Fabric shrinkage is a common phenomenon that occurs when fabric is exposed to heat or washing, resulting in a reduction in size. It can have significant implications for product manufacturing and development, affecting the fit, quality, and performance of garments. Manufacturers need to have a thorough understanding of fabric shrinkage in order to provide accurate care instructions and minimize production issues. Testing for fabric shrinkage is crucial to ensure customer satisfaction and avoid costly mistakes during manufacturing.
This article will explore the importance of fabric shrinkage testing and how it can boost testing efficiency. It will discuss different fabric shrinkage test methods, principles, and standards. Additionally, it will introduce two commonly used testing apparatus: the traditional fabric shrinkage testing machine and the advanced SmartShrink Rate Tester. The benefits and features of the SmartShrink Rate Tester will be highlighted, explaining why it is a preferred choice for fabric shrinkage testing. By utilizing this innovative testing equipment, manufacturers can enhance their testing processes, improve efficiency, and ultimately deliver high-quality products to consumers.
What is fabric shrinkage?
Fabric shrinkage occurs when fabric is exposed to heat or washing and consequently reduced in size; this change may occur both lengthwise (warp) and widthwise (weft). Many factors contribute to fabric shrinkage; natural fabrics like cotton and wool tend to experience greater shrinkage than synthetic ones like polyester and nylon; weaving techniques and finishes also have an impactful influence on how much the material shrinks.
Some textiles may be treated to resist shrinkage, yet these processes don’t always apply uniformly across the industry. Even without treatment for shrinkage, fabrics may still experience substantial dimensional change due to factors like improper washing and drying methods, harsh detergents or other chemicals used during treatment, or rough handling.
Textile professionals need a strong grasp of fabric shrinkage because it plays such an integral role in product manufacturing and product development activities. When apparel made of material that shrinks after laundering and drying results in improper fit for customers, leading them to express discontent with the purchase decision. In order to prevent customer frustration, manufacturers need to know an approximate percentage of shrinkage so they can build it back into patterns or take other steps that minimize it.
Fabric shrinkage after cutting and sewing can result in misshaped seams and poor fit, negatively affecting brand reputation as well as costing manufacturers money in production and materials costs. Testing accurately for fabric shrinkage allows manufacturers to provide consumers with accurate care instructions, leading to increased consumer satisfaction.
Temperature and water alone cannot determine how much fabric will shrink; other factors include its type. Cotton and wool fabrics tend to shrink when washed in hot water while synthetic fabrics like nylon may contract under extreme heat conditions. Furthermore, yarn used can have an effect on shrinkage rate.
There are various methods available to manufacturers for reducing fabric shrinkage rate, such as using mercerization and preshrunk techniques, but these approaches can be costly and time-consuming. Testing prior to production is the best way to lower fabric shrinkage; testing will enable a manufacturer to anticipate potential production issues before they arise and avoid making costly mistakes during manufacturing.
Comparison between Fabric Shrinkage and Fabric Shrinkage Rate
Fabric Shrinkage: Shrinkage is a phenomenon in which the absorption of water by a fiber causes the fiber and yarn to expand laterally and the yarn to flex more, resulting in a shorter length and greater thickness of the fabric, which cannot be recovered after drying. It is usually expressed by shrinkage rate.
Fabric Shrinkage Rate: The shrinkage rate of a fabric is the percentage of fabric shrinkage after washing or soaking in water. The shrinkage rate is the smallest for synthetic fibers and blended textiles, followed by woolen fabrics, linen fabrics, and cotton fabrics in the middle of the silk fabric shrinkage, while the largest is viscose fiber, rayon, and artificial wool fabrics. Domestic standards are generally characterized by the rate of change in washing size, corresponding to the rate of change in dry cleaning size.
What are the Factors Affecting Shrinkage Rate?
①A fabric’s raw material and shrinkage rate differ. Generally speaking, the hygroscopicity of the fiber, after immersion in water, fiber expansion, diameter increase, length shortening, and shrinkage rate is large. Such as viscose fiber water absorption rate of up to 13%, while synthetic fabric moisture absorption is poor, its shrinkage rate is small.
