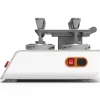
Application of Martindale Abrasion and Pilling Tester
The Martindale abrasion and pilling tester can test cotton, hemp, and silk woven fabrics. It can also test other textiles and membranes. These include knitted fabrics, woolen textiles, and artificial leather. It can also test gloves and labor protection materials.
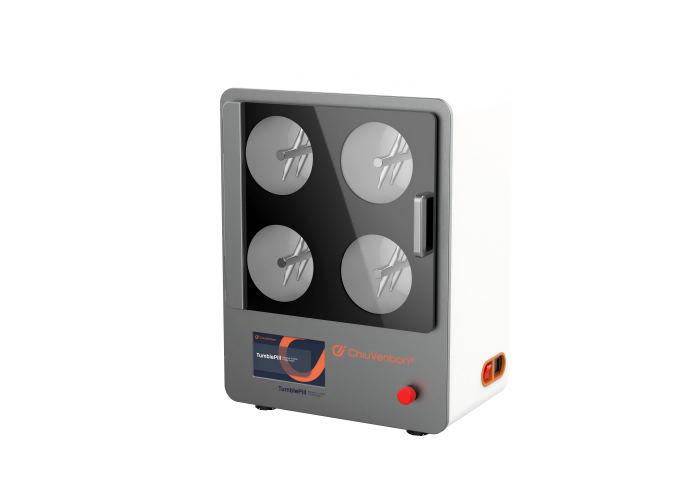
Smart Martindale Tester
The instrument is connected via IoT to the SmarTexLab APP in the phone/PC. And The app can connect to ERP/LIMS via an API. Or, the fabric abrasion tester can connect directly to ERP/LIMS. There are test orders and sample information in the system, and the Martindale Tester can start the test and record the sample info, test process, and test or rating results. The system will then summarize these into a Martindale abrasion and pilling test report. The report can be sent to SmarTexLab or ERP/LIMS. The relevant parties can view the report in real-time.
Test men can monitor tests for many Martindale Abrasion Testers at once. They can also change test requirements, get alerts before tests end, and stop or repeat tests remotely.
