The air permeability test for fabric measures the ease with which air passes through a fabric. It is commonly used to assess the breathability of textiles. The air is passed through the fabric from a unit cross-sectional area by applying constant and different pressures.
What is the Air Permeability of a Fabric?
What is the Air Permeability of a Fabric?
The air permeability of a fabric measures how easily air can pass through it. Ease of air passage and flow rate are important factors in choosing a good permeable cloth.
The rate of air passage through the textile varies according to its end use, such as industrial filters, tents, sailcloths, parachutes, raincoat materials, shirting, waterproof fabrics, and airbags.
The air porosity of a cloth gives the wearer a comfortable feel and good breathability. The aeration capacity of outdoor garments and sportswear should be good.
Impermeable clothes are unsuitable for sports activities because they irritate the player during the game and can cause skin allergies and health hazards if worn for a long time.
Now, the question is how to measure the cloth’s air transmissibility capacity. For this purpose, some international standards are followed to perform this test.
Let’s see the air permeability test standards for textiles.
Textile Air Permeability Test Standards
There are several test standards for airflow permeability of textiles. The primary testing standards are below.
- ASTM D737
- EN ISO 9237
The above standards use some technical terms to test cloth’s aeration capacity. Let’s look at these terms before starting the standard testing procedure.
Definitions
To understand the fabric’s breathability we must know the differences between air permeability and air resistance. These terms are reciprocal to each other.
Air Permeability
The air permeability of a fabric is the volume of air measured in cubic centimeters passed per second through 1 cm2 of the fabric at a pressure of 1 cm of water.
Air Resistance
The air resistance of a fabric is the time in seconds for 1 cm3 of air to pass through 1 cm2 of the fabric under a pressure head of 1 cm of water.
Air Porosity
The porosity of a fabric is the ratio of air space to the total volume of the fabric expressed as a percentage.
S = total volume of sample in cubic centimeters
F = Total volume of fiber in cubic centimeters
Air Porosity P = (S – F) / S × 100
ASTM D737 Air Permeability of Textile Fabrics
ASTM D 737 measures the breathability of textile fabrics. This standard evaluates the aeration capacity of woven, nonwoven, airbag, blanket, napped, knitted, layered, and pile fabrics.
This method can be applied to untreated, heavily sized, coated, and resin-treated fabrics. The SI units for test results are inch-pound.
Test Method
Air is passed through the fabric’s cross-sectional area at a controlled rate. The airflow is adjusted until a pressure difference is created between the fabric’s front and back surfaces.
By measuring the airflow rate that passes through the fabric, we know the air permeability of the material.
Significance and Use
The breathability of a fabric is an important parameter, especially for textile materials such as gas filters, fabrics for airbags, clothing, mosquito netting, parachutes, sails, tents, and vacuum cleaners. The filtration process directly relies on the air permeability rate.
Air infiltration is a prominent parameter for weather-resistant, rainproof, and coated fabrics. It helps researchers and manufacturers ensure quality and make necessary changes in the manufacturing processes according to desired quality production.
Industrial and military fabrics have a significant requirement for air permeability parameters.
Fabric construction and types of finishes have a direct effect on air transmission. They can change the airflow path and direction. For example, hot calendaring flatters the fabric, reducing its breathability.
Weave Structure
The nature of the weave structure varies the air permeability rate because each structure has a different path for airflow, which may be longer or shorter.
Yarn Twist
Yarn twist in woven fabrics plays an essential role in wind permeability because when a yarn is twisted, its circular diameter reduces, covering less space and generating airflow.
Yarn Crimp
Similarly, yarn crimp also tends to change the air permeability. If a fabric can stretch easily, the gap between the threads increases, which helps the Material’s breathability.
Quality Assurance
- This standard is used to ensure the quality of textiles before shipment. It is widely used and gives almost the same results when performed in different laboratories.
- If two laboratories have different results, the test can be performed in a third-party lab to obtain the most accurate results.
- Keep your specimen uniform for all different laboratories to avoid any chance of variation in results. The specimen should be taken from the same area of the fabric to reduce the risk of variations.
- After that, specimens should be randomly given to different labs to evaluate the results. The results of two different labs should be analyzed statistically.
Apparatus
AirFicient Air Permeability Tester
The air permeability tester should meet the following requirements.
- The test head has a circular area of 38.3 cm2, and a clamping system secures the specimen by applying a load force of 50 N.
- A 20 mm wide and 3 mm thick clamping ring is used around the test area to hold the specimen firmly and avoid leakage.
- Air flows perpendicularly through the fabric surface. The airflow is adjusted between 100 Pa and 2500 Pa, which creates a pressure difference for the air passage between the front and back surfaces of the fabric that is under testing.
- The tester should be able to provide a minimum pressure difference of 125 Pa for the test sample.
- A specimen-cutting template is also used to cut the sample from the fabric according to the instrument’s clamping area.
Sample Preparation
The fabric sample is cut into a specified square, usually 100 cm2 or 38.8 cm2. It can be cut using a specimen template. Five samples should be cut diagonally from the 1-meter conditioned fabric to obtain more accurate results.
Instrument Setup & Calibration
The parameters of an instrument’s setup may vary between companies. Prepare the instrument according to the manufacturer’s standard operating procedure. You can set the parameters according to the test type and requirements. By using AirFicient, you can finish the set one click on the screen:

It is wise to set up the instrument according to supplier instructions and recommendations for better results.
The machine’s working can be verified by performing an air permeability test on a known fabric material. The working condition is fine if the results match a known value.
The verification should be done based on airflow values and pressure differences between the fabric surfaces.
Testing Procedure
The specimen should be conditioned before the testing at 21 + 1°C (70 + 2°F) and 65 + 2 % relative humidity for at least 04 hours. Take the sample that has to be tested carefully without altering the original state of the specimen.
Place each specimen on the testing head of the instrument and perform the test according to the manufacturer’s operating conditions.
If the specimen is coated, place the coated surface of the fabric towards the low-pressure side to avoid leakages from the edges. Set up according to the AirFicient air permeability tester instructions.
According to your test requirements, you can select the air permeability unit cm3/s/cm2 or in inch-pound units as ft3/min/ft2 and air permeability test standards accordingly ASTM D 737.
For the testing of fabrics that have special finishes that may cause edge leakage, you can perform multiple tests to measure the amount of air leakage during each test and obtain more accurate results.

Place the fabric sample on it, ensuring it covers the entire opening.
Start the air permeability tester to initiate the test. The air permeability tester will measure the rate of airflow passing through the fabric under a specified pressure differential.
The AirFicient Air Permeability Tester can be connected through Wi-Fi with the SmarTexLab app installed on smartphones. You can monitor the test status for accurate results.
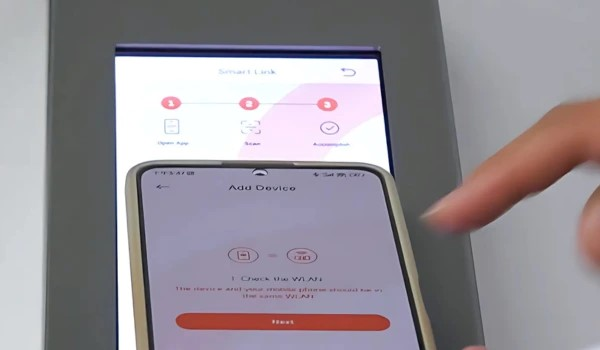
Connected through Wi-Fi with the SmarTexLab app
It is common to conduct multiple tests, and the results are displayed on the instrument screen and can also be viewed on smartphones, which allows you to share the results with the quality control department or brand buyers.
After performing the test, remove the specimen from the test head.
High air permeability values indicate that the fabric allows more air to pass, suggesting better breathability.
EN ISO 9237 Determination of the Permeability of Fabrics to Air
ISO 9237 is the standard of the International Organization of Standardization, which ensures the quality of garments and textiles regarding air permeability.
This factor is essential for outdoor garments and sportswear, as it maintains body temperature during hot weather, sports, and exercise. The EN ISO 9237 measures textiles’ air transmission rate, including woven, knitted, non-woven, and industrial fabrics.
Principle
This standard measures the rate of airflow that passes through the known area of the fabric perpendicularly at a specific pressure differential over a known period.
Parameters
It has the parameters of pressure difference, time, and specific area of fabric.
Application
It is widely used in the textile sector and covers all clothes for air permeability tests.
Apparatus & Accessories
Air permeability testers are used to perform this test, which can give results directly by applying the specimen to the test head. The tester works on the principle of pressure difference between fabrics’ front and back sides.
EN ISO 9237 Air Permeability Tester
You can manually calculate the air permeability by taking the pressure difference values. The test can be performed from 0.2 – 11838mm/s range.
Orifice Area
The tester has different values of the orifice by changing the plate. Using different orifice plates, you can perform the test for 5cm2, 20cm2, 50cm2, and 100cm2. The tolerance on the test area should be not more than 0.5%.
Clamps
Clamps prevent the specimen from disordering. Otherwise, there will be air leakage. If some air leakage occurs during the test, it will be calculated separately and should be subtracted from the test results.
Guard Ring
The guard rings are used additionally to secure the specimen from leakage during the test.
Pressure Gauge
The pressure gauge is connected to the test head to measure the pressure drop to the test specimen for 50 Pa, 100 Pa, 200 Pa, or 500 Pa. It can measure the pressure difference with less than 2% variation.
Flow Meter
It is connected to measure the airflow rate in cubic decimeters per minute (liters per minute) units.
Sample conditioning
Like ASTM D 737, the fabric sample must be conditioned according to standard atmospheric conditions before the test procedure.
Recommended Standards
According to recommended testing standards, the test surface area is 20cm2, the pressure drop for apparel fabrics is 100 Pa, and the pressure drop for industrial fabrics is 200 Pa.
Specimen Mounting
The specimen is mounted in the circular ring of the testing head, and it should be stretched lightly to remove the wrinkles and creases. This should be done carefully so that the fabric does not become distorted from its place of testing.
The specimen should be cut away from the selvage and avoid folded areas. If a fabric has different air exchange rates between its front and back surfaces, the report should mention this.
The specimen with a coated surface should be clamped and placed on the testing head with a face toward lower pressure to avoid air leakage or sample distortion.
Test Procedure
- Air permeability testers have a fixed flow rate mode and a fixed pressure mode. The fixed pressure mode is a more traditional way method for testing.
- You can set the target test pressure for the test and this pressure corresponds to the pressure difference between the top and the bottom surface of the test specimen which is clamped on the testing head.
- The machine will control the flow rate so that the pressure difference across the specimen meets your target value. The flow rate is measured and calculated to produce the permeability index.
- The unit for the permeability index includes all of these options that you can choose from to meet the requirements of different standards.
- The fixed flow rate test a measurement of the breathability of a fabric is also called the flow resistance of the fabric. So it measures how difficult it is for the air to move through the fabric
- The five-centimeter squared test head is used which requires 8 liters per minute flow rate.
Cautions
- When doing the test the machine will control the flow rate flowing through the phase max to be eight liters per minute and then the pressure across the pass is the main measurement that is required by the test and it will be used as the result.
- We can use flow rate meters to calibrate this machine. Apparatus has six different types of test heads of different test areas.
- Changing the test head is also very easy first remove the test specimen and remove the pipe connector it’s a gentle push then loosen this screw then you can pull the test head out and put a new test head in.
- To remove the bottom cast head you just need to put your finger on the side of the test head and then lift it up.
Results & Calculation
Note the airflow rate after one minute once steady conditions are achieved.
To get more accurate results, repeat the test up to 10 times and take values from different positions of the fabric.
Taking the average of 10 results is the best way to get reliable results.
Difference between ASTM D737 & ISO 9237
Both standards are valid for evaluating a fabric’s air permeability. Their working testing behavior is almost the same, with minor differences.
Let’s see all the differences between the ASTM D 737 & IS 9237.
ASTM D 737
- It is given by the American Society for Testing and Materials
- Test results are measured in cubic feet per minute per square foot of fabric (CFM/ft2)
- Specifies a pressure differential of 0.5 inches of water
- Widely used in the United States
- Allows for a wider range of pressure differentials to be used, from 0.5 to 2.0 inches of water (125 to 500 Pa).
- The sample should be conditioned in standard atmospheric condition
- The specimen should be crease or wrinkle-free and mounted on the test head without tension
- Specifies a test area of 38.5 cm2 (6 in2)
- The instrument consists of a circular test area with a diameter of 38mm, and the airflow rate is measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM) at a pressure differential of 0.5 inches of water.
- The test area is circular and smaller
ISO 9237
- It is given by the International Organization for Standardization
- Test results are measured in liters per square meter per second (L/m2/s)
- Allows for a range of pressure differentials from 1 to 10 millibars
- Used internationally and is considered the standard test method
- Specifies a pressure differential of 100 Pa (approximately 0.4 inches of water)
- The sample can be conditioned at different temperatures and humidity levels
- Specimen mounted on the test head with slight tension to remove wrinkles
- Specifies a test area of 20 cm2 (3.1 in2)
- The instrument has a rectangular test area with dimensions of 20cm x 20cm, and the airflow rate is measured in liters per square meter per second (L/m2/s) at a pressure differential of 100 Pa.
- The test area is rectangular and larger than ASTM D 737
Conclusion
The air permeability test for fabric measures the ease with which air passes through a fabric. It is commonly used to assess the breathability of textiles. The air is passed through the fabric from a unit cross-sectional area by applying constant and different pressures.
ASTM D 737 and ISO 9237 are two major testing standards for measuring a fabric’s air permeability value. Both testing methods have almost the same testing behavior but vary in result units and instrument surface head.
For more information on textile testing methods/standards
or textile testing machines, contact us:
What’s App: +86 180 2511 4082
Tel: +86 769 2329 4842
Fax: +86 769 2329 4860
Email: sales@chiuvention.com
