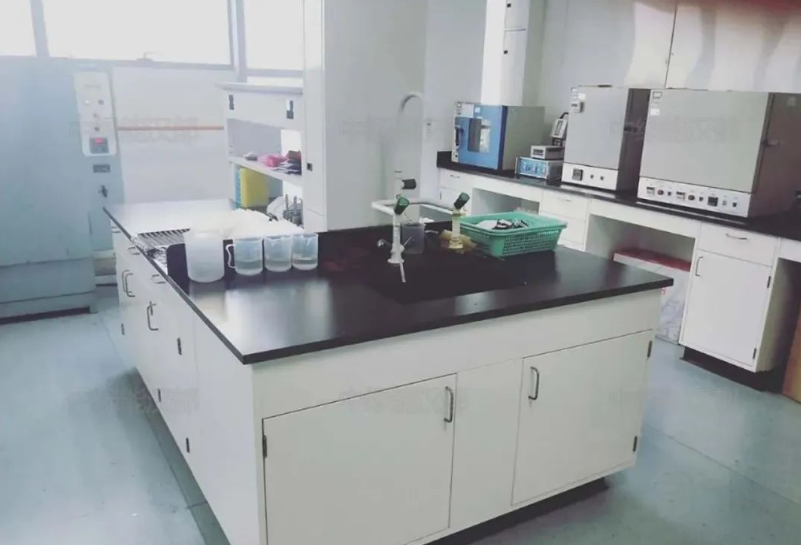
15. Pre-treatment room: the pre-treatment room is the main area of experimental operations, textile laboratories contain organic and inorganic project testing, so in the laboratory planning to consider two functional rooms: an organic pre-treatment room and an inorganic pre-treatment room. The organic pretreatment room is mainly organic project sample processing, in the test process needs to use a variety of organic reagents because most of the organic reagents are volatile, so must be carried out in the fume hood, and the room should be well-ventilated and makeup air. Therefore, the main equipment in the organic pre-treatment room is a fume hood, central table, reagent cabinets, and of course, the necessary safety devices: emergency sprinklers. The inorganic pre-treatment room is mainly for inorganic project sample pre-treatment, in the test process needs to use strong corrosive acid, so in this area, the furniture should be considered corrosion-resistant materials, and the room should be well-ventilated and make-up air.
16. Instrumental analysis room: The instrumental analysis room environment has higher requirements than the pre-treatment room because the instrumental analysis room usually needs to consider temperature and humidity control, dust, exhaust, make-up air, gas supply and vibration, and other requirements. In the textile chemical laboratory, there is usually a Chromatography-mass spectrometer, liquid chromatograph, ICP\atomic absorption spectrometer, spectrophotometer, etc., and so on.
17. Constant temperature and humidity room: About the textile, the temperature and humidity set value are generally 20 ± 1 ℃, relative humidity of 65% ± 2%, the air circulation is 15-30 times/hour, the noise should be less than 55 dB, but there also should be a new air supplement, constant temperature, and humidity laboratory is generally divided into three areas: buffer room, independent air conditioning and constant temperature and humidity room.
18. Sample preparation room: mainly test sample preparation area, which is equipped with sewing machines, fabric sample cutting equipment, laboratory tables specimen storage racks, and so on.
19. Component Analysis Room: The fiber quantification in textiles is mainly achieved by the chemical dissolution method, and the component analysis room is mainly for fiber dissolution. This function will be placed in the fume cupboard, experimental table, and spray device, and needs to consider ventilation and water requirements.
For more textile testing knowledge, instrument knowledge, and textile testing laboratory knowledge, please contact us at sales@chiuvention.com.
WhatsApp +86 180 2511 4082