In SmarTexLab, you can set up programs to start or stop the Martindale Tester. You can chat with ChiuVention service staff for quick support. You’ll get reminders that the Martindale Abrasion Tester needs calibration, maintenance, and new consumables. Regular OTA remote upgrades are available.
Calibration-free
The dual action of the servo driver and position sensor allows the Martindale Tester Machine to achieve accurate testing continuously.
Flip-up cover for easy observation and operation
The upper cover can be easily flipped up and locked with one hand, making it easy for the operator to observe the Martindale test. It also greatly facilitates the installation of consumables and samples, and the cover’s slow-lowering device ensures the safety of the operator and the Martindale abrasion machine.
Easy to use
Many world-class textile testing institutes use this Martindale pilling tester, which testers recognize as easy to use.
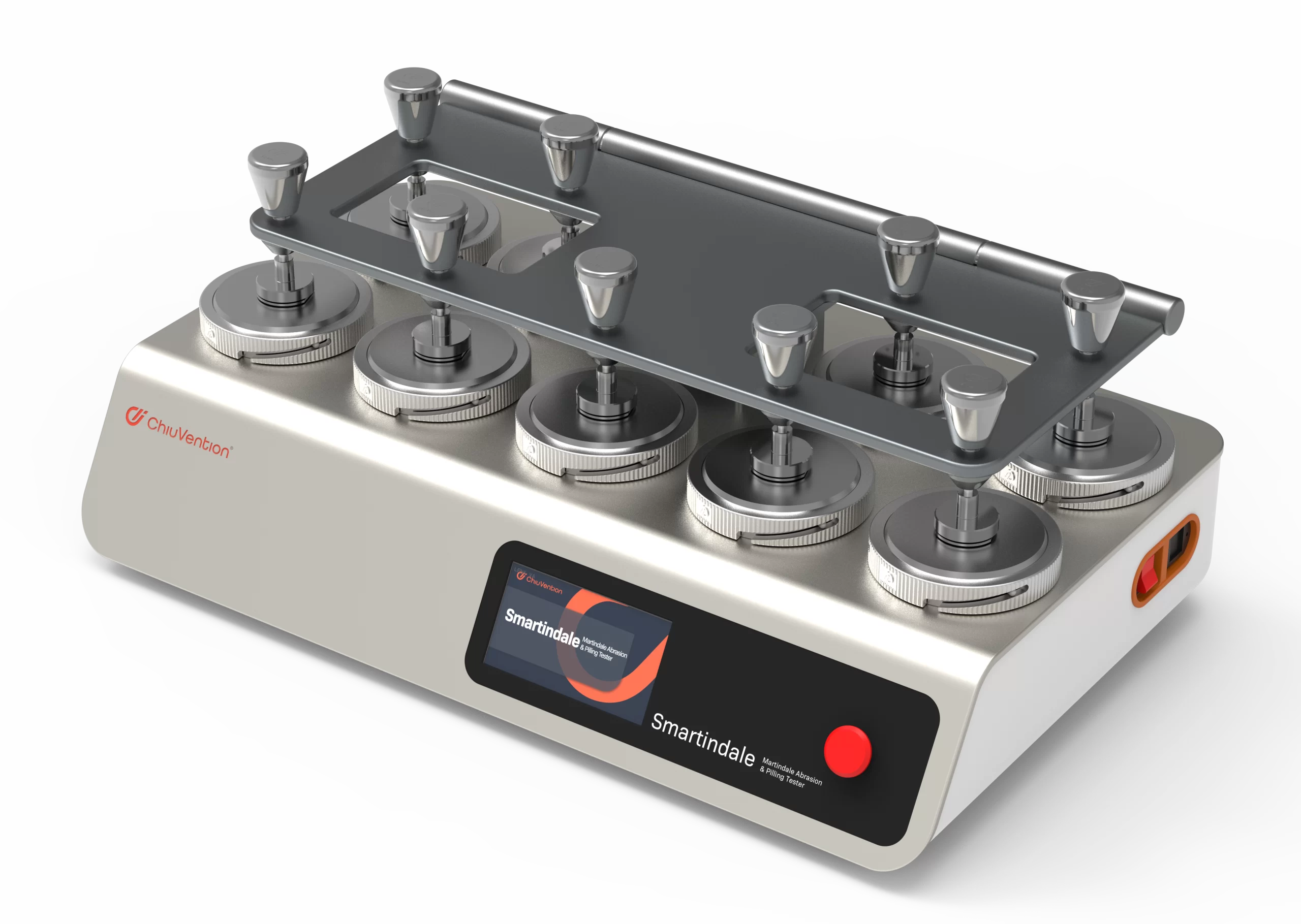
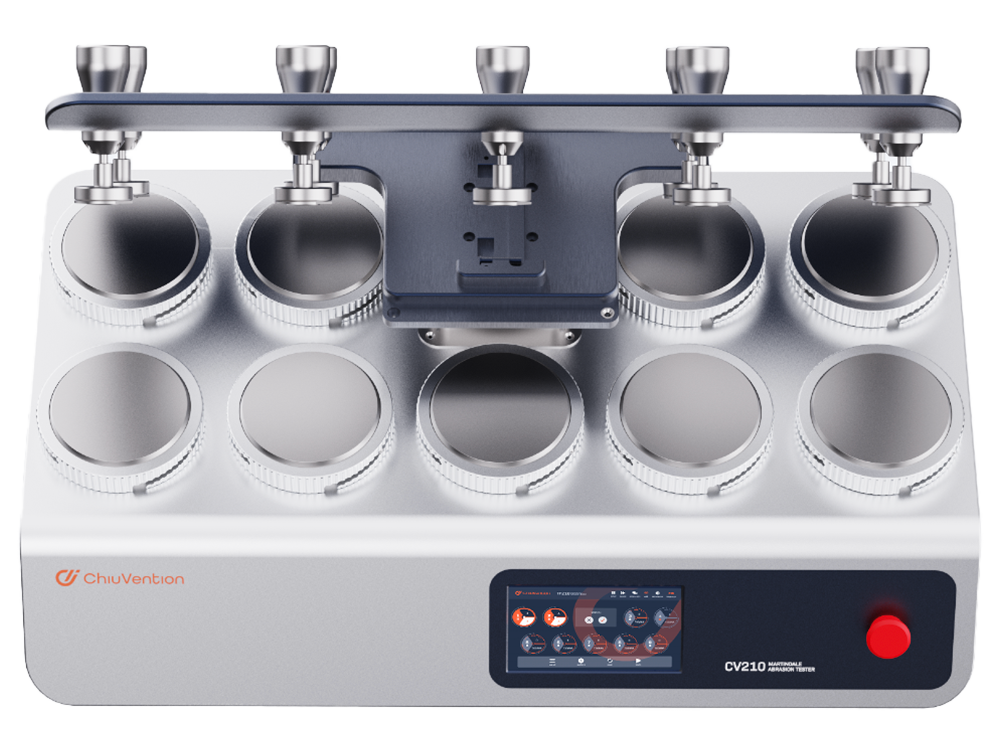


The original digital drive achieves a higher level of test accuracy.