② There is a difference in fabric density and shrinkage. If the density of the warp and weft the similar, the warp and weft to the shrinkage rate is also close to the warp density of the fabric. Nearly, the warp density of fabrics, warp shrinkage is large, and vice versa, weft density is greater than the warp density of fabrics, weft shrinkage is also large.
③ The fabric yarn thickness is different, as is the shrinkage rate. The yarn thickness of cloth shrinks rapidly, whereas the yarn fine fabric shrinks slowly. The shrinkage rate of fabrics with thick yarn count is large, and the shrinkage rate of fabrics with thin yarn count is small.
Different fabric production processes result in different shrinkage rates. Generally speaking, the fabric in the weaving and dyeing process, the fiber should be stretched many times, the processing time is long, the fabric shrinkage rate of the fabric with greater applied tension is large, and vice versa is small.
Fabric Shrinkage Test
Fabric shrinkage testing is an examination of how fabric changes dimensions after being washed or used, whether contraction shrinkage occurs (decrease in dimensions), or expansion shrinkage occurs (increase). Testing should take place prior to sewing garments made out of these fabrics.
Typically, fabric samples are marked using unchangeable markers on their edges (Selvage side). Next, these marked pieces of fabric are washed, dried, and measured to identify dimension changes in width terms. Fabric that experiences more contraction shrinkage should not be used for clothing production and should instead be preshrunk prior to being sewn together into garments.
Test Methods
There are different methods for conducting fabric shrinkage tests, depending on the specific requirements and industry standards. Here are some commonly used methods:
Laundering Shrinkage Test: This method involves washing fabric samples according to specific washing instructions, including water temperature, detergent type, and cycle. The samples are then air-dried or tumble-dried, and their dimensions are compared before and after laundering.
Heat Shrinkage Test: This method involves subjecting fabric samples to high temperatures, either by placing them in an oven or using a heat press. The samples are exposed to heat for a specified period, and their dimensions are measured before and after the heat treatment.
Steam Shrinkage Test: This method utilizes steam to simulate shrinkage. Fabric samples are exposed to steam under controlled conditions, and their dimensions are measured before and after the steam treatment.
Moisture Shrinkage Test: In this method, fabric samples are subjected to high humidity or wet conditions. The samples are soaked or steamed, and their dimensions are measured before and after the moisture treatment.
Test Principles
The test principles for fabric shrinkage involve comparing the dimensions of fabric samples before and after specific treatment methods. The difference in dimensions indicates the amount of shrinkage experienced by the fabric. The percentage of shrinkage is calculated by dividing the difference in dimensions by the initial dimensions and multiplying by 100.
The principles may also vary depending on the specific test method employed. For example, in laundering shrinkage tests, the fabric is subjected to washing and drying cycles to simulate real-life usage. Heat shrinkage tests focus on the fabric’s response to high temperatures, while steam and moisture shrinkage tests evaluate the fabric’s reaction to steam or wet conditions.
Test Standards
Fabric shrinkage tests can be conducted following various industry standards and specifications. These standards ensure consistent testing procedures and enable accurate comparisons across different fabrics. Some commonly used standards for fabric shrinkage testing include:
- ASTM D3774: Standard Test Method for Width of Textile Fabric
- ASTM D4970: Standard Test Method for Pilling Resistance and Other Related Surface Changes of Textile Fabrics
- ISO 6330: Textiles – Domestic washing and drying procedures for textile testing
- AATCC TM135: Dimensional Changes in Automatic Home Laundering of Woven and Knit Fabrics
Test apparatus
Fabric shrinkage testing requires the use of specific apparatus to accurately measure the dimensional changes of fabric samples. Two commonly used testing machines are the traditional fabric shrinkage testing machine and the SmartShrink Rate Tester. Let’s explore these apparatus in more detail:
Traditional Fabric Shrinkage Testing Machine
The traditional fabric shrinkage testing machine is a mechanical device designed to subject fabric samples to controlled conditions and measure their dimensional changes. It typically consists of the following components:
Sample Holder: This part of the machine securely holds the fabric sample in place during the testing process. It ensures that the sample remains flat and taut, allowing for accurate measurements.
Treatment Chamber: The treatment chamber provides a controlled environment for subjecting the fabric sample to specific conditions such as washing, drying, or pressing. It can simulate different settings, including temperature, humidity, and mechanical forces.
Dimensional Measurement System: The machine is equipped with a measurement system that allows for precise dimensional measurements of the fabric sample before and after the treatment. This system may include rulers, calipers, or optical scanners, depending on the specific design of the machine.
Controls and Display: The machine is operated through controls that enable the user to set the desired treatment parameters and initiate the testing process. The results of the dimensional measurements are displayed on a screen, providing immediate feedback to the operator.
The traditional fabric shrinkage testing machine offers a reliable and established method for conducting fabric shrinkage tests. However, it may require manual operation and interpretation of the results, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error.
SmartShrink Rate Tester
The SmartShrink Rate Tester is an advanced apparatus that utilizes automation and smart technology to measure fabric shrinkage accurately. It incorporates various features that enhance the testing process and improve efficiency.
Choosing SmartShrink, the normal fabric factory can save 800 minutes, or 2 laborers per day, based on the need of testing 200 samples and printing 200 test records per day. Counting a salary of $ 9000 per person in USA & European Countries, 1 set of SmartShrink can save $200,000 for the fabric factory per year.
Speed up the preparation of orders: SmartShrink can complete a large number of shrinkage calculations every day, thus the textile enterprises can make faster decisions and speed up the preparation of orders.
More reliable test results: Visual inspection algorithm, more accurate, especially in large batch testing, can effectively avoid manual deviation, which is meaningful for getting more reliable test results.
Output multiple data at one time, reflecting the quality of fabric more comprehensively and objectively: Multiple shrinkage-related indexes (such as warp and weft shrinkage, seam twist, vertical twist, diagonal twist, etc.) can be output at one time, useful to evaluate the quality of the fabric.
What’s more, SmartShrink is equipped with high & soft brightness of LED lighting, no flicker, and is eye-friendly.
Why choose Chiuvention SmartShrink Rate Tester?
SmartShrink Rate Tester is an advanced fabric shrinkage tester that utilizes proprietary visual algorithms to automatically capture warp and weft data, identify QR codes, and record information within textile factory environments.
SmartShrink provides significantly higher test efficiency compared to conventional Martindale abrasion and pilling testers, requiring only one click of the screen to switch testing modes from abrasion to pilling testing modes, resulting in greater test efficiency.
Chiuvention SmartShrink Rate Tester is a specific device designed for fabric shrinkage testing. Here are some reasons why one might choose the Chiuvention SmartShrink Rate Tester:
Application
The Chiuvention SmartShrink Rate Tester is commonly used in textile laboratories, quality control departments, and fabric manufacturing facilities. It is suitable for testing the shrinkage rate of various fabrics, including woven, knitted, and non-woven fabrics.
Functions
The SmartShrink Rate Tester offers several important functions for fabric shrinkage testing, including:
Precise Temperature Control: The tester allows precise control of temperature during heat treatment, ensuring accurate and consistent test conditions.
Programmable Test Parameters: Users can set specific test parameters, such as temperature, time, and number of cycles, to simulate different real-life conditions.
Automatic Data Collection: The tester automatically collects and records the dimensional measurements of fabric samples before and after the shrinkage test, simplifying the data collection process.
Calculation of Shrinkage Percentage: The SmartShrink Rate Tester calculates the shrinkage percentage based on the dimensional changes of the fabric samples, providing accurate and reliable results.
Features
The Chiuvention SmartShrink Rate Tester offers several features that enhance the fabric shrinkage testing process:
User-Friendly Interface: The tester has an intuitive interface, allowing easy programming of test parameters and monitoring of test progress.
Multiple Sample Capacity: The device can accommodate multiple fabric samples simultaneously, enabling efficient testing of multiple samples in a single run.
Adjustable Test Conditions: Users can adjust test conditions, such as temperature and time, to meet specific testing requirements or conform to industry standards.
Data Analysis and Reporting: The tester provides options for data analysis and reporting, allowing users to generate comprehensive test reports and analyze results for further evaluation.
Durability and Reliability: The Chiuvention SmartShrink Rate Tester is built with high-quality materials and components, ensuring durability and reliable performance over time.
SmartShrink Testing Procedures
- Connect the SmartShrink to the computer and install the software.
- Start the software, the camera light turns on automatically.
- “ Camera is ready ”is displayed on the software interface, it indicates that the machine is successfully connected to the computer.
- Learn more about the management items of this software, such as “settings, size, calibration, smart link, and project information”.
- “Marker” means the recording of the dimensions before washing; “Measure” means the series of shrinkage data after the washing; “Report” means a universal test results report.
- “Size” means the sample test size, and Loop means the times of sample being washed. “W1, W2, W3” means the width dimensions between the 2 borderline marked points. “L1, L2, L3” means the length dimensions between the 2 borderline marked points. WD means width shrinkage rate, LD means length shrinkage rate, and DT means diagonal twist. CF means credibility.
- “Dot” means that the marked symbol is a point, and “Cross” means that the marked symbol is a cross.
- “Auto” means that the machine automatically determines the color of the tag, and “Yellow ” means that the color of the tag is yellow. Same meaning as Black and Red.
The following are the detailed steps for conducting the test by using Smartshrink Rate Tester
- Use a shrinkage plate to mark a total of 8 points in the warp and weft direction of the fabric sample (refer to the test standard) and make sure that the position of these 8 points conforms to the standard. (note: the sample is before the washing now)
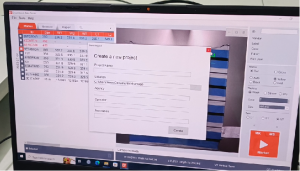
- Create a project for this test. Click “New Project”, fill in the test information, and click“Create”.
- Scan the bar code of the sample, the software of SmartShrink will identify the ID and other information of the sample, and show it on the screen.
- Click the “marker” button on the computer screen or press the button “MK” right on the machine, the SmartShrink camera will collect the dimensions of marked positions, and the software will calculate the shrinkage rate automatically. (note: the sample is after the washing now. )
- A universal test report is generated. Including warp and weft shrinkage, seam twist, vertical twist, diagonal twist, etc. All can be output at one time, useful to evaluate the quality of the fabric more comprehensively. You can export this report and share it to your customers.
Useful Discussion
1. Cotton and linen non-elastic woven fabrics, its weft shrinkage control process in the control of mercerizing door width, rather than heat setting. Cotton and hemp fibers do not have the same thermoplasticity as polyester nylon fibers (or in other words, the glass transition temperature of cotton and hemp fibers is too high. The current sizing machine can not reach, and even if it can be reached, it will be the first caramelized rather than softened, so it is meaningless), so the thermal sizing does not make it like chemical fiber fabrics to obtain dimensional stability, only through the mercerisation of the internal stress relief, you can obtain good dimensional stability. Only through the mercerisation of the internal stress elimination, can get good dimensional stability.
2. In practice, for some cellulosic fiber non-elastic fabrics first weft to pull to the extreme, and then again over water retraction door width, may also partially improve its weft shrinkage, guess there are two reasons.
One is that in the case of pulling the weft to the extreme, the weft yarn is partially untwisted, resulting in improved weft shrinkage. From this level, this method is only effective for thin and light fabrics, because the tension provided by the shaping machine is not enough to untwist the weft yarns of heavy fabrics; for heavy fabrics, the weft yarns are partially untwisted. It is more effective on coarse stiff yarns with low twists, which are more susceptible to untwisting.
Another reason may be due to the rigidity of the fibers themselves, similar to ironing a pleat on a garment at high temperatures, which will not be easily eliminated from the fiber. The more rigid the fiber is when it is ironed in its current state of curvature, the more likely it is to acquire a “mechanical fixation” when the weft is drawn at high temperatures.
Get a “mechanical shaping” effect (different from the glass transition temperature of chemical fiber shaping), from this point of view, hemp is greater than cotton, and cotton is greater than human cotton, because in terms of fiber rigidity, hemp is greater than cotton, and cotton is greater than human cotton. This type of improvement is only a partial improvement, shrinkage improvement data is usually only 1-3%, and the adaptability of the fabric is a last resort to save the day. The normal practice should be to improve the mercerisation process.
3. Cotton polyester or cotton brocade interwoven fabrics’ warp shrinkage is usually not as big as cotton fabrics, the reason is 8.1 described, it is only “drying and shaping” deformation and shrinkage, and no weft fiber swelling caused by the increase in the winding range of the shrinkage of the cotton long car factory is usually surprised at interwoven fabrics dyeing plant never do the pre-shrinking machine pre-shrinkage, is the need is not as strong as pure cotton fabrics. Necessity is not as strong as cotton fabrics.
4. Spandex-containing elastic fabrics must be heat-set to make it get a good shrinkage, here there is a time-temperature equivalent effect Here there is a time-temperature equivalence effect, higher temperature x shorter setting time and lower temperature x longer setting time in the fabric to obtain good shrinkage Higher temperatures x shorter setting times and lower temperatures x longer setting times are equivalent in terms of obtaining good shrinkage in the fabric, but the former is economically better and the latter has a better resilience of the fabric.
5. Shrinkage and shrinkage are two different concepts. Shrinkage refers to the rate of change in the size of the fabric after washing, while shrinkage Shrinkage is the rate of change of fabric size washing, while shrinkage refers to the warp direction elongation or shortening of fabric due to the change of weft density in the process of dyeing and finishing. Shrinkage = (bad fabric weft density – finished product (bad cloth weft density – finished product) “Wye cloth weft density, fabric flow shrinkage does not mean that the fabric shrinkage rate is large, the fabric flow shrinkage is that the fabric In a particular dyeing process in order to obtain a particular style of “material consumption” situation, while the shrinkage rate is the fabric itself. For example, in the case of warp-elastic fabrics, we can have a variety of shrinkage rates through different heat-setting processes, but the shrinkage rate can be kept at 5.5 percent. The shrinkage rate can be maintained at about 5%.
Conclusion
Fabric shrinkage testing is a critical aspect of textile manufacturing and product development. It enables manufacturers to understand the shrinkage behavior of fabrics and take appropriate measures to minimize issues such as poor fit, misshaped seams, and customer dissatisfaction. By conducting accurate fabric shrinkage tests, manufacturers can provide consumers with precise care instructions, improve product quality, and avoid costly mistakes during production.
The SmartShrink Rate Tester stands out as an advanced apparatus that significantly boosts testing efficiency. Compared to traditional fabric shrinkage testing machines, the SmartShrink Rate Tester offers automation, smart technology, and non-contact measurement systems that streamline the testing process and provide highly accurate results. Its features, such as automated treatment cycles, precise temperature control, programmable test parameters, and data analysis capabilities, enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
Choosing the Chiuvention SmartShrink Rate Tester brings numerous advantages. Its application versatility makes it suitable for various fabric types, and its functions, including temperature control, automatic data collection, and shrinkage percentage calculation, ensure precise and reliable testing results. The user-friendly interface, multiple sample capacity, adjustable test conditions, and data analysis and reporting options further enhance its usability. Additionally, its durability and reliability make it a long-term investment for textile laboratories, quality control departments, and fabric manufacturing facilities.
Incorporating the SmartShrink Rate Tester into fabric shrinkage testing processes empowers manufacturers to enhance their testing efficiency, improve product quality, and ultimately deliver high-quality garments that meet customer expectations. By investing in innovative testing equipment like the SmartShrink Rate Tester, manufacturers can stay at the forefront of the industry and maintain a competitive edge in today’s demanding market.
Let’s experience SmartShrink right now!