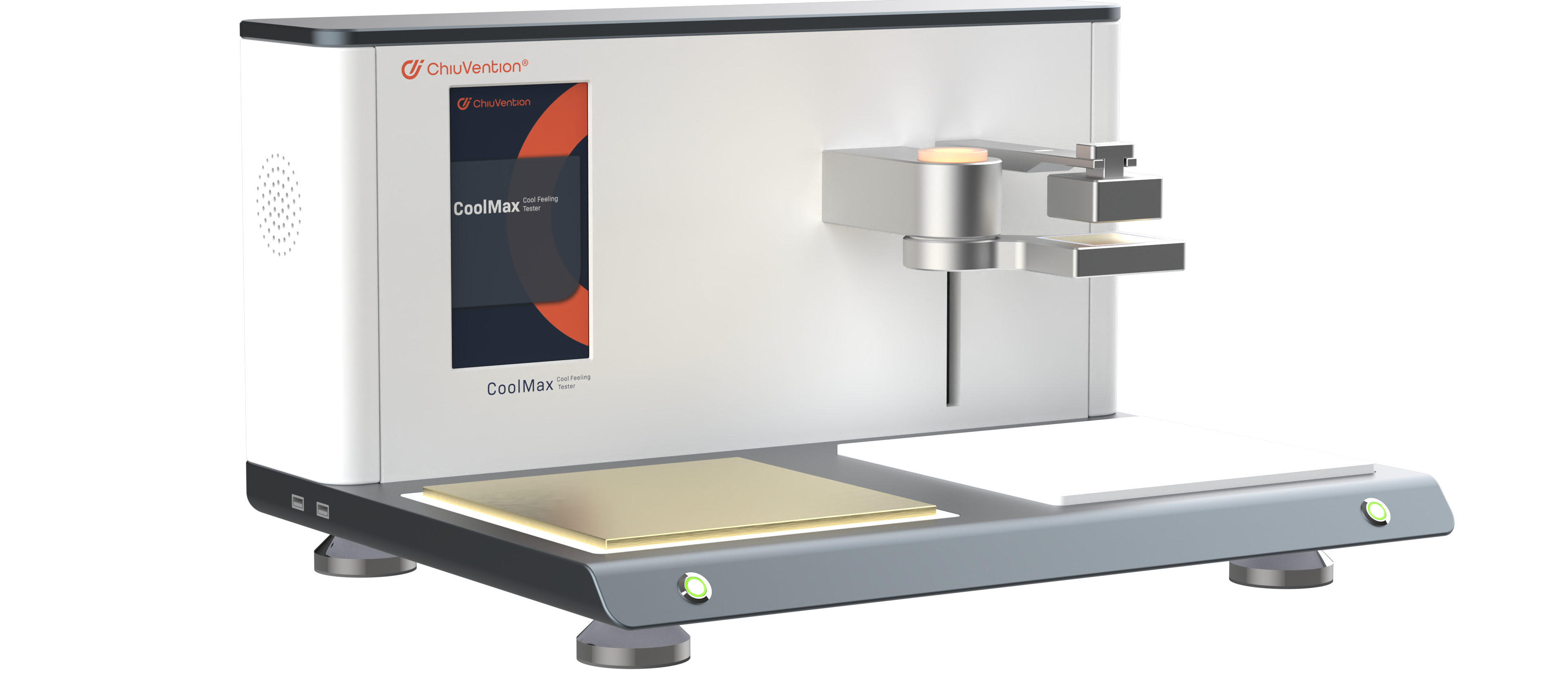
Why should I choose ASTM D7984 for Cool Feel Fabrics?
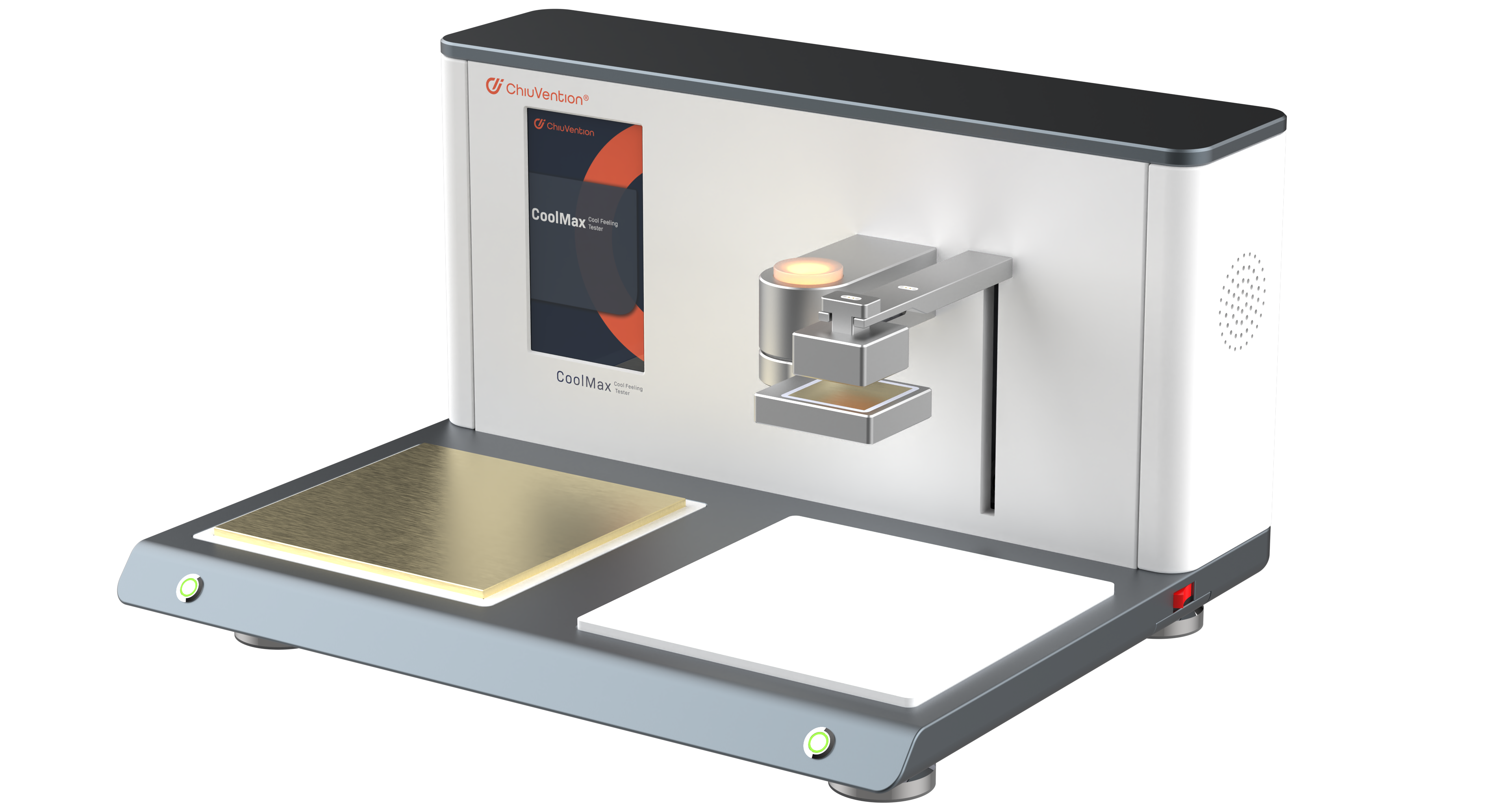
They chose ASTM D7984 for Cool Feel fabric testing. It measures a textile’s thermal conductivity and fugacity. This quantifies a fabric’s insulation and conductivity. This method uses a modified transient planar heat source (MTPS) method. A single-sided heat sensor heats the sample surface for 1-3 seconds. This directly measures the material’s thermal conductivity and thermal fugacity. It also describes its thermophysical properties in detail.
ASTM D7984 is a fast, non-destructive way to measure fabric structure. It also supports the sample. For testing, we simply place the fabric flat on top of the probe and take the measurement. Researchers can also use this method to measure samples in liquid, powder, and paste form. ASTM D7984 offers the following advantages over traditional heat transfer test methods:
1. Fast: ASTM D7984 test time is short, usually only a few seconds to complete.
2. ASTM D7984 testing does not require destructive testing. It does not damage the sample structure.
3. Supports the sample: The ASTM D7984 test can support the sample. It avoids deforming or damaging it.
What can we apply ASTM D7984 testing to in Cool Feeling Fabrics?
ASTM D7984 tests the thermal conductivity of fabrics and other materials. It helps garment and fabric makers understand how warm or cool their fabrics are. This helps consumers find more comfortable clothes. The ASTM D7984 method tests functional textiles. It compares their heat control. This is vital for new textiles, better quality, and meeting consumer needs.
The ASTM D7984 test method applies to cool-feeling fabrics in these ways:
Testing fabrics for warmth and heat dissipation:
The ASTM D7984 test method measures a textile’s thermal conductivity. Researchers can then analyze it for its thermal insulation. This method helps apparel and fabric manufacturers. It tests fabrics for warmth and heat dissipation. This ensures they provide a comfortable wearing experience.
Designing better fibre weaves:
Manufacturers can use the ASTM D7984 test. It will help them design more efficient fibre weaves to improve thermal efficiency.
Designers can use this method:
Assess material use.
Create more comfortable products, like bedding, furniture, and car interiors.
Evaluating Material Efficiency:
The ASTM D7984 test measures a material’s thermal conductivity and escape rate. It helps designers and manufacturers understand its thermophysical properties. They can then make better design choices.
What are the test methods for cool-feeling fabrics?
The main testing methods for cool-feeling fabrics include the following:
Temperature sensor direct measurement method:
This method is to dry the sample in an oven at a specific temperature. Then, place it in an oven with controlled temperature and humidity. The sample is quickly folded after dripping in the center of the specimen. A temperature sensor records the temperature change. According to the recorded temperature data, we can obtain a temperature-time curve. The cooler the curve’s lowest point, the stronger the cooling sensation. Also, the cooler the end temperature, the longer the fabric stays cool.
Qmax method:
The test follows the national standard ASTM D7984. It is for “Testing and Evaluating the Instant Cool Feeling of Textiles.” Testing aims to contact a sample with a hotter thermal test plate. Then, measure the test plate’s temperature change over time. Finally, calculate the contact coolness coefficient (Qmax). the larger the value of Qmax indicates that the degree of coolness felt by the skin is stronger.
Maximum heat flow method:
Researchers base this method on transient heat conduction theory. It simulates the heat transfer process of human skin in contact with the fabric. It measures the heat flow change curve in real time. The Maximum Heat Flow Method was proposed by Japanese scholar Kawabata. It can assess the warmth or coldness felt when fabrics touch.
Heat Absorption Coefficient Method:
A Czech scholar, Hes, proposed it. It tests fabrics’ warmth by measuring their heat absorption when in contact with a human body. The heat absorption coefficient is a measure of the fabric’s ability to absorb body heat.
Contact Cooling Tester:
This is a specialized device. It tests and evaluates textiles’ cooling properties on contact. And itmeasures heat transfer by mimicking the human touch. It tests the coolness of textiles. Many industries, including fibre fabrics, cosmetics, and food, use the equipment.
Each method has pros and cons. They suit different fabric testing needs. The test purpose and fabric traits will determine the best method.
What should I pay attention to when testing ASTM D7984 for Cool Feeling Fabrics?
ASTM D7984 is a professional test. It requires specific knowledge and lab skills. For ASTM D7984 testing, seek help from experts. This ensures accurate, reliable results. Also, ASTM D7984 test results depend on the environment, like temperature and humidity.
When you conduct ASTM D7984 testing, note the following matters:
Environmental conditions:
You should conduct the test in a room with constant temperature and humidity. The temperature must be 20 ± 2 ℃, and the humidity 45 ± 4%.
Test method:
The ASTM D7984-21-2021 method tests the thermal conductivity of fabrics. It gives a heat absorption coefficient that measures their cold and warm sensation. We then evaluate the fabrics with these indexes to assess their coolness and warmth.
Subjective feeling evaluation:
In the subjective feeling test, we place fabric samples on the inner arm. Each contact lasts 2 seconds. We use the subjects’ feelings to evaluate the fabric.
Evaluation standard:
In the cool and warm feeling tests of the fabric, we used a 3-point scale. We ranked the fabric’s performance in 3 grades: A, B, and C. A is warmest, C is coolest.
The above precautions can ensure the accuracy of cool feeling fabrics in ASTM D7984 testing.
What are the steps and principles of the ASTM D7984 test for Cool Feeling Fabrics?
Test Principle:
The ASTM D7984 test method is based on the modified transient planar heat source (MTPS) method. It tests fabrics, fibers, and other materials. And it measures their thermal escape rate and conductivity. It quantifies the thermal conductivity of textiles. It does this by measuring the change in heat flow during transient heat transfer.
The MTPS method directly measures a material’s thermal conductivity and fugacity. It does this by applying a constant heat source to the sample’s surface for 1-3 seconds. Someone uses a single-sided heat sensor.
Test Steps:
Someone places the fabric flat on top of the probe and measures it.
This method is fast and does not damage the fabric. It can also measure samples in the form of liquids, powders, and pastes.
Under the test conditions, a thermal plate is hotter than the specimen. They place it in contact with the specimen. We measure the change in the thermal plate’s temperature over time. The calculation determines the contact coolness coefficient (q max). This characterises the specimen’s instantaneous coolness in contact with the sample. A larger q max means the skin feels the coolness more. A smaller q max means the skin feels it less. The test procedure is as follows:
1. Cut 5 specimens, each about 200mm x 200mm. Avoid defects and folds that could affect the test results.
2. Set the sample-carrying platform to (20±0.5)℃. Lay the specimens flat on it, with the fabric side facing up.
3. Set the heat detection plate to (35±0.5)℃. You must maintain a temperature difference (△T) of 15°C with the sample carrier. If you use other temperatures, specify them in the report.
4. When the heat detection plate reaches and holds the temp from step 2, cut off its heat source. Then, quickly place it vertically on the specimen. The copper plate’s surface must touch the fabric. Record q max, to 3 decimal places, in J/(cm2-s).
Calculate the mean of q max for 5 samples. Round the result to two decimal places per ASTM D7984.
If needed, test the samples’ coolness at the moment of contact.
What are the uses and importance of the ASTM D7984 test for cool feeling fabrics?
Application Scene:
Many areas that need comfort use Cool Sense fabrics. These include summer clothes, sports gear, and home furnishings. These fabrics keep users cool and comfy in hot weather. They dissipate heat well.
Garment manufacturers:
Testing fabrics for warmth and heat dissipation to ensure consumers are more comfortable.
Fabric manufacturers: designing better fibre weaves to improve thermal efficiency.
Designers:
Assess material use to design more comfortable products. These include bedding, furniture, and car interiors.
Importance:
It helps manufacturers and designers control heat. It also helps them design better fabrics and products.
Provides detailed thermal-physical property descriptions to ensure product comfort and functionality.
The ASTM D7984 test method measures the thermal conductivity of cool-feeling fabrics. It ensures they work as intended and enhances product comfort and functionality.
What is the purpose and scope of the ASTM D7984 Cool Feeling Fabrics test?
The primary purpose of the ASTM D7984 standard is to test and quantify the thermal conductivity and thermal fugacity of cool-feeling fabrics in order to assess their performance as thermal insulators or conductors.
Test Objectives
Quantify the thermal conductivity and thermal fugacity of cool-feeling fabrics: The Modified Transient Planar Thermal Source (MTPS) method allows for rapid and accurate measurement of the thermal conductivity and thermal fugacity of a material, which can be used to analyse its thermal insulation or thermal conductivity properties.
Evaluate the comfort of cool-feeling fabrics: Test results can help manufacturers design better fibre weaves to improve thermal efficiency, and designers can evaluate the efficiency of materials to design more comfortable products such as bedding, furniture, and automotive interiors.
Test Scope
The ASTM D7984 standard applies to all types of textiles, including but not limited to fabrics, fibres, etc. The standard is applicable to all types of textiles, including but not limited to fabrics and fibres. It is particularly suitable for testing cool-feeling fabrics to help manufacturers and designers better control heat and enhance the comfort and functionality of their products.
What are the factors that affect the results of the ASTM D7984 Cool Feeling Fabric test?
The main factors that affect the results of the ASTM D7984 Cool Feel Fabric test include the following:
Ambient Temperature and Humidity: Changes in ambient temperature and humidity can have a significant impact on test results. If there is a difference in temperature between the sample and its surroundings, this can lead to airflow, which can affect the test results.
Sample hygroscopicity or volatility: The hygroscopicity or volatility of the sample can also have an effect on the test results. If the sample is highly hygroscopic, its weight will increase; if the sample is volatile, its weight will decrease.
Calibration and Maintenance of Test Equipment: The calibration and maintenance of test equipment has a direct impact on the accuracy of the test. If the equipment is not properly calibrated, or if it is not properly maintained during use, it may lead to inaccurate test results.
Sample size and shape: The size and shape of the sample can also affect test results. If the sample size does not meet the standard requirements, or if it is irregularly shaped, it may result in uneven heat flow distribution, which may affect the accuracy of the test results.
Handling during testing: During the testing process, the operator’s method of operation can also have an impact on the results. For example, using tweezers when picking up and placing samples instead of using hands directly can reduce human error.
Sample Surface Preparation: The way in which the surface of the sample is prepared can also affect the test results. For example, the use of thin-necked containers, lids, or stoppers can reduce volatilisation or moisture absorption of the sample during testing.
Specifics of the ASTM D7984 standard and how to use it:
The ASTM D7984 standard is a test method for measuring the thermal diffusivity of materials. The method evaluates the thermal conductivity of a material by measuring its thermal diffusivity under a transient planar heat source. Specific steps include placing the sample in a temperature-controlled sample holder, then placing a hot plate on the upper surface of the sample, and recording and measuring the temperature of the hot plate and the profile of the heat flow density on the contact surface over time2 .
By understanding these influencing factors and the specifics of the criteria, the testing of cool-feeling fabrics can be carried out in a better way to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results.
Conclusion
The ASTM D7984 test is a method for measuring textiles. It gauges their thermal conductivity and thermal escape rate. It helps fabric and garment manufacturers understand their warmth and heat dissipation. This allows consumers to wear more comfortable garments. The ASTM D7984 test has benefits and uses. By knowing them, we can better understand textiles’ thermal conductivity. It will help us develop new textiles and improve quality. It will also help us meet consumer needs.
For more information on textile testing methods/standards
or textile testing machines, contact us:
What’s App: +86 180 2511 4082
Tel: +86 769 2329 4842
Fax: +86 769 2329 4860
Email: medium@chiuvention.com