This Martindale Pilling Tester runs on an exclusive and patented digital algorithm. It drives dual servo motors and precision slide rails. This replaces the traditional analog drive. It can generate a perfect Lissajous curve. Using rubber simulation specimens and double weight, we tested over 10 million times (equal to three years non-stop) at ultra-high friction. The Lissajous curve is still accurate and perfect. So, the Martindale Test is more reliable.
One-click to shift the testing modes
This Martindale Tester is easier than the conventional one. You don’t need to remove the top plate and change the pins. Just click one key to switch the testing modes. You can switch from abrasion to pilling test(e.g. Abrasion, Pilling, Line).
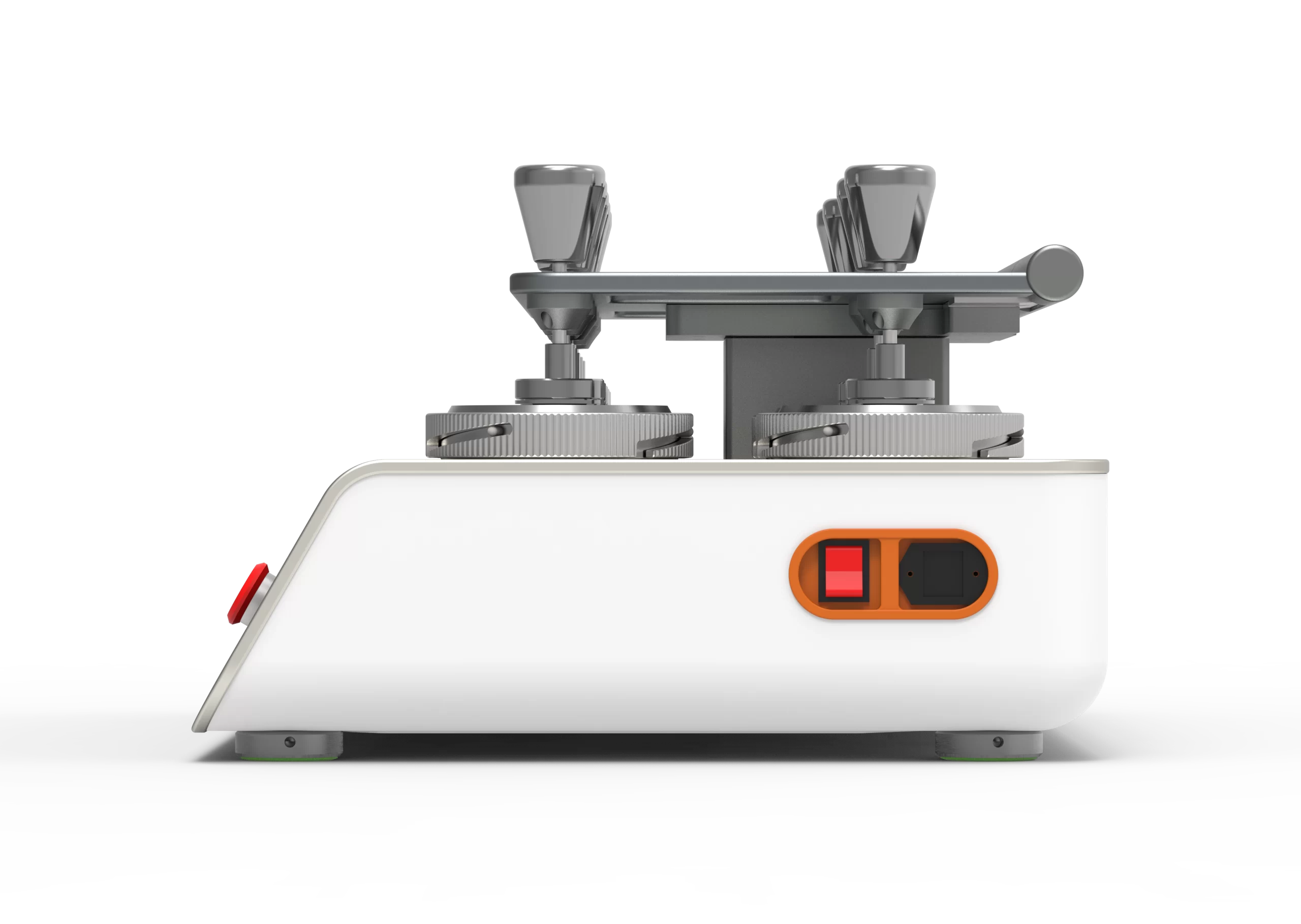

Ergonomic design
You can move the guide plate of this Martindale Tester with one hand. It closes and has an anti-collision function. This pilling tester machine is friendlier to operators.
Reliable Martindale Test
The machining and assembly are accurate. This makes the abrading table and specimen holder run parallel. The holder in this Martindale Tester has a small run out to the table (less than 0.05mm). This is better for getting reliable Martindale test results.
Designed in Germany, quality is our life.
All our textile testing equipment is developed in-house and in cooperation with a team of renowned German industrial designers, which makes our textile testing machines of outstanding quality. 100% source factory and factory price.

Customer Feedback
“I purchased this Martindale Tester through ChiuVention’s agent-ATI Corp., who has more than 20 years of experience in textile testing instrument marketing and service in the U.S., and they can support me very timely. This Martindale Abrasion Tester does well both in testing accuracy and functional design (such as switching test mode from the screen and friendly details for testers, etc.).”
“We knew about this Martindale Tester at ChiuVention’s French agent. It is very stable and has a unique design. Its features are on par with top brands of test instruments. And It has a very reasonable price. So, without a doubt, it became our final choice.”
OUR BROCHURE
FLYER
Martindale Test Standards
ISO 12945-2-2020 ISO12947-1-1998 ISO12947-2-2016
ISO12947-3-1998 ISO12947-4-1998
GB/T 21196.1-2007 GB/T 21196.2-2007
GB/T 21196.3-2007 GB/T 21196.4-2007
GB/T 4802.2-2008
ASTM D4970/4970M-22
ASTM D4966-22
BS EN 530-2010
Optional standards
BS EN 388-2016+A1-2018 Protective gloves for mechanical hazards;
SATRATM31 A/B Abrasion Resistance Test for Leather;
PUMA; BS EN 16094-2012 Laminated wood flooring,
Test method for the determination of micro-scratches;
ISO 20344-2021 Item 6.12 Personal protective equipment,
Test methods for footwear and boots;
BS EN 13520-2002 Test methods for footwear, uppers,
linings and insoles, abrasion resistance;
ISO 5470-2-2021 Rubber or plastic,coated fabrics,
determination of abrasion resistance
ISO 17076-2-2011 GB/T 39507-2020
TECHNICAL DATA
Abrasion test
(198±2)g
Weight of holder and spindle
60.5±0.5mm Max stroke of movement
Pilling test
(155±1)g
Weight of holder and spindle
24±0.5mm
Max stroke of movement
INSTALLATION
220v/110v 50/60Hz
Power Supply
| Smartindale 4 | 65kg | 650*510*280mm |
| Smartindale 6 | 75kg | 650*510*280mm |
| Smartindale 9 | 90kg | 510*850*300mm |
Climatic Environment
The unit is intended to operate within the following conditions
25+/-5 deg Celsius Temperature | 30-65 RH % Humidity |
<2000m above sea level Altitude | -25-+ deg Celsius.Storage |
For more information, please check the Download Brochure
Accessories of Martindale Abrasion Tester
Accessories
Fuse tube 2pcs
Foam wool 9 pcs Φ38 mm
Wool felt 18 pcs Φ90 mm,Φ140 mm
Wool abrasive 9 pcs Φ140 mm
Sampling plate 3 pcs Φ38 mm,Φ90 mm,Φ140 mm
Sampler 1 pc for pilling test
Sampler 1 pc for abrasion test
Press 1 pc Φ126mm,2.5kg
Fixture1 9 sets for pilling test
Fixture 2 9 sets for abrasion test
Weight 1 9 sets 12Kpa
Weight 2 9 sets 9Kpa
Rubber ring 9 pcs
Test pen 1pc
Connection shaft 9pcs for pilling test
Connection shaft 9pcs for abrasion test
Stainless steel ring 9pcs 260g
Optional Accessories
EMPA990 rating chart card 1 set Knitted + Woven
SM50 rating chart card 1 set IWS + ASTM
SM25 abrasion-resistant wool cloth 1 pack 1.6 X 5m/pack
SM26 woven wool felt 1 box 24 pcs/box Φ140mm
SM26 woven wool felt 1 box 24 pcs/box Φ90 mm
SM28 polyurethane ether foam 1box 250 X 200mm/pc, 25pcs/box
Ball Plate Φ120mm
We also provide another type of Pilling Tester.
You can also click here to learn more about the Martindale Test.
GET A QUOTE
The Martindale abrasion and pilling test is widely used. It assesses the durability and wear resistance of textiles. This test simulates natural wear. It evaluates how fabrics stand up to abrasion and pilling. Here’s an overview of the test principles:
Abrasion Test Principle
The Martindale abrasion test determines the fabric’s resistance to abrasion. The principle is to rub the fabric against a standard abrasive material. This is done under controlled conditions.
The samples are cut into circles. They are then placed on holders.
Test setup: The samples are placed against an abrasive material. This material is usually a standard wool or worsted fabric mounted on a circular plate.
Load Application: A specified weight or load is put on the specimen holder. This applies constant pressure on the fabric.
Movement Pattern: The sample is subjected to a Lissajous figure motion. This motion is complex and non-repeating. It ensures abrasion in many directions.
Cycle Count: The test runs for a set number of cycles. The fabric is inspected for wear during the cycles.
The test continues until the fabric shows wear or a hole, or a set number of cycles finish.
The degree of abrasion is evaluated by eye. Or, by measuring fabric mass loss.
Pilling Test Principle
The Martindale pilling test evaluates how fabrics tend to form pills. Pills are small balls of tangled fibers on the surface.
Sample Preparation: We cut fabric samples into circles. Then, we mount them on holders.
Test Setup: The samples are rubbed against a standard fabric under controlled conditions.
Load Application: A specified weight is put on the specimen holder. This weight exerts a constant pressure on the fabric.
It has a similar movement pattern to the abrasion test. The samples undergo Lissajous figure motion. This motion simulates natural wear and tear.
Cycle Count: The test is run for a specified number of cycles.
After the test, the samples are inspected. They are rated based on the amount of pilling.
Pilling is assessed using a standard scale. It usually ranges from 1 (severe) to 5 (none).
Summary
Both tests use the same Martindale machine. But, they focus on different aspects of fabric wear. The abrasion test measures the fabric’s ability to withstand rubbing. The pilling test measures the formation of pills on the fabric due to wear. Both tests provide useful data. They are about the strength and performance of textiles in daily use.
Instrument, sample, and conditioning preparation
Prepare the Martindale Tester
Conduct an abrasion test according to the following requirements:
ISO 12947-1、ISO 12945-2
The abrasion table shall be covered with a circle of woven or non-woven felt (non-woven fabric is only used for M & S test). Both kinds of felt are available from the laboratory. Then, cover the wear table with standard wear fabric. The standard wear fabric shall meet the requirements of iso12947-1 and can be obtained from ChiuVention.
All samples and standard fabrics shall be conditioned in a standard atmosphere for testing.
All wear and pilling tests shall be conducted in a standard atmosphere: 20 ± 2 ° C and 65% ± 2% RH.
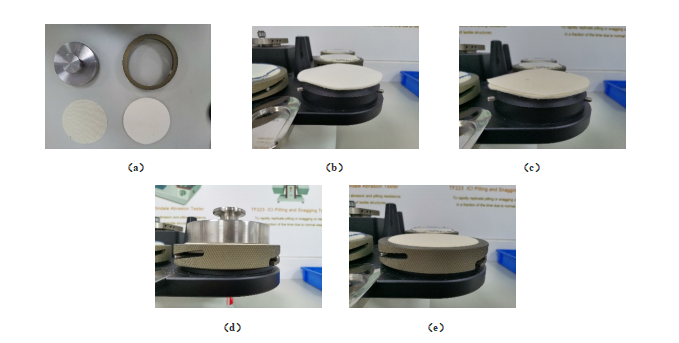
Take the Abrasion test as an example
Prepare abrasive
- After adjusting the felt and standard fabric, cut a group of felt and standard fabric from the felt and standard fabric respectively according to the test requirements;
- Place the felt in the center of the grinding table as shown in Figure 1-(b);
- Place the standard fabric in the center and cover it on the felt as shown in Figure 1- (c);
- Put the snap ring on the grinding table and press the standard felt with a heavy hammer as shown in Figure 1-(d).
- Tighten the snap ring and remove the heavy hammer as shown in Figure 1-(e);
- Repeat the above operation for the rest of the grinding table of the machine
Prepare test samples
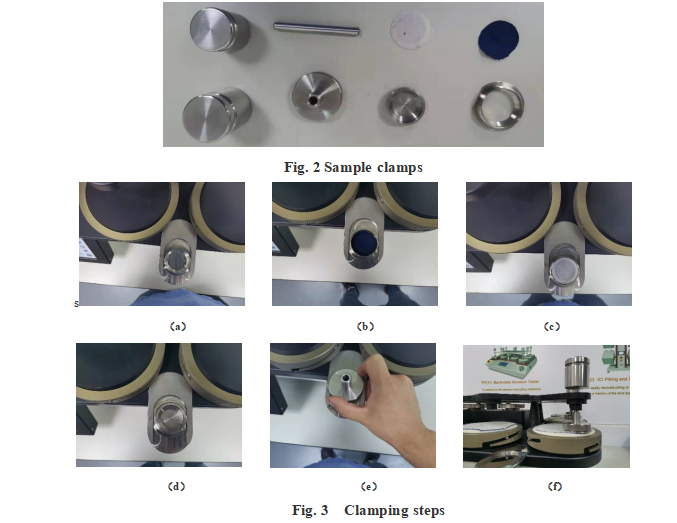
After adjusting the foam and the tested samples, a group of foam and the samples to be tested are cut from the foam and tested samples according to the standard test requirements.
- Put the compression nut into the clamping table as shown in Figure 3 – (a);
- Put the sample to be tested face down into the compression nut as shown in Figure 3 – (b);
- Place the sponge on the sample to be tested as shown in Figure 3- (c);
- Place the fixture inserts on the sponge with the conical part downward As shown in Figure 3- (d);
- Screw the clamp socket onto the compression nut as shown in Figure 3- (E). (Ensure that the fixture is tightened to prevent the sample from falling off during the friction test)
- Insert the fixture pin shaft through the shaft sleeve and into the assembled fixture as shown in Figure 3 – (f). And put the weight required for the test requirements;
Note: all parts of a grinding station are numbered. The correct number of parts must be used in the correct station. For example, all components marked with No. 1 should be assembled and used in station 1.
- Repeat the above process for all samples to be tested;
- Set the Martindale Tester machine parameters and start the test according to the steps
Lissajous pattern Inspection method
Obtain each table’s Lissajous graphs as follows.
Move the material from the grinding table. Cover the table with a piece of white paper. The paper should be round, with a diameter of (100±5) mm. It should be very flat and have a minimum mass of 100 g/m2.
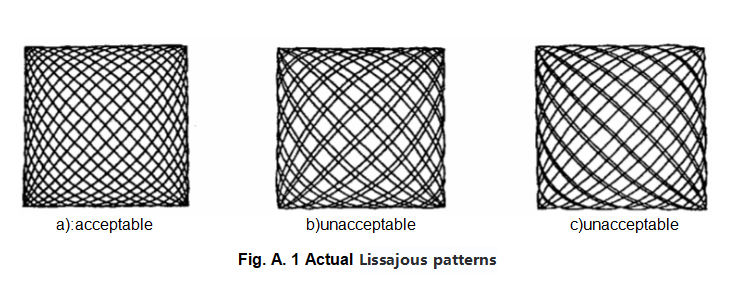
Put a steel sleeve in the guide. It should match the specimen pin’s diameter. Then, put in a common ballpoint pen so that its tip touches the paper. A complete Lissajous pattern is formed after 16 times of friction.
Draw two lines that are parallel. They should intersect the outer curves of the Lissajous pattern. Draw two more lines for the other two sides. Make sure that these lines cross at right angles. Measure each side properly to an accuracy of 0.2 mm. Check the 31 lines drawn and, importantly, the symmetry of the Lissajous pattern. If the curves coincide with each other or are unevenly spaced (see Figure A.1), please consult us.
Clean the Martindale Abrasion and Pilling Tester often. Do this after each use. It stops dust and debris buildup. Use a soft cloth and mild cleaning solution to wipe down the surfaces.
Lubrication: Check the tester’s moving parts. Lubricate them as the manufacturer recommends. This will help prevent friction and ensure smooth operation.
Calibration: calibrate the Martindale Test Equipment to maintain accurate results. Follow the calibration instructions provided by ChiuVention.
Inspect it often. Look for signs of wear, damage, or loose connections. Replace any damaged parts promptly.
Consider scheduling professional maintenance checks. Do this with a qualified technician to ensure that all parts work correctly.
Documentation: Keep track of maintenance schedules, repairs, and any issues you encounter. This can help you troubleshoot problems more efficiently in the future.
Contact us for specific maintenance guidelines, troubleshooting tips, and spare parts. We will help you care for your Martindale Abrasion and Pilling Tester.
If you have issues or need help fixing or maintaining your Martindale Machine, please give details. Then, we can offer more tailored advice.
Frequently Asked Questions of Martindale Tester
The Martindale Tester has dual servo driver motors and precision slide rails, replacing the traditional mechanical analog drive, to generate a perfect Lissajous curve; We also have done strict sample tests: with rubber analog specimens, and double pressure weight, more than 10 million times (equal to three years of non-stop) of ultra-high-strength friction life test, the Lissajous curve is still accurate and perfect, and the operation is extremely stable. So the testing accuracy and stability of this Martindale Tester is higher.
To ensure better Martindale test results for your fabric samples, consider the following strategies based on best practices and insights from industry standards:
1. Proper Sample Preparation
- Cut Samples Correctly: Ensure that fabric samples are cut to the required dimensions (usually circular) and are free of any defects. This helps in achieving consistent results.
- Conditioning: Condition the samples in a controlled environment (typically at 21°C and 65% relative humidity) for at least 24 hours before testing to stabilize the fabric.
2. Select Appropriate Abrasive Materials
- Use Standardized Abrasives: Choose the correct abrasive material (worsted wool, sandpaper, or wire mesh) as specified by the testing standard. This ensures that the test conditions are consistent with industry norms.
- Check Abrasive Condition: Regularly inspect and replace abrasive materials to maintain their effectiveness and consistency.
3. Optimize Testing Parameters
- Adjust Load Settings: Use appropriate weights (commonly 9 kPa or 12 kPa) during testing to simulate realistic wear conditions for the specific fabric type.
- Cycle Count: Determine an appropriate number of cycles based on the expected use of the fabric. For example, upholstery fabrics may require higher cycle counts compared to decorative fabrics.
4. Conduct Multiple Tests
- Replicate Tests: Perform multiple tests on different samples to obtain an average result, which can help account for variability in fabric performance.
- Use Different Test Methods: Consider using both the specimen breakage method and mass loss method to gain a comprehensive understanding of fabric durability.
5. Evaluate and Analyze Results Thoroughly
- Visual Assessment: After testing, conduct a thorough visual inspection using standardized grading scales to assess pilling and abrasion accurately.
- Document Findings: Keep detailed records of test conditions, results, and observations to identify trends over time or issues with specific fabric batches.
6. Regular Maintenance of Testing Equipment
- Calibrate Equipment: Ensure that the Martindale tester is regularly calibrated according to manufacturer specifications to maintain accuracy.
- Clean Components: Regularly clean the testing surfaces and components to prevent contamination that could affect test results.
7. Training and Knowledge
- Educate Staff: Ensure that personnel conducting tests are well-trained in operating the Martindale tester and interpreting results accurately.
- Stay Updated on Standards: Keep abreast of any changes in testing standards or best practices within the textile industry to ensure compliance and accuracy.
By implementing these strategies, you can enhance the reliability and accuracy of Martindale test results for your fabric samples, leading to better insights into their abrasion resistance and overall durability.
The results of the Martindale Abrasion Pilling Test are usually expressed in terms of abrasion counts and pilling ratings. The criteria for passing or excelling in these two metrics for scores will vary depending on the test criteria, the type of product, and its use scenario. The following are common determination criteria:
- Abrasion count
The abrasion resistance test evaluates by recording the degree to which a material is worn under a specified friction pressure and number of times. Usually a higher number of abrasion counts indicates a better durability of the fabric. The following are some common reference values:
General textiles (e.g. everyday clothing)
Pass standard: 10,000 times or more
Excellent standard: 20,000 cycles or more
High-demand textiles (e.g. furniture fabrics, car interiors, outdoor equipment)
Qualifying criteria: more than 15,000 times
Standard of Excellence: 30,000 cycles or more
Some products with high durability requirements, such as furniture fabrics used in public places, can even reach 50,000 to 100,000 times of abrasion, which is considered to be an excellent performance of abrasion resistance.
- Pilling grade
Pilling grade is usually based on visual evaluation and is classified from 1 to 5:
Grade 1: Very severe pilling
Grade 2: Significant pilling
Grade 3: Moderate pilling, still acceptable
Grade 4: Slight pilling, almost negligible
Grade 5: No visible pilling
Generally, a pilling level of 3 is considered acceptable, while a level of 4 or above is considered excellent.
Standards for different industries
Everyday clothing: Pilling level 3 or above is considered acceptable, level 4 or above is considered excellent.
Home textiles and furnishing fabrics: usually more demanding, with a level 4 or above of pilling to pass strict quality control.
Outdoor and Functional Fabrics: Due to the more demanding environments, they are usually required to have an abrasion resistance of 30,000 times or more, and a pilling level of 4 or higher to be considered excellent.
Different products and industries have specific requirements, so it is recommended to refer to the corresponding industry standards and customer requirements, such as ISO 12945, ASTM D4970 and so on.
There are a variety of commonly used textile abrasion pilling test equipment, which are mainly selected according to different test methods and standards. The following are a few common types of equipment and their characteristics:
Martindale Abrasion Pilling Tester
Usage: The Martindale tester is the most common textile abrasion and pilling test equipment and is widely used for flat abrasion and pilling tests on fabrics.
Principle: Friction is applied to the sample through a defined pressure and movement path (usually circular) to simulate the abrasion and pilling of the fabric during actual wear.
Applicable materials: For knitted fabrics, woven fabrics, non-woven fabrics and other textiles.
Standards: Conforms to international standards such as ISO 12945-2 and ASTM D4970.
Advantages: Reliable test results, widely used, applicable to a wide range of textile types.
Suggestion for selection: Martindale is a good choice if you need a test that meets international standards and handles a wide range of fabrics.
Purpose: Mainly used for textile pilling test, especially suitable for woolen fabrics and knitted fabrics.
Principle: By putting the textile sample into the pilling box, it simulates the friction of the clothing when wearing in the rotating process, so as to observe its pilling property.
Applicable materials: Knitted fabrics, woolen fabrics and other fabrics that are prone to pilling.
Standard: Comply with ISO 12945-1, BS 5811 and other standards.
Advantages: Particularly suitable for woolen fabrics and materials with high risk of pilling, and the testing conditions are closer to the actual use environment.
Suggestion: If you mainly test woolen fabrics or knitted fabrics, choose ICI pilling box to simulate the real wearing environment better.
Usage: Used to test the abrasion resistance of textiles, not the pilling test. It is suitable for harder materials, such as industrial fabrics, leather, synthetic materials, etc.
Principle: By rotating two abrasive wheels on the surface of the sample, it simulates a strong abrasive action and measures the abrasion of textiles under specific conditions.
Applicable materials: industrial textiles, carpets, leather and other materials with high abrasion resistance requirements.
Standards: Conforms to ASTM D3884 and other standards.
Advantages: Suitable for abrasion resistance testing, especially for industrial use textiles.
Suggestion: If you need to test the abrasion resistance of textiles, especially for industrial use textiles, Taber abrasion tester is the right choice.
Purpose: To simulate the pilling of textiles due to friction during washing and wearing.
Principle: Simulates the pilling of textiles in use by placing the sample in a rolling device and utilizing the friction created by the cork and the friction device.
Standard: ASTM D3512.
Advantages: The simulated environment is more realistic and is particularly suitable for assessing the pilling of textiles during washing.
Selection advice: If you are concerned about pilling during the washing process, this device may be ideal.
Selection advice:
Choose according to your testing needs:
The Martindale tester is the most common and versatile choice when a wide range of fabrics need to be tested for pilling and abrasion resistance.
For pilling of woolen or knitted fabrics, the ICI Pilling Box Tester is more suitable.
If you are testing technical textiles or need to pay special attention to abrasion resistance, the Taber abrasion tester is more suitable.
Choose according to the test standard:
You need to make sure that the equipment complies with the test standard you are using, such as ISO 12945, ASTM D4970, etc. If you are testing textiles for export or international markets, special attention needs to be paid to matching standards.
Key parameters include:
- Load: The weight applied during testing, typically around 9 kPa.
- Number of cycles: The total number of rubbing cycles, often set to 1000 or more depending on the test requirements.
- Speed: The rate at which the fabric is rubbed, which can be adjusted based on fabric type.