Overview of the ISO 9237 standard for assessing air permeability for fabric
ISO 9237 is an international standard. It tests the air permeability of textile fabrics. The standard tests the air permeability of textiles. It applies to a wide range of textiles, including wovens, knits, and nonwovens. Air permeability refers to the ability of air to pass through a textile. Good air permeability lets the body breathe. It prevents bacteria and extends the life of textiles.
Specific content of ISO 9237 standard
The ISO 9237 standard describes how to test air permeability. It covers methods, conditions, the test area, differential pressure, and time. The standard ensures tests are consistent and comparable. It also provides a reliable basis for assessing the air permeability of textiles.
Application of the ISO 9237 standard
The ISO 9237 standard is widely used in the production and quality control of textiles. It applies to all textiles. It also sets a standard for international textile trade.
Testing principle of ISO 9237
ISO 9237 defines air permeability testing. It measures the air flow rate through a specimen vertically for a set time. It uses a specific test area and pressure difference. The result is the air permeability rate. We can measure the airflow rate directly. You can convert it by finding the pressure difference between the two sides of the flow aperture. The test range is 0.2-11838mm/s. There are various measurement units, such as mm/s, cfm, and cm3/cm2/s. There are also options for the test area: 5cm2, 20cm2, 50cm2, and 100cm2. The testing accuracy is ≤±2%. The testing pressure is 0-500pa or 0-5000pa.
Test Methods of ISO 9237 Standard
For air permeability tests, use professional instruments. Examples are the differential pressure method and mass flow meter air permeability testers. The Differential Pressure Tester tests air permeability. It measures the pressure difference across the specimen. The Mass Flow Meter Tester does this by measuring the mass flow rate of air through the specimen.
Factors affecting the results of the ISO 9237 standard
ISO 9237 test results depend on several factors. These include the specimen’s thickness, density, and porosity. The lab technician must process the specimen during the test. This will ensure the test results are accurate.
ISO 9237 Sampling
We take samples per the product standard, or by agreement. Without such provisions, you may use Appendix B as a basis.
ISO 9237 Standard atmospheres for humidification and testing
Use ISO 139 for pre-conditioning, conditioning, and testing atmospheres. For arbitration tests, use secondary standards.
ISO 9237 Test apparatus
We must measure and verify the test apparatus per the regulations for apparatus.
① Specimen round table:
With a test area of 5cm, 20cm, 50cm or 100cm of circular ventilation holes, the test area error does not exceed ± 0.5%. For a larger test area of the vent should be appropriate specimen support network.
② fixture:
Can fix the specimen flat, should ensure that the specimen edge does not leak.
③ Rubber gasket:
Used to prevent air leakage, and fixture ②) match.
④ Manometer or pressure gauge:
It can show a 50Pa, 100Pa, 200Pa, or 500Pa drop in pressure on both sides of the specimen, connected to the test chamber. Its accuracy is at least 2%.
⑤ Smooth airflow intake device (fan):
It can let in air of standard temperature and humidity to the specimen round table. It can also create a 50-500Pa pressure drop by passing air through the specimen.
⑥ Flow meter, volumetric meter or measuring orifice:
Can show the flow rate of airflow unit of dm / min (L / min), accuracy of not more than ± 2%.
Note: 1. As long as the flowmeter, volumetric meter can meet the accuracy of ± 2%, it can measure air flow of 3 cm/s or other units.
2. Use a differential pressure flowmeter. It should check if the difference in permeabilities of the calibration plate is within 2%.
Test conditions
If the parties cannot reach the above pressure drop, or find it inapplicable, they can use, after consulting, 50Pa, 500Pa, 5cm, 250cm, or 100cm of test area.
If the team uses other test areas, they should include a note in the report:
To compare test results, use the same test area and pressure drop.
Operating Procedure
Check and calibrate the instrument.
Clamp the specimen on the round table. The test point should avoid the cloth’s edge and folds. Use enough tension to make the specimen flat, but not deformed. To prevent air leakage, we should gasket the specimen round table side. If the air permeability differs between the fabric’s front and back, the report should indicate the test side.
Start the suction fan or other devices to pull air through the specimen. Adjust the flow rate. Do this to bring the pressure drop to the specified value after 1 minute, or until it stabilizes. Then, record the air flow rate.
Note: If using a volumetric flowmeter, measure at least 10 dm3. This will achieve the required accuracy.
For instruments with differential pressure flow meters, choose a suitable aperture. Then, record the differential pressure on both sides of it.
Under the same conditions, measure at least 10 times in different parts of the same sample.
If there is a leak at the fixture, measure it as specified. Then, subtract that value from the reading.
Calculation and presentation of results
Calculate the mean qv and the coefficient of variation (to the nearest 0.1%) of the measured values.
Calculate the air permeability R using equations (1) or (2). Trim the result to 2% of the measuring range (full scale of the measuring gear).
Calculate the 95% confidence interval for the permeability. Use the same units and precision as in 10.2.
Test report
The test report shall include the following contents:
a) General information
1) The number of this standard, i.e. ISO 9237:1995 and the date of test;
2) The name of the sample, its spec, and, if required, the airflow direction through the fabric.
3) Test area adopted;
4) The pressure drop adopted;
(5) The number of test samples;
(6) Moisture regulation and test with a standard atmosphere;
7) Any details of deviation from this standard.
b) Test results
1) Air permeability R,mm/s or m/s;
2) Coefficient of variation, %;
3) 95% confidence interval, mm/s or m/s.
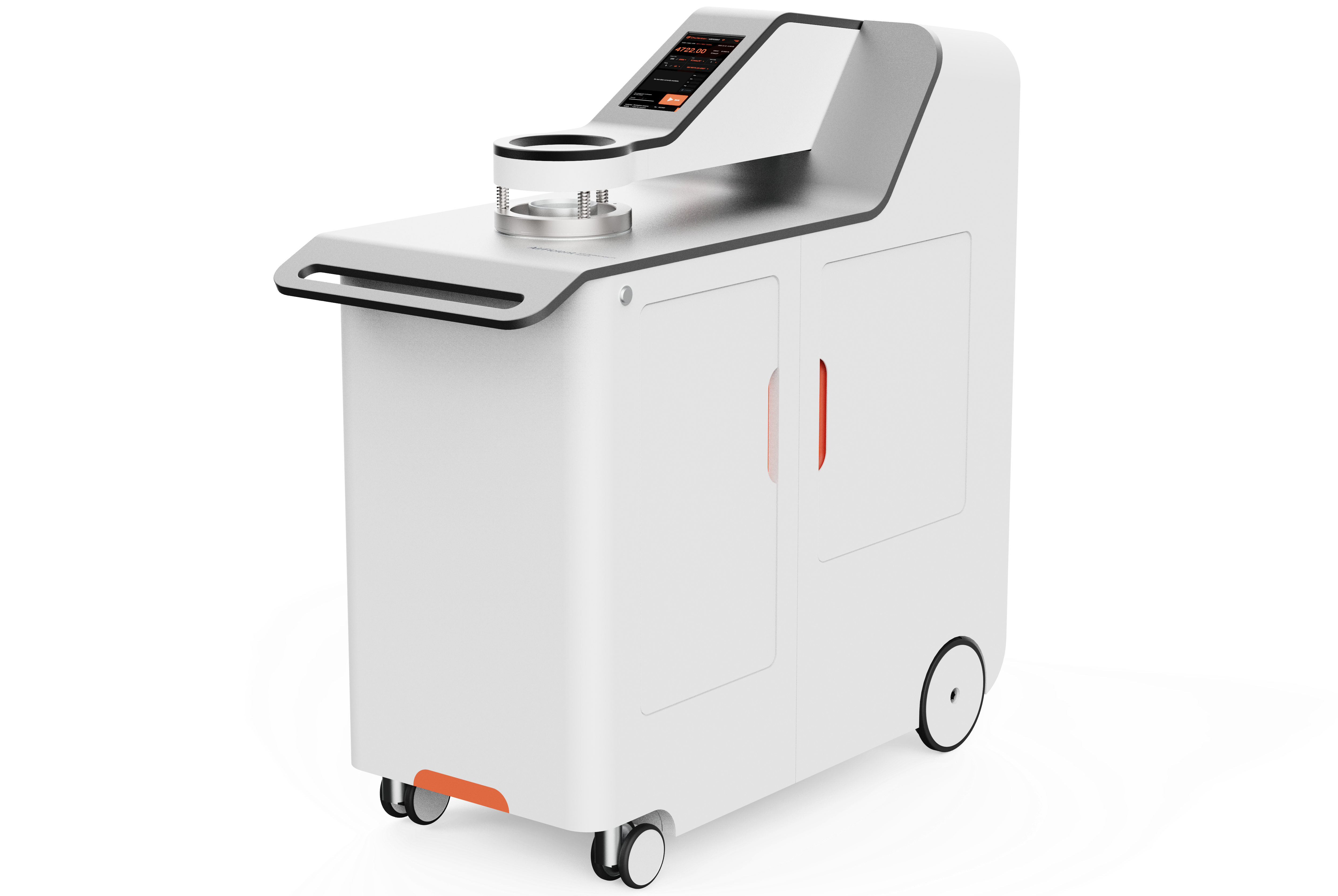
AirFicient Intelligent Air Permeability Tester Introduction
The Air Permeability Tester lets you quickly get reliable air permeability test results. It is a smart air permeability test apparatus. You can set limits and check the test status from your smartphone. This greatly improves work efficiency. This Air Permeability Tester is for many textiles. These include technical fabrics, non-woven fabrics, and other breathable products.
such as sponges, paper, and other materials for air permeability testing. Our air permeability meter is applicable to GB/T5453, ISO 9237, ISO 9073:15, JIS L1096
Item 8.26: Method C, BS 3424-16, BS 6F 100 3.1, NWSP 070.1 RO (15), GB/T 24218.15, etc.
AirFicient Intelligent Air Permeability Tester vantage point
Tests are easy and fast.
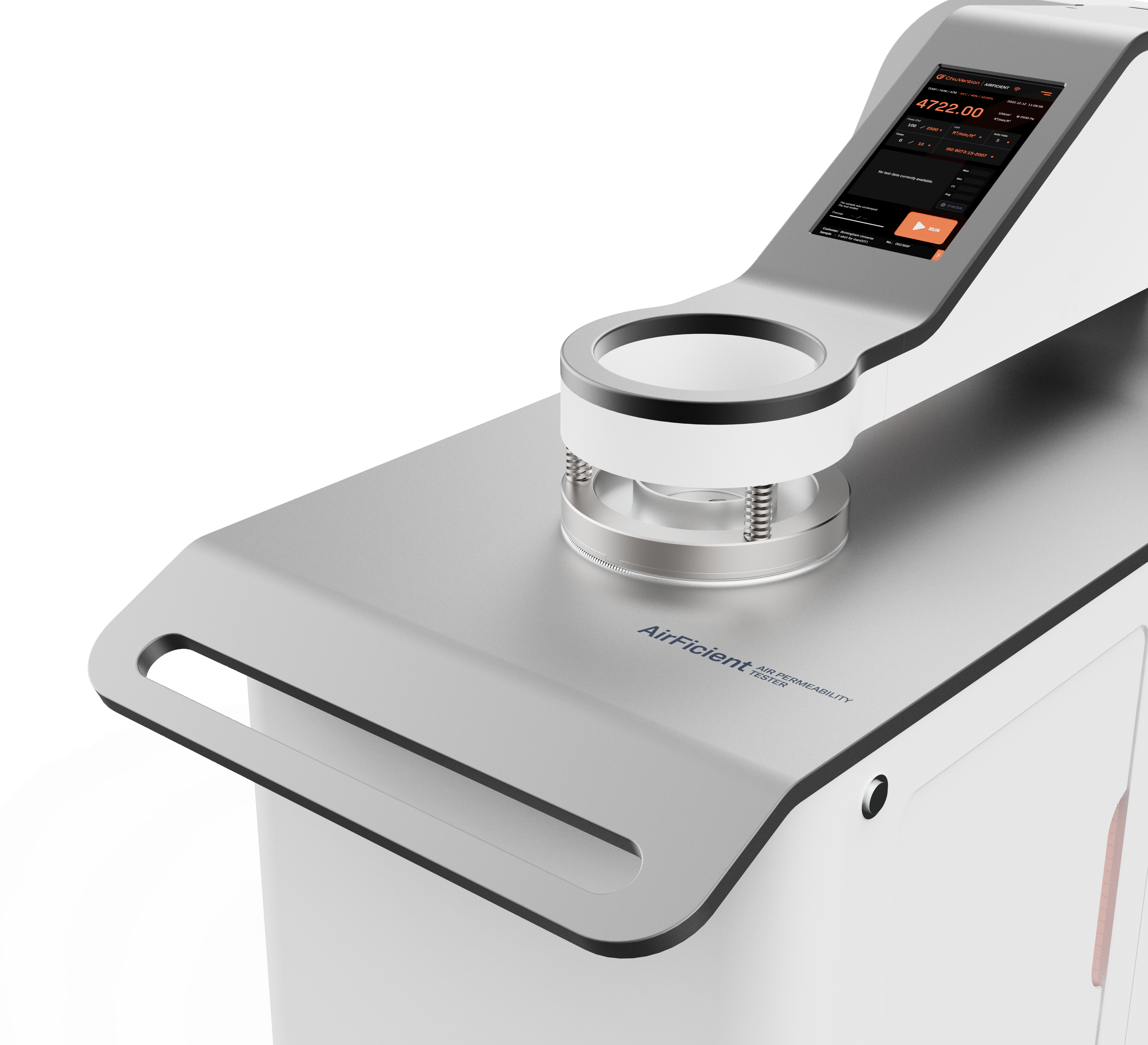
The Air Permeability Tester is easy to use. You can select the air permeability test standards and units from the operation screen. The Air Permeability Tester can recognize the test fixture head’s different ranges. You can start the air permeability testing and get the result.
The air passes up through the fabric. This forms a pressure difference between the front and back of the fabric. We measure the amount of air that goes through the fabric under a certain pressure. This gives us the fabric’s air permeability value.
More reliable air permeability test results
The range conversion components of this Permeability Tester for fabric are innovative. They are maintenance-free and have no loss. They bring high repeatability and reliability to air permeability testing results.
The core components are high-quality. They include pressure sensors from famous brands. These parts further ensure the accuracy of the airflow resistance test results.
Self-designed calibration system ensures accurate testing at all times
A third party tested the calibration system. It is now authoritative and reliable. Users can now calibrate the instrument at any time.
Smart Air Permeability Testing
The IoT connects the air permeability testing machine to the SmarTexLab APP on the phone/PC.
And The app can connect to ERP/LIMS via an API. Or, the air permeability test apparatus can connect directly to ERP/LIMS. The system has test orders and sample info. The instrument can record all related data, including test results.
The system will then summarize these into an air permeability test report. The relevant parties can view the report in real-time. You can monitor tests for many air permeability test equipment at once. And, change test requirements. Get alerts before tests end. And, stop or repeat tests remotely.
In the SmarTexLab App, you can chat with ChiuVention staff for quick support. You’ll get reminders that the air permeability tester needs calibration, maintenance, and new consumables. Regular OTA remote upgrades are available.
Designed in Germany, quality is our life.
We developed all our textile testing equipment in-house. We partnered with a team of renowned German industrial designers. Our textile testing machines are now of outstanding quality. 100% source factory and factory price.
Air Permeability Test Method or Air permeability Test Procedure
Sample Preparation:
Cut a sample of the material to the needed size. The size is set by the testing standard.
Ensure the sample is clean, dry, and free from any defects affecting the test results.
Calibrate the equipment.
Calibrate the air permeability tester based on our instructions. Also, follow the relevant testing standard. Ensure that the pressure gauges and flow meters are accurate.
Mount the Sample:
Secure the sample in the test chamber of the air permeability tester. To prevent any air leakage around the edges, clamp the sample tightly.
Set the pressure differential.
Adjust the air permeability test apparatus. It should create a specific pressure difference across the sample. The pressure difference is usually chosen based on the material and its use. Testing standards specify common values.
Initiate Airflow:
Start the airflow through the material. The air permeability tester will draw air through the sample or blow air through it.
Measure airflow rate:
Measure the rate of air passing through the sample. The flow rate is often recorded using built-in sensors. It is then shown on the equipment’s readout panel. Ensure that someone takes the measurement after the airflow has stabilized.
Record Environmental Conditions (Optional):
Record the temperature and humidity if the test standard requires it. These can affect the air permeability of some materials.
Calculate Air Permeability:
The test results for air permeability will express units such as cm³/s/cm², CFM/ft², or other types. (You can select the Air Permeability Units from the operation screen)
Repeat the test (optional):
To ensure the accuracy of air permeability testing, repeat the test on multiple samples or different areas of the same sample. Then, calculate the average air permeability.
Key Points to Consider:
Follow the guidelines for sample size and shape. The guidelines are in the air permeability testing standard (e.g., ASTM D737, ISO 9237).
Use the pressure differential from the standard or suitable for the material type.
Equipment Calibration: Calibrate the air permeability tester often. Also, maintain it to ensure accurate results.
The test standard may require you to control or record the temperature and humidity.
Common Air Permeability Test Standard:
ASTM D737: Standard Test Method for Air Permeability of Textile Fabrics.
ISO 9237: Textiles – Determination of the Permeability of Fabrics to Air.
BS 5636: Method for Determination of the Air Permeability of Fabrics.
Follow these steps and the relevant standards. Then, you can get reliable air permeability measurements for various materials. You can also reproduce them.
AirFicient Intelligent Air Permeability Tester Repair and Maintenance
You should ground the instrument shell reliably. Its grounding resistance should be ≤1Ω.
Clean the filtering steel mesh once a month. The mesh is stainless steel. It is best to blow it with high-pressure gas or wash it with water. To wash with water, put it into the instrument after drying. Place the mesh in the designated location.
Take out the lower fixture, and see the filtering stencil.
You can use the sealing rubber sheet, supplied as an accessory, to test the air tightness of the device. Please contact ChiuVention to replace the rubber sheet when it wears out.
If you turn off the power switch, do not restart it within 1 minute. Wait until you discharge the electrical system before restarting the unit.
Specialists should fix the instrument when it malfunctions. Or, the manufacturer should check it. Non-professionals cannot open the door of the electrical box. That door has a safety device. Press the button where the arrow points. Go to the bottom without releasing it. At the same time, open the door to access the circuit. It’s forbidden to open the door, otherwise, there’s a danger of electric shock.
ISO 9237 Standard Air Permeability Levels
ISO 9237 is a standard from the ISO. It measures the air permeability of fabrics. Air permeability is a gas’s ability to pass through a fabric. It is usually measured as air permeability in m3/m2/s or l/cm2/s. According to ISO 9237, experts can classify air permeability according to the following classes. 1:
1. Air permeability class 0: Air permeability less than 0.1 per cent.
Fabrics with a breathability rating of 0 are airtight. Gases cannot pass through the fabric. This type of fabric is usually used for waterproof or airtight products, such as mackintoshes and windproof jackets.
2.Air permeability class 1: Air permeability range 0.1-0.9
Fabrics in Permeability Class 1 are less breathable, but still slightly air permeable. These fabrics are for uses that need some breathability. They are for outdoor sportswear and light-duty workwear, etc.
3. Air permeability Class 2: Air permeability range 1.0-4.9
Fabrics with a air permeability rating of 2 are moderately breathable. They are, therefore, good. Manufacturers use these fabrics in sports and outdoor wear. They are vital for breathability.
4. Air permeability class 3: Air permeability range 5.0-9.9
Class 3 fabrics are more air permeability. They have a higher air permeability. These fabrics suit uses that require high breathability, like outdoor and summer sportswear.
5. Air permeability class 4: Air permeability range 10.0-19.9
Fabrics with a air permeability rating of 4 are very breathable. They have a high air permeability. These fabrics are often used for high-performance garments. They include outdoor sportswear and mountaineering gear.
6. Air permeability class 5: Air permeability greater than or equal to 20 per cent
Fabrics with a air permeability rating of 5 are very breathable. They have a high air permeability. These fabrics are often used in niche areas. They are in athletes’ uniforms and high-intensity sports gear.
ISO 9237 allows for selecting breathability based on fabric and use. Different levels of breathability are suitable for different environments and conditions of use. The breathability rating can help consumers choose the right fabric. For outdoor sports or work, breathability is essential. It affects comfort and function.
What are the advantages of the ISO 9237 air permeability standard over other standards?
The ISO 9237 breathability standard has key advantages over others. It applies to many uses, has standardised test methods, and is very relevant.
The ISO 9237 Permeability Standard has the following advantages over other standards:
ISO 9237 tests the breathability of many textiles, both natural and synthetic. It has a wide range of applications. Studies show a high correlation between tests using ASTM D737-2004 and GB/T 5453-1997. This means the ISO 9237 standard aligns well with other international standards.
Standardised test methods: ISO 9237 provides a test method. It ensures comparable results between labs and testers. This standardisation is important to ensure product quality and control.
High correlation: Tests using ASTM D737-2004 and GB/T 5453-1997 show a high correlation. Thus, the ISO 9237 standard agrees with other international standards in test results. This shows that ISO 9237 agrees with other international tests.
ISO 9237 applies to textiles and other materials, like automotive and packaging ones. This shows its wide use across many industries.
What are the factors affecting air permeability testing under ISO 9237?
There are four main factors in ISO 9237 air permeability testing. They are: fabric material, fabric structure, fibre properties, and yarn structure. It also depends on environmental conditions.
Firstly, fabric material is one of the main factors affecting breathability. Fabrics made of different materials, like cotton and wool, vary in air permeability. Shaped fibre fabrics are generally more breathable than round ones.
Secondly, fabric structure also significantly affects breathability. Air permeability depends on the fabric’s tightness, yarns’ twist, and their density. In general, the looser the fabric organisation, the better the air permeability.
Also, air permeability depends on fibre properties and yarn structure. The fibres’ moisture, shape, and cross-section affect air permeability. For example, shaped fibres are more conducive to air circulation than round fibres.
Finally, environmental conditions are also important factors affecting air permeability. Changes in temperature and humidity can affect how air permeable a fabric is. In general, higher temperatures boost air permeability. But, higher humidity lowers it.
In summary, ISO 9237 requires some factors in air permeability tests. This ensures the test results are accurate and reliable.
What are the applications of the ISO 9237 standard?
The ISO 9237 standard is mainly applied to the testing of air permeability of textiles. The standard provides methods to test the breathability of textiles. It applies to a wide range of textiles, including woven, knitted, and nonwoven fabrics.
Air permeability testing is very important in textiles. It affects their comfort, health, and practicality. Good breathability allows for smooth breathing. It also prevents bacteria and extends textiles’ life.
Apart from textiles, breathability testing is also widely used in other fields.
For example, we measure air permeability and resistance in:
automotive interior components,
building materials to assess indoor air quality,
packaging to ensure the quality of the contents, and
electronics to ensure the components function.
Why is air permeability of fabrics important to test?
Air permeability is another important factor affecting the comfort of fabrics. Sportswear, windproof, and coldproof clothing have higher requirements for air permeability of fabrics. Parachutes and filter cloths are types of industrial textiles.
They have special needs for air permeability. The air permeability of fabrics depends on the number and size of gaps. These gaps are between the warp and weft yarns and between the fibers. It also relates to factors like yarn density, fineness, and twist. These factors relate to fiber properties, yarn structure, fabric thickness, and density. The “air permeability” refers to a fabric’s performance.
It lets air pass through when there is a pressure difference on both sides. Under the specified pressure difference, air passes through the fabric. This happens on both sides of the fabric. Air flows only when a pressure difference is on both sides of the fabric.
For more information on textile testing methods/standards
or textile testing machines, contact us:
What’s App: +86 180 2511 4082
Tel: +86 769 2329 4842
Fax: +86 769 2329 4860
Email: medium@chiuvention.com