Hydrostatic pressure index is one of the important indexes of waterproof and moisture permeable fabrics. Hydrostatic pressure refers to the resistance encountered by the water through the fabric, under standard atmospheric pressure conditions, the fabric to withstand a continuous rise in water pressure, until the back of the fabric seepage water droplets, at this time, the measured value of the water pressure that is the hydrostatic pressure. The greater the hydrostatic pressure the fabric can withstand, the better the waterproofness or resistance to seepage. There are different test methods for different fabric materials.
AATCC 127-2003 Water Resistance: Hydrostatic Pressure Method Purpose and Scope
Researchers use this test method to determine the resistance of a fabric to water penetration under hydrostatic pressure. This method applies to all types of fabrics, including those with water-repellent and water-rejecting finishes. Water resistance depends on how well the fibres and yarns resist water, as well as on the fabric structure. The results that this method obtains differ from those that AATCC’s rain or water spray method obtains. This method determines the resistance of a fabric to water penetration by hydrostatic pressure.
AATCC 127-2003 Water Resistance: Hydrostatic Test Principle.
The technician fixes the specimen on a standardized test area, and an air compressor adds 0-5 bar of air to a tank filled with distilled water, which they then apply to the specimen at a certain pressure. Either dynamic or static methods can carry out the test.
(1) Dynamic method: by testing a certain rate of pressure increase in the specimen is not in contact with the water on one side of the specimen exudes a fixed number of water droplets when the pressure to determine the hydrostatic pressure resistance of the specimen.
(2) Static method: by testing a certain hydrostatic pressure, the specimen to maintain the pressure for a certain period of time after the water seepage to determine the hydrostatic pressure resistance of the material.
AATCC 127-2003 Water Resistance: Terminology of Hydrostatic Method.
Hydrostatic Pressure: The distribution of pressure by water over an exposed area. Water Resistance: Resistance to moisture and water penetration. Water resistance: In textiles, the resistance of a fibre, yarn or fabric to moisture.
AATCC 127-2003 Water Resistance: Hydrostatic Method Apparatus and Materials
1. Hydrostatic Pressure Tester: Option 1, Hydrostatic Pressure Tester; Option 2, Hydrostatic Head Tester.
2. Distilled or deionised water.
AATCC 127-2003 Water Resistance: Hydrostatic Pressure Test Sample
1. Take at least 3 representative samples of the fabric diagonally across the width of the fabric, with each sample measuring at least 200 x 200 mm. 2.
2. Touch the samples as little as possible to avoid folding and contamination of the test piece.
3. Place the specimens at 21±2°C and 65±2% relative humidity for at least 4 hours before testing.
4. You must indicate the side of the fabric in contact with the water, as the results will differ for the front side compared to the back side of the fabric. Label the front and back of each specimen on the corner.
AATCC 127-2003 Water Resistance: Hydrostatic Test Procedure:
1. Check that the temperature of the water in contact with the test specimen is 21±2℃.
2. Dry the surface of the fixture.
3. Clamp the specimen with the test surface facing the water.
4. Operation
Option 1 – Hydrostatic Head Tester, start the engine, press and hold the lever to increase the overflow rate to 10mm/s, and close the vent when the water flows out.
Option 2 – Hydrostatic Head Tester, select a gradient of 60 mbar/min and press the start button.
5. Ignore water droplets within 3mm of the edge of the fixture and record the hydrostatic pressure when the water droplets ooze out at three different locations.
6. AATCC 127-2003 Water Resistance: Hydrostatic Pressure Method.
Calculate the average hydrostatic pressure of each sample.
7. Reporting
The value of each specimen and the average value of each sample.
Test material and test surface
Water temperature and type of water
Gradient (rate of rise in water pressure)
permitted tester
Any amendments to this measure
8. Accuracy and Error
Accuracy, test results related to the tester
Suter hydrostatic testing machine (option 1).
In 1993, researchers carried out a study in a limited number of laboratories, involving six laboratories, each with two operators, who tested two fabrics (three samples of each fabric). There was no prior evaluation of the relative levels of competence of the participating laboratories in carrying out each version of this test measure.
The two fabrics differ in principle in size (the first fabric is approximately 810 mm; the second fabric is approximately 340 mm), and the residual variance of the two fabrics is different. Therefore, we should provide the accuracy of each fabric separately.
Users of this test measure should be aware of the limited nature of this study and use the results with caution.
In a single laboratory study, six different laboratory technicians tested three specimens of five materials.
The five materials differed in size: A = 103, B = 33, C = 37, D = 12 and 10.3.2 E = 77. This study expresses the obtained data in millibars (International System of Units). Because of the difference in residual variance of the five materials, it is necessary to give the accuracy for each material separately.
By analysing the data set for each material, we can obtain a critical difference, and for a suitable accuracy parameter, the difference between the two averages of (N) permitted tests should meet or exceed the values in the table. Values are important to record at the 95 per cent confidence level.
This selection does not establish inter-laboratory precision. Until such accuracy information is available, the user of this measure should use principle recording techniques to compare test results for inter-laboratory averages.
Errors
A permitted perimeter can only define the water resistance according to one test measure. There is no independent arbitration method for determining the true value. There are no known errors in this test measure.
9. Notes
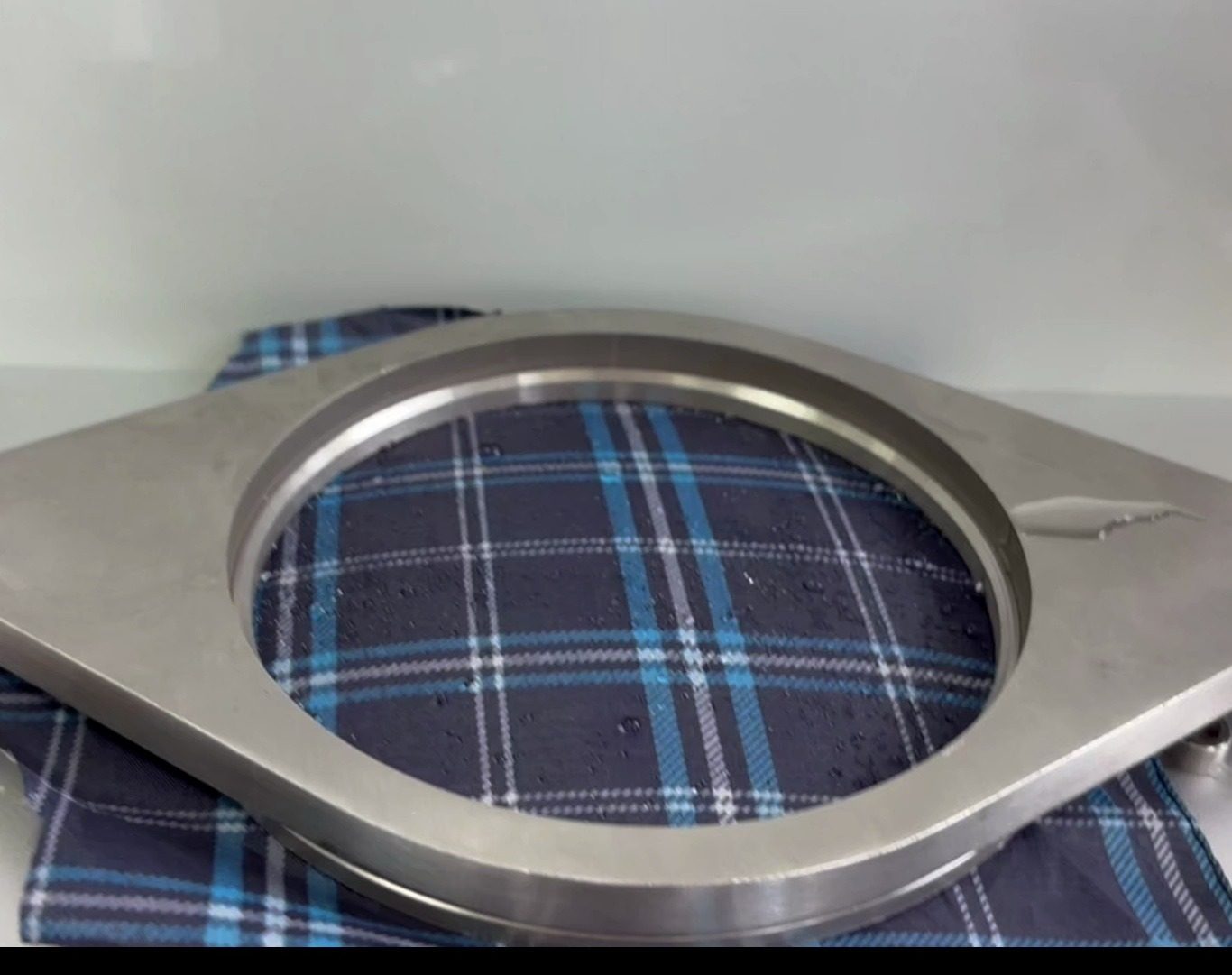
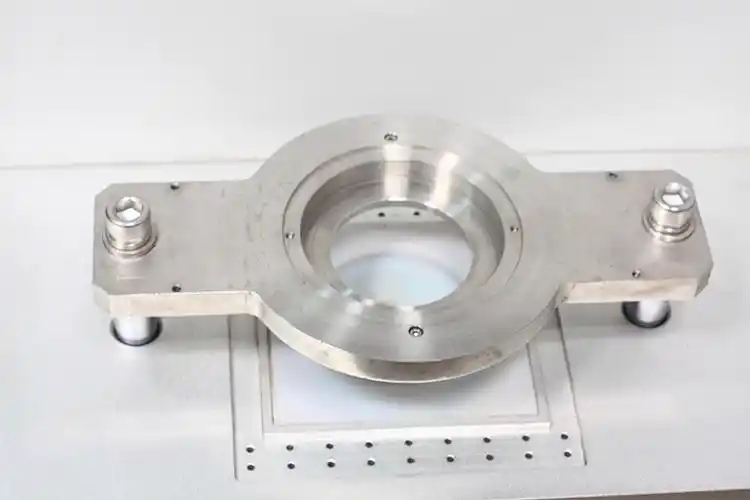
This apparatus basically has an inverted conical well with a coaxial ring fixture. The coaxial ring fixture clamps the fabric specimen to the bottom of the well. The apparatus injects water at a rate of 10.0 ± 0.5 mmH O per second from above a specimen area of 114 mm in diameter. The operator uses a mirror placed underneath the specimen to form a picture of the liquid penetration into the specimen based on the water droplets. They equipped the well with a flap for ventilation.
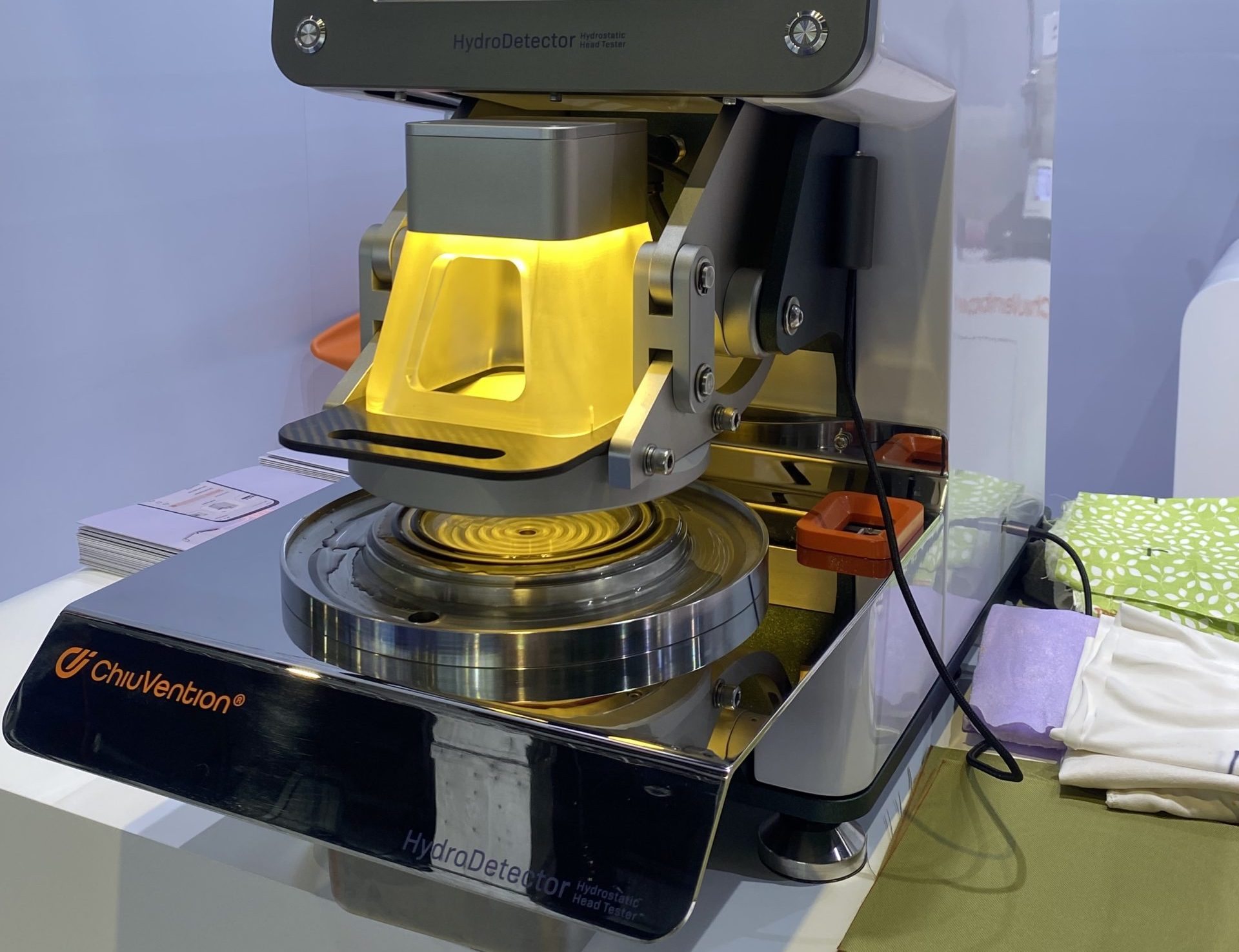
Hydrostatic head tester
This tester uses an electronically controlled pump to apply hydrostatic pressure to the underside of the fabric at a speed of 60 mbar/min (speed adjustable). Fill a container with a 100 ± 5 cm (>> 4.5 inch diameter) circular test area with distilled or deionised water. The operator holds the fabric specimen in place using a coaxial fixture fitted with an observation light to assist in observing the penetration of the water droplets. A digital readout displays the pressure. An RS232 data port is available for dissemination of data for storage and logging analysis.
Some laboratories use room temperature water. If someone does not carry out testing at 20±2°C, they should note this.
1mbar = 1.02cmH2O
Side leaks can be minimised by using a paraffin sealing fabric in the fixture area.
Hydrostatic Tester Test Method:
Hydrostatic pressure tester is generally used for outdoor sports clothing waterproof test, waterproof fabric test, medical protective clothing protective material liquid permeability, blood permeability test.
Conformity standards:
GB/T 4744, AATCC 127, ERT 120-1 160-0, BS EN20811/3321/3424, AFNOR G07-057, ISO 811, JIS L1092A, JIS L1092.B-a, JIS L1092 B-b, ASTM F903C, ASTM F1670, ASTM F1671, EN 1734, ISO 1420, FZ/T01004
Technical parameters:
1. Test pressure: 0-5000mbar (5000cmW.G)
2.Pressure accuracy: resolution 0.1 mbar
3.Test area: 100cm2 (optional 10cm2, 19.63cm2, 26cm2, 28cm2)
You can select the pressure growth rate according to the standard, or you can enter the specified value.
You can select the test unit (mbar/kPa/Pa/cm w.c/mm w.c).
6.Maximum thickness of sample:40mm
7.Compressed air requirements: 6-8 bar (clean dry air)
8. Alarm time: 0- 9,999 min (according to the pressure or time settings)
9.Pneumatic fixture
Test method:
Researchers use dynamic tests, static tests, and customised procedure methods to test the water repellency of textiles under a certain pressure. The technician fixes the specimen on the standard specified area of the test area. The air compressor adds 0-5 bar air to a tank filled with distilled water, and the tank connects to the test head, applying a certain pressure to the specimen. The operation screen displays the pressure curve in real time, and it includes various test standards for the convenience of users.
Fabric water permeability tester test method:
Fabric water permeability tester is mainly used for testing waterproof clothing, mackintosh, tent, waterproof bag, waterproof gloves series of products.
Conformity standards:
GB/T 4744 ;AATCC 127 ;ERT 120-1 160-0;BS EN20811/3321/3424;AFNOR G07-057;ISO 811;JIS L1092A;JIS L1092.B-a;JIS L1092 B-b;ASTM F903C;ASTM F1670. astm f1671;en 1734;iso 1420;fz/t01004
Test Method:
By adding a certain water pressure, the pressure gauge can indicate the size of the pressure on the test object and determine whether the test object qualifies under this pressure.
Technical parameters:
1.The implementation of standards: in line with gb4744-84, also in line with iso-811
2.Measuring range: waterproof fabrics, tents, down jackets, ski jackets, mountaineering clothing, rubber bags, cold weather clothing, umbrellas, mackintoshes, fabrics, etc.
3.Technical parameters: place the specimen horizontally, applying pressure below the specimen.
4.Pressure area: 100cm2, d = 11.28cm
5.The water column height ranges from 0 to 10000mmH2O (you need to customize for 10000mmH2O or more).
6.Rsing speed: 10 ± 3mmH2O (standard rate) 60 ± 20 mmH2O
7.Standard rate: 100±30 mmH2O (increase rate)
8.Sensitivity: 1mmH2O, the maximum display value of 10000mmH2O
Geomembrane hydrostatic pressure tester test method:
Geomembrane hydrostatic pressure tester is mainly used to determine the permeability of non-woven geotextiles and geosynthetics.
Conforms to the standard:
GB/T 17642-1998 ‘composite geomembrane permeability performance determination’, GB/T 17642-2008 ‘geosynthetics non-woven composite geomembrane’, GB/T 19979 ‘geosynthetics impermeability performance’, JTG E50-2006
Technical parameters:
1、Measuring range:0~4.0MPa
2、Resolution: 0.05 MPa
3、Collector inner diameter: 200mm
4、Porous plate porous diameter: 3±0.05mm
5, porous plate pore spacing: 6mm
Test method:
Increase the hydraulic pressure difference between the two sides step by step and maintain it for a certain period of time. When the seepage flow increases rapidly, it indicates that the specimen is sustaining damage, meaning that we obtain the hydrostatic pressure value.
Test steps:
1. Cut the test fabric into 100mm × 100mm size specimen, then put the specimen into the fixture, screw the fixture fixed.
2. Press the rising button, the metal container containing 700ml of water under the drive of the motor began to rise at a uniform speed, the specimen in the fixture to increase the water pressure, through the fixture plastic window to observe the specimen covered in filter paper on the indicator paper colour change to measure the water penetration.
3. When the initial signal of the colour change of the indicator paper (from blue to pink) appears, immediately read out the height of the water level of the scale, expressed in Pa (mmH20), and press the rising button again to stop the metal container rising.
4. Record the reading as the test data of water permeability of filter paper.
5. Open the fixture, remove the specimen and indicator paper, dry the stretcher window of the fixture with a soft cloth and check the water level in the fixture. If necessary, refill the water.
6. Reposition the fixture with another specimen and indicator paper and repeat the above test steps for the test.
Safety Precautions
Note: These safety precautions are for reference only. The testing process intends them only as an aid and does not find them exhaustive. It is the user’s responsibility to use a safe and permissible technique to settle the sample during testing. You must seek full details, such as material safety data sheets, and advice from other manufacturers. Everyone must follow all OSHA principles and rules.
1. Researchers should follow laboratory practices. Wear safety goggles in all laboratory situations.
2. Follow the manufacturer’s safety recommendations when operating laboratory test equipment.
AATCC 127 Hydrostatic Pressure Test Scope of Application
The AATCC127 Hydrostatic Pressure Test is applicable to all types of fabrics, including those treated with water-resistant or water-repellent finishes. Resistance to water penetration depends on the water repellency of the fibres and yarns as well as on the structure of the fabric. Therefore, you should base the choice of test method on specific needs and fabric characteristics.
Notes on AATCC 127 Hydrostatic Testing
1. The results obtained from the AATCC 127 Hydrostatic Test may differ from those obtained using other AATCC rain or water jet resistance test methods. Therefore, specific needs and fabric characteristics should guide the choice of test method.
2. Before conducting the test, ensure that the test device is well sealed to avoid errors in the test results.
3. When carrying out the test, you should take care to control the rate of increase of water pressure to avoid errors in the test results caused by going too fast or too slow.
4. During the test, the team should pay attention to the size and shape of the fabric sample to ensure the accuracy of the test results.
5. To obtain more information about the AATCC127 hydrostatic test, consult textile industry books or textile industry professionals.
In conclusion, the AATCC127 hydrostatic test is a reliable method to assess the water penetration resistance of fabrics, which can help practitioners in the textile industry to evaluate the waterproof performance of fabrics and provide strong support for product development and production
AATCC 127 Hydrostatic pressure test method:
Step by step, increase the hydraulic pressure difference between the two sides and maintain it for a certain period of time. When the amount of seepage increases rapidly, it indicates that the specimen is receiving damage, which means you obtain the hydrostatic pressure value.
AATCC 127 hydrostatic pressure test procedure:
1. Cut the test fabric into 100mm × 100mm size specimen, and then put the specimen into the fixture, screw the fixture fixed.
2. Press the rising button, the metal container containing 700ml of water under the drive of the motor began to rise at a uniform speed, the specimen in the fixture to increase the water pressure, through the fixture plastic window to observe the specimen covered in filter paper on the indicator paper colour change to measure the water penetration.
3. When the initial signal of the colour change of the indicator paper (from blue to pink) appears, immediately read out the height of the water level of the scale, expressed in Pa (mmH20), and press the rising button again to stop the metal container rising.
4. Record the reading as the test data of water permeability of filter paper.
5. Open the fixture, remove the specimen and indicator paper, dry the stretcher window of the fixture with a soft cloth and check the water level in the fixture. If necessary, refill the water.
6. Reposition the fixture with another specimen and indicator paper and repeat the above test steps.
Common Problems in Hydrostatic Testing
Problems caused by improper operation during hydrostatic testing
① Before clamping the specimen, make sure there is no air between the specimen and the water, and then clamp the specimen for the test. If there is air between the test specimen and the water during the test, the water can not be completely in contact with the specified experimental area, there will be part of the specimen area can not appear water droplets, which will have an impact on the results of the experiment.
② During the test, try to ensure that the edge of the specimen clamping device does not seep or leak. If the specimen seeps or leaks at the edge of the clamping device, water will seep out from the edge of the clamping device during the test, and the test pressure of the specimen will rise erratically, which will not ensure the accuracy of the experimental results, and will have an impact on the experimental results.
Problems arising from the determination of the test endpoint
The test standard of hydrostatic pressure, ‘Testing and Evaluation of Textile Waterproof Performance Hydrostatic Pressure Method,’ stipulates that testers should record the hydrostatic pressure value when the third water droplet appears on the specimen, and they define the test endpoint as the appearance of the third water droplet. If the test endpoint is not correctly selected during the test, it will have a direct impact on the reading of the results of the experiment and ultimately give incorrect results.
Some special cases are as follows:
If the third water droplet appears at the edge of the clamping device and lowers the hydrostatic pressure value of the third water droplet below the lowest value of other normal specimens of the same sample, we should reject this data and test additional specimens until we obtain normal experimental results. The clamping device can damage the edge of the specimen. The test may cause water to seep from the edges. We must then analyze the test results. If the test value is lower than the lowest value of other normal specimens, we need to add more specimens.
In the standard notes, record the pressure value when the fabric ruptures, when the water column sprays, or when composite fabrics show the bulging phenomenon filled with water, and explain these experimental phenomena in the report. The occurrence of the above conditions should be the end point of the test of the experiment.
Handling problems of abnormal situations
If the hydrostatic pressure test results show a large coefficient of dispersion and the average test results qualify, but an individual test single value fails, the recommendation is to align the judgement with the report indicating the individual unqualified test single value.
If the water wets the specimen when it comes into contact before the test of the experiment, the test result records as 0, and the report indicates that the water wetted the specimen upon contact.
Why choose AATCC 127 for hydrostatic testing?
The main reasons for choosing AATCC 127 for hydrostatic testing include the following:
Wide scope of application: The AATCC 127 standard is applicable to all types of fabrics, including those treated with water-resistant or water-repellent finishes. This makes the standard widely applicable in the textile industry.
Scientific Test Principle: AATCC 127 determines the water penetration resistance of fabrics by subjecting them to hydrostatic pressure. The test specimen undergoes hydrostatic pressure on one side, which the operator increases at a rate until three water outlets appear on the other surface of the test specimen. This method enables a scientific assessment of the water penetration resistance of fabrics.
Results are informative: Results obtained using the AATCC 127 standard may differ from those obtained using the AATCC rain or water jet test method. This demonstrates the unique application of the standard in evaluating the water resistance of fabrics.
Standardisation and consistency: Using the AATCC 127 standard ensures consistency and comparability of test results, which helps researchers obtain reliable data when they repeat tests in different laboratories or at different times.
In summary, we chose AATCC 127 for hydrostatic pressure testing because it has a broad scope of application, follows scientific testing principles, delivers informative results, and provides standardised and consistent test results.
For more information on textile testing methods/standards
or textile testing machines, contact us:
What’s App: +86 180 2511 4082
Tel: +86 769 2329 4842
Fax: +86 769 2329 4860
Email: medium@chiuvention.com