Fabric shrinkage, or elastic elongation, is the ratio of its length increase to its original length. Under certain conditions, we apply a tensile force at this point. It measures a fabric’s elasticity. It often describes its ability to deform under an external force.
The stretch of a fabric has a significant impact on the fit, comfort and durability of a garment. High-elasticity fabrics suit sportswear and swimwear. They need good stretch. Low-elasticity fabrics are best for formal wear and shape-retaining dresses.
Factors that produce shrinkage in fabrics
Shrinkage is due to the fibre, the fabric’s structure, and the production methods.
1. Fibre factors
All kinds of fibre fabrics may stretch in spinning, weaving, dyeing, and finishing. This causes the warp and weft threads to elongate and deform. Some deformation may be permanent. It creates a hidden contraction force from residual internal stress in the fabrics. Soaking the fabric in water causes water molecules to enter its internal fibres. This puts the fibres in a natural state. It promotes the recovery of their elastic deformation, causing the fabric to shrink. Different textile fibre shrinkage degree is not the same.
2. Density factor
In many fabrics, due to different density of yarn, shrinkage performance is not the same. High-density fabrics, like wadatan and khaki, use tightly-woven warp yarns. When exposed to heat and humidity, the warp yarns have little leeway. This limits the weft yarn’s shrinkage. In contrast, low-density fabrics have a loose weave. When heated and humid, the warp yarns can expand. This causes the warp yarns to zigzag, leading to greater shrinkage.
3. Fabric yarn factor
Fabric yarn thickness is different, the shrinkage rate is also different. Yarn thick fabrics, like denim, have a high shrinkage rate. Yarn fine fabrics, like plain fabric, have a low shrinkage rate.
4. Dye factor
In the finishing process, high pulp content in the fabrics causes high shrinkage. After sizing clothing fabrics, their curvature decreased and stiffness increased. But, after washing, the pulp washed off. This increased the fibre gaps, water absorption, and curvature, raising the shrinkage rate.
5. Technological factors
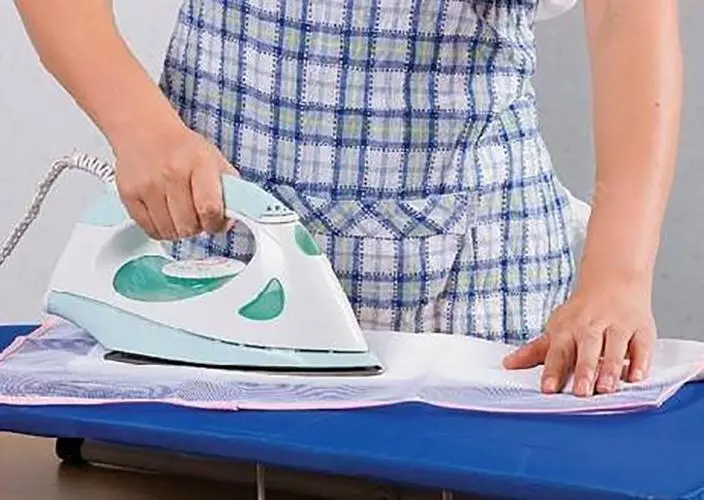
The dyeing and finishing process, including fabric ironing, will tension the fabrics. This will cause them to elongate. But this elongation is temporary. Once the fabric is underwater, it will dissolve. It will lose the tension from external forces. As a result, the fibers will shrink, causing the fabric to shrink.
Test method of fabric natural, dry heat, damp heat and washing stretch rate
After water and damp heat stimulate the fabric, the fibre shifts from a temporary to a stable state. This causes it to expand. The expansion rate is the degree of this expansion. The fabric expansion rate mainly depends on the raw materials. It also depends on the processing and treatment methods. For example, a strong, hard pull can stretch the fabric. It will increase its expansion rate. Also, the density of the warp and weft affects elongation. Usually, the warp density is greater than the weft density. Then, the warp shrinkage is greater than the weft shrinkage. Conversely, the weft shrinkage is greater than the warp shrinkage. The test will give us accurate data on the expansion rate. We can use this as a basis for scaling the board sample’s length and width. It will ensure the garment specs meet the design requirements.
Therefore, the test items relate to the process of processing the garment. There are generally the following items:
1. Natural shrinkage
Natural shrinkage is the change in a fabric’s expansion and contraction. It occurs without human influence. It is due to air, moisture, temperature, and internal stress in its natural state. Woven fabrics shrink more than knitted ones. Flexed yarns make up knitted fabrics. In them, the coils can lose their grip and stretch. Different fibers in the materials cause different expansion and contraction.
The test method is: First, take a package of raw material from the warehouse. Measure its length and width against the door’s width. Record the data. Then, disassemble and shake the raw material. After that, store it at room temperature for 24 hours without any pressure. Finally, re-test it to calculate the fabric’s expansion rate.
2. Thermal shrinkage
In garment processing, we use four methods to process fabrics: water immersion, water spray, and dry and wet ironing. It has a shrinkage rate with the size of the unprocessed fabric. This is due to external factors and fabric shrinkage. We know the process of wet heat shrinkage.
To grasp the law of this shrinkage, we must test the fabric for shrinkage after these processes.
(1) Dry ironing shrinkage test
Dry ironing shrinkage is fabric shrinkage from using a hot, dry iron. It is due to the heat produced by the iron. The test method is as follows:
Sampling: Remove more than 1m from the head or tail of the cloth due to a significant change in weaving tension. Also, remove several metres from the head. Then, take a 50cm long sample. Remove 10cm from both sides due to tension differences that affect test accuracy. Remove 10cm from each side of knitted and static flocking fabrics. Record the length and width.
Dry ironing temperature conditions: 190-200℃ for printed and dyed cotton. For synthetic and blended printed and dyed fabrics: 150-170℃.
Viscose fibre printed and dyed cloth: 80~100℃; printed and dyed silk fabric: 110~130℃; woolen fabric: 150~170℃.
Dry ironing time: After ironing the specimen for 15s, cool it. Do this under various temperature conditions.
Test: After cooling, measure the specimen’s length and width. Then, calculate the fabric’s shrinkage.
(2) Test of wet ironing shrinkage
Wet ironing shrinkage is when fabric shrinks from moisture in ironing. There are two wet ironing shrinkage test methods, based on the process. They are: water spray ironing and wet cloth ironing.
Water spray ironing test method
Sampling: From the raw material, take a 50cm sample from 1m in the head or tail. Remove the cloth on both sides of the road.
Wet conditions: spray water on the specimen to wet it. The moisture must be evenly distributed.
Ironing conditions: Use an electric iron on the specimen. Iron back and forth, keeping the dry time appropriate.
After drying the specimen, measure its length and width. Then, calculate the shrinkage rate.
Covering wet cloth ironing test method
Sampling: The same as the water spray ironing test method.
Temperature condition: same as water spraying and ironing test method.
Wet condition: Soak a piece of de-pulped woolen white flat cloth with water and wring it out for spare.
Ironing conditions: Put the wet cloth over the test specimen. Then, with an iron, iron the test specimen back and forth, as per the temperature conditions. Time it so the cover cloth is dry.
After cooling the specimen, measure its length and width. Then, calculate the shrinkage using the wet ironing shrinkage formula.
(3) Test of water immersion shrinkage
Water immersion shrinkage is when fabric shrinks after soaking it in water. The test methods are as follows:
Sampling: The method is the same as the dry ironing test method.
Wet conditions: Immerse the sample in 60℃ warm water for 15 min. Stir it by hand to fully wet the fibres. Then, stroke it dry and air dry it at room temperature (do not wring it). You can also use this test to test the shrinkage machine.
Measurement and calculation: Measure the length of the specimen. Then, calculate the shrinkage rate.
Calculation method and steps of shrinkage rate of garment plate making
When a customer places an order, check if they washed the garment in water or fabric.
One can also see the customer’s garment samples. For washed garments, there is puckering on the open line, just like on the side seams of the jeans we usually wear. There is also a change in the depth of the fabric’s lines. If you wash it in fabric, you won’t experience that phenomenon. You do not need to control fabric wash shrinkage. After receiving the bulk fabric, go to the laundry and wash it as required. Control the shrinkage of the fabric.
There are several washing methods for readymade garments.
These include normal washing, enzyme washing, sand washing, and stone washing. Get a sample of the bulk fabric from the customer. It should be at least 5 metres above the whole fabric. Cut three pieces of fabric 1.2 metres long and 1 metre square and mark the fabric with a reserve line.
According to the customer’s request, inform the washing factory of the washing requirements.
After washing, give the customer a copy of the tested fabric. Some customers also need sleeve or trouser leg samples. They should keep a copy for themselves.
Fabrics tested by the laundry must be thoroughly dried.
They must be dry to the touch. Measure the size of the fabric on the top line. We use all three of the above fabrics for testing to ensure the accuracy of the shrinkage rate. You can take intermediate values for comparison and reference. A 97% length in the vertical dimension (straight grain) means the fabric shrinks 7% in length. A horizontal grain length of 92% means the fabric shrinks 8% across.
Use the measured shrinkage above.
Then, use the standard method to find the plate shrinkage from the washing tests. The required length of the garment size is 78cm, so when making the sample, ① 78cm × (1 + 3%) = 80.34cm;
② 56cm × (1 + 8 percentage points) = 60.48cm.
To prevent errors, the factory must retest the correct bulk fabric when it arrives.
In each batch, cut each roll of fabric to the size of 1.2 metres door width and wash it again. If there are several batches with shrinkage differences over 3 to 5 cm, you must make two or more samples.
Here, we must test the fabric repeatedly for shrinkage and never be afraid of trouble. The same garment may require different shrinkage versions. This is due to the fabric’s different shrinkage.
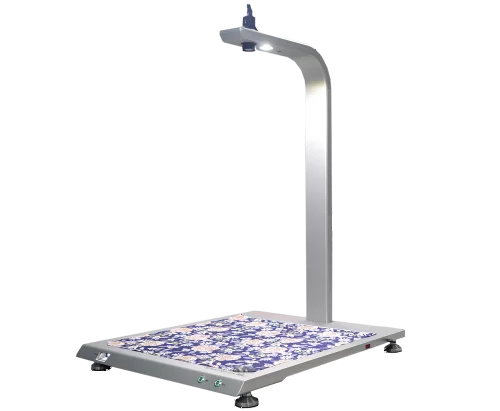
SmartShrink Shrinkage Tester
The SmartShrink Shrinkage Tester measures fabric shrinkage. It does this in under 5 seconds after washing, steaming, and dry cleaning.
SmartShrink takes a picture of the fabric sample using its top camera. It then measures the distance between the marked points. Finally, it calculates the fabric shrinkage rate using ChiuVention’s patented algorithm. The SmarTexLab app, on computers and smartphones, shows test results in real time via IoT.
SmartShrink measures fabric shrinkage and calculates the test results. It avoids manual errors and makes the test more accurate and reliable.
It automatically saves test data and sample photos. It lets you share and send test results in real time. This makes the test more transparent and reliable.
The test now takes just 5 seconds, down from 6 minutes. It is faster and costs over 90% less.
Fabric Shrinkage
Shrinkage rate of general fabrics
Floral fabric: 3-3.5%
Rayon silk interweave: 5%
Cotton: 44%~10
Maolan cloth: 5~7%
Chemical fibre: 4%~8%
Youth spinning, Fuchun spinning:8~10%
Cotton-polyester: 3.5%~55
Lining silk cloth: 3~4%
Native white cloth: 3%
Dusky silk: 5%
Poplin: 3~44.5%
Bleached cloth: 3~4%
Twill cloth: 4%
Silk silk: 5%
Labour cloth: 10%
Woolen blue cloth: 3~4%
Artificial cotton: 10%
Note: A big difference in the values may mean the fabric process is substandard.
Textiles shrink at different rates due to their processing.
For more information on textile testing methods/standards
or textile testing machines, contact us:
What’s App: +86 180 2511 4082
Tel: +86 769 2329 4842
Fax: +86 769 2329 4860
Email: medium@chiuvention